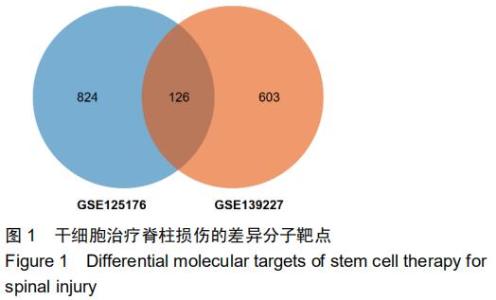
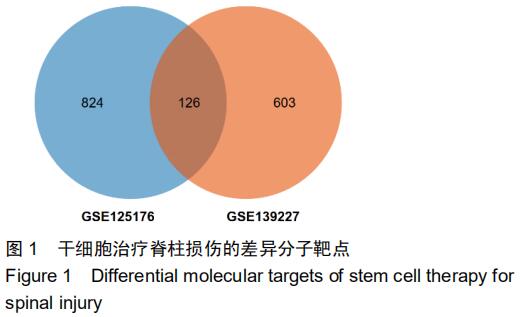
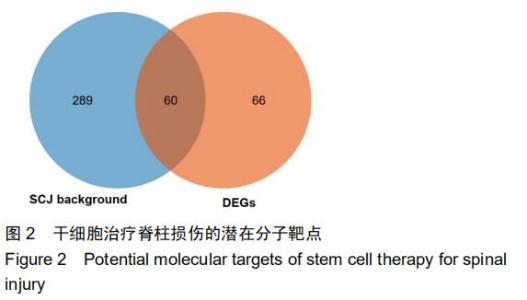
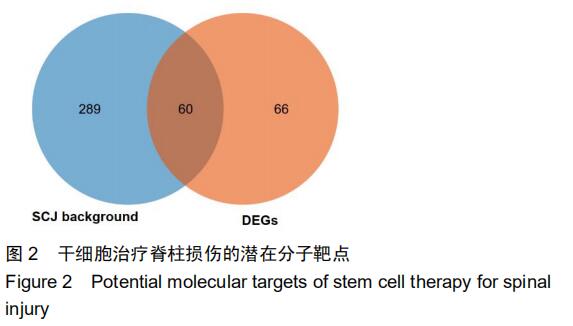
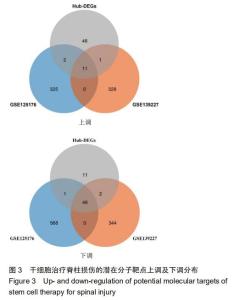
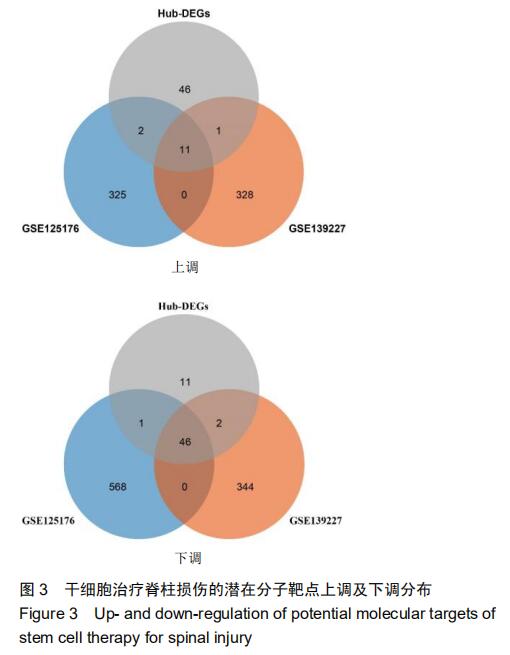
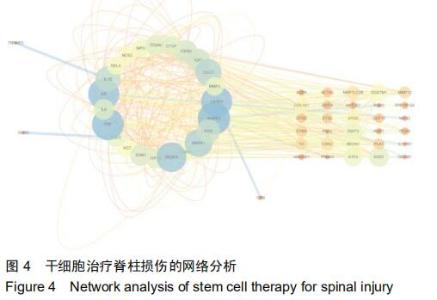
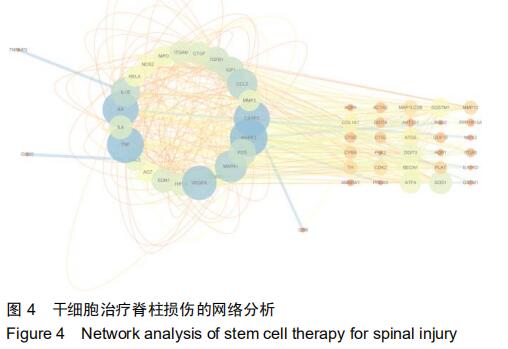
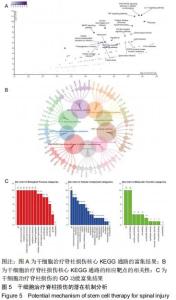
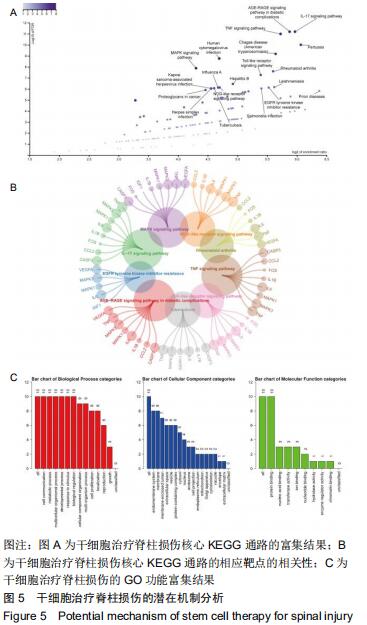
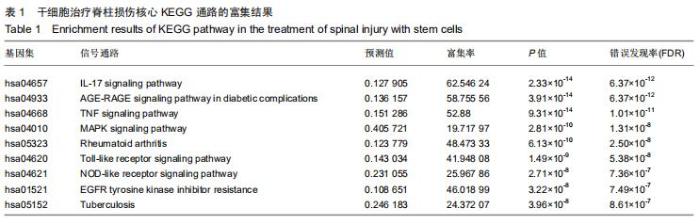
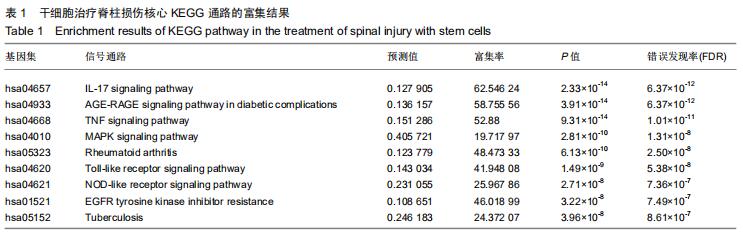
|
[1] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Nature Reviews Disease Primers.2017;3(1):1-21.
[2] 郭艳苏,曹河圻.脊髓损伤再生修复研究现状及展望[J].中国科学基金, 2018,32(4):354-357.
[3] COBB JE, LEBLOND J, DUMONT FS, et al. Perceived Influence of Intrinsic/extrinsic Factors on Participation in Life Activities After Spinal Cord Injury. Disabil Health J. 2018;11(4):583-590.
[4] AHUJA CS, MARTIN AR, FEHLINGS M. Recent advances in managing a spinal cord injury secondary to trauma. F1000Res. 2016;5. pii: F1000 Faculty Rev-1017.
[5] 王维,齐社宁,赵红斌,等.地塞米松复合聚己内酯胶原支架材料的构建及性能评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(3):402-407.
[6] HODGETTS SI , HARVEYA R. Neurotrophic Factors Used to Treat Spinal Cord Injury.Vitam Horm. 2017;104:405-457.
[7] ZHAO Y, XIAO Z, CHEN B, et al. The Neuronal Differentiation Microenvironment Is Essential for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Organogenesis.2017; 3(3):63-70.
[8] ALIZADEH A, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Microenvironmental Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Replacement and Remyelination in Spinal Cord Injury.J Physiol. 2016;594(13):3539-3552.
[9] KUCHER K, JOHNS D, MAIER D, et al. First-in-man Intrathecal Application of Neurite Growth-promoting Anti-nogo-a Antibodies in Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2018;32 (6-7):578-589.
[10] NAGOSHI N, TSUJI O, NAKAMURA M, et al. Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury Using Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Regen Ther. 2019;11:75-80.
[11] 李惠民,申才良.干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报,2019,54(4):164-168.
[12] CUI C, CUI Y, GAO J, et al. Intraparenchymal Treatment with Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-conditioned Medium Exerts Neuroprotection Following Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(4):2374-2382.
[13] HASAN A, DEEB G, RAHAL R, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Traumatic Brain Injury. Front Neurol. 2017; 8(2): 28.
[14] HAKIM R, COVACU R, ZACHARIADIS V, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplanted Into Spinal Cord Injury Adopt Immune Cell-like Characteristics. Stem Cell Res Ther.2019; 10(1): 115.
[15] CHUNG W, EUM HH, LEE H, et al. Single-cell Rna-seq Enables Comprehensive Tumour and Immune Cell Profiling in Primary Breast Cancer. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15081.
[16] GUO J, GROW EJ, YI C, et al.Chromatin and Single-Cell RNA-Seq Profiling Reveal Dynamic Signaling and Metabolic Transitions during Human Spermatogonial Stem Cell Development. Cell Stem Cell.2017; 21(4): 533-546.
[17] HSU F, KENT WJ, CLAWSON H, et al. The UCSC Known Genes. Bioinformatics.2006; 22(9):11.
[18] DAVIS AP, GRONDIN CJ, JOHNSON RJ, et al. The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: update 2019.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47(D1):D948-D954.
[19] WANG J, VASAIKAR S, SHI Z, et al. WebGestalt 2017: a more comprehensive, powerful, flexible and interactive gene set enrichment analysis toolkit. Narnia. 2017; 45(W1): 0-0.
[20] ORGANIZATION WH. International Perspectives on Spinal Cord Injury. Weed Res.2013; 11(4): 314-316.
[21] 黄潇,谷亚坤,程雪燕,等.星形胶质细胞作为脊髓损伤治疗靶细胞的研究进展[J].生理学报,2017,69(6):794-804.
[22] 李向哲,王灿,吴勤峰,等.脊髓损伤后脑源性神经营养因子神经生物学效应的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2018,24(2):160-164.
[23] ORR MB, GENSEL JC. Spinal Cord Injury Scarring and Inflammation: Therapies Targeting Glial and Inflammatory Responses. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):541-553.
[24] LIU S, XIE YY, WANG B. Role and prospects of regenerative biomaterials in the repair of spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(8):1352-1363.
[25] SHAHREZAIE M, MANSOUR RN, NAZARI B, et al. Improved stem cell therapy of spinal cord injury using GDNF-overexpressed bone marrow stem cells in a rat model. Biologicals. 2017;50: 73-80.
[26] 李惠民,申才良.干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报,2019,54(4):662-666.
[27] RICCI-VITIANI L, CASALBORE P, PETRUCCI G, et al. Influence of local environment on the differentiation of neural stem cells engrafted onto the injured spinal cord. Neurol Res. 2006;28(5): 488-492.
[28] MUKHAMEDSHINA YO, GRACHEVA OA, MUKHUTDINOVA DM, et al.Mesenchymal stem cells and the neuronal microenvironment in the area of spinal cord injuryNeural Regen Res. 2019;14(2): 227-237.
[29] SYKOVÁ E, HOMOLA A, MAZANEC R, et al. Autologous Bone Marrow Transplantation in Patients with Subacute and Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplantation.2006;15(8):675-687.
[30] OKUDA A, HORII-HAYASHI N, SASAGAWA T, et al. Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Sheets May Promote Axonal Regeneration and Functional Recovery with Suppression of Glial Scar Formation After Spinal Cord Transection Injury in Rats.J Neurosurg Spine. 2017;26(3):388-395.
[31] SATAKE K, LOU J, LENKE LG. Migration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through Cerebrospinal Fluid Into Injured Spinal Cord Tissue. Spine.2004;29(18): 1971-1979.
[32] 林建华,雷盛民,康德智,等.静脉注射骨髓间质干细胞对脊髓损伤修复作用的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,30(9):48-51.
[33] KIM BJ, SEO JH, BUBIEN JK, et al. Differentiation of Adult Bone Marrow Stem Cells Into Neuroprogenitor Cells in Vitro. Neuroreport. 2002; 13(9):1185-1188.
[34] 郝强,郝飞,胡悦,等.过表达Sox2基因可增强人骨髓干细胞向神经元分化[J].神经解剖学杂志,2019,35(2):113-121.
[35] DAI G, LIU X, ZHANG Z, et al. Transplantation of Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Complete and Chronic Cervical Spinal Cord Injury.Brain Res. 2013;1533:73-79.
[36] IMPELLIZZERI D, MAZZON E, ESPOSITO E, et al. Effect of Apocynin, an Inhibitor of Nadph Oxidase, in the Inflammatory Process Induced By an Experimental Model of Spinal Cord Injury. Free Radic Res. 2011;45(2):221-236.
[37] AMO-APARICIO J, MARTÍNEZ-MURIANA A, SÁNCHEZ- FERNÁNDEZ A, et al. Neuroinflammation Quantification for Spinal Cord Injury.Curr Protoc Immunol. 2018;123(1):e57.
[38] TRUFLANDIER K, BEAUMONT E, CHARBONNEY E, et al. Mechanical Ventilation Modulates Pro-inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Spinal Cord Tissue After Injury in Rats. Neurosci Lett. 2018;671:13-18.
[39] SCHNEIDER L, REICHERT E, FAULKNER J, et al. CNS inflammation and neurodegeneration: sequelae of peripheral inoculation with spinal cord tissue in rat. J Neurosurg. 2019; 1: 1-12.
[40] PATERNITI I, CAMPOLO M, CORDARO M, et al. PPAR-α Modulates the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Melatonin in the Secondary Events of Spinal Cord Injury. Mol Neurobiol. 2017; 54(8):5973-5987.
[41] YUE X, GUO L, WANG Z, et al. Inhibition of Mir-17-5p Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Repair Spinal Cord Injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(9):3899-3907.
[42] FIGLEY SA, LIU Y, KARADIMAS SK, et al. Delayed Administration of a Bio-engineered Zinc-finger Vegf-a Gene Therapy Is Neuroprotective and Attenuates Allodynia Following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Plos One.2014;9(5):e96137.
[43] PAPA S, VISMARA I, MARIANI A, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Encapsulated Into Biomimetic Hydrogel Scaffold Gradually Release Ccl2 Chemokine in Situ Preserving Cytoarchitecture and Promoting Functional Recovery in Spinal Cord Injury. J Control Release. 2018;278:49-56.
[44] KNERLICH-LUKOSCHUS F, JURASCHEK M, BL?MER U, et al. Force-dependent Development of Neuropathic Central Pain and Time-related Ccl2/ccr2 Expression After Graded Spinal Cord Contusion Injuries of the Rat. J Neurotrauma. 2008;25(5): 427-448.
[45] 涂冬萍,马小军,莫长明,等.FOS蛋白的研究进展及生物信息学分析[J].湖北农业科学,2015,54(7):11-16.
[46] HAN J, KIM S, KO I, et al. Afferent Pathway-mediated Effect of α1 Adrenergic Antagonist, Tamsulosin, on the Neurogenic Bladder After Spinal Cord Injury. Int Neurourol J. 2017;21(3):178-188.
[47] MOGHADDAM A, SPERL A, HELLER R, et al. Elevated Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Levels in Patients with Neurological Remission After Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Plos One. 2016; 11(7): e159764.
[48] FERBERT T, CHILD C, GRAESER V, et al. Tracking Spinal Cord Injury: Differences in Cytokine Expression of Igf-1, Tgf-b1, and Scd95l Can Be Measured in Blood Samples and Correspond to Neurological Remission in a 12-week Follow-up. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34(3):607-614.
[49] ALLAHDADI KJ, DE SANTANA TA, SANTOS GC, et al. Igf-1 Overexpression Improves Mesenchymal Stem Cell Survival and Promotes Neurological Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):146.
|