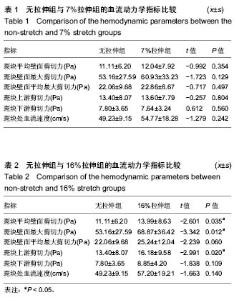
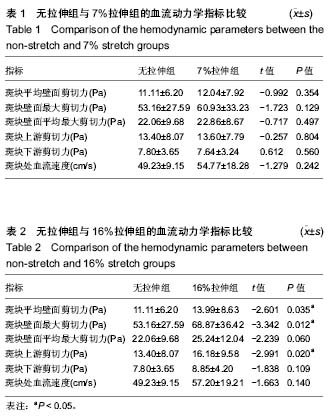
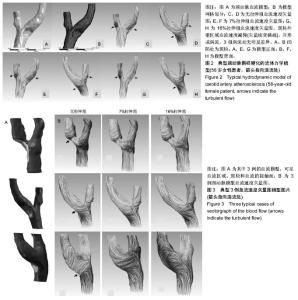
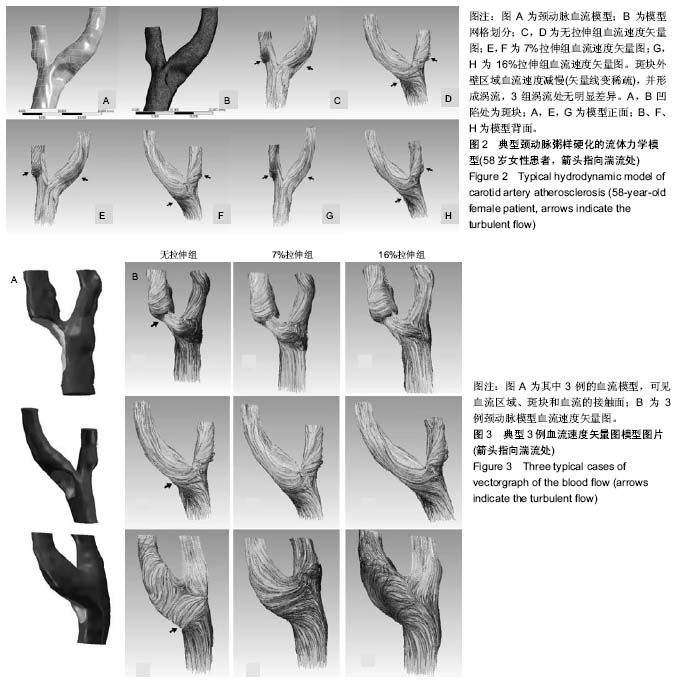
| [1] 李义凯.脊柱推拿的基础与临床[M].北京:军事医学科学出版社, 2001:1-2.[2] Haldeman S,Carey P,Townsend M,et al.Arterial dissections following cervical manipulation:the chiropractic experience. CMAJ.2001;165(7): 905-906.[3] Caro CG. Discovery of the role of wall shear in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(2):158-161.[4] Cibis M,Potters WV, Gijsen FJ, et al. Wall shear stress calculations based on 3D cine phase contrast MRI and computational fluid dynamics: a comparison study in healthy carotid arteries.Nmr in Biomedicine.2014;27(7): 826-834.[5] Lee SW,Antiga L,Spence JD,et al.Geometry of the Carotid Bifurcation Predicts Its Exposure to Disturbed Flow.Stroke. 2008;39(8): 2341-2347.[6] 荆利娜,高培毅,林燕,等.基于磁共振成像的颈动脉粥样硬化斑块局部血流动力学平台研究[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志, 2014, 14(7): 608-614.[7] Gao H, Long Q, Sadat U, et al. Stress analysis of carotid atheroma in a transient ischaemic attack patient using the MRI-based fluid-structure interaction method.Br J Radiol.2009;82 Spec No 1(special_issue_1):S46.[8] Banks J, Bressloff NW.Turbulence modeling in three-dimensional stenosed arterial bifurcations. J Biomech Eng. 2007;129(1):40-50. [9] 谌祖江,李义凯.颈部推拿引起脑卒中的临床概况及其发生机制[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,35(1): 50-53.[10] Gao H, Long Q, Graves M, et al. Carotid arterial plaque stress analysis using fluid-structure interactive simulation based on in-vivo magnetic resonance images of four patients. J Biomech. 2009;42(10):1416-1423.[11] Li ZY, Howarth SP, Tang T,et al.Structural analysis and magnetic resonance imaging predict plaque vulnerability: a study comparing symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45(4):768-775.[12] 张明明,贾化平,梁会泽,等.联合应用颈动脉超声及经颅多普勒超声对缺血性脑卒中的诊断价值[J].中国超声医学杂志,2015, 31(3): 197-200.[13] Herzog W,Tang C,Leonard T. Internal Carotid Artery Strains During High-Speed, Low-Amplitude Spinal Manipulations of the Neck.J Manipulative Physiol Ther.2015;38(9): 664-671.[14] 谌祖江.旋转手法对早期动脉粥样硬化斑块稳定性的影响[D].广州:南方医科大学, 2015.[15] 刘冬梅,何文.血流剪切力与颈动脉粥样硬化的关系[J].中国卒中杂志, 2008, 3(10):778-782.[16] 危当恒,王贵学,唐朝君,等.剪切应力特性对血管内膜增生及动脉粥样斑块形成的影响[J].中国动脉硬化杂志, 2006,15(6): 410-414.[17] 邱菊辉,王贵学,雷道希.血流动力学与动脉粥样硬化斑块的稳定性及其机制[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2009, 17(6): 495-497.[18] Fry DL.Certain histological and chemical responses of the vascular interface to acutely induced mechanical stress in the aorta of the dog. Circ Res. 1969;24(1):93-108.[19] Miyazaki Y,Nomura S,Miyake T,et al.High shear stress can initiate both platelet aggregation and shedding of procoagulant containing microparticles.Blood.1996;88(9): 3456.[20] Cecchi E,Giglioli C,Valente S, et al. Role of hemodynamic shear stress in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis.2011;214(2): 249-256.[21] Martin D,Zaman A,Hacker J,et al.Analysis of haemodynamic factors involved in carotid atherosclerosis using computational fluid dynamics. Br J Radiol. 2009 Jan;82 Spec No 1:S33-8.[22] 刘莹,罗院明,殷艳飞,等.动脉内流-固耦合作用下两相血流动力学数值模拟[J].介入放射学杂志, 2017,26(3):253-257.[23] 王淑萍,石永峰.涡流的形成及其对血液流变性的影响[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报, 2000,21(1): 104-105.[24] 王汝良,胡霖霖,郭金兴,等.颈动脉分叉的非稳态数值模拟分析[J].软件, 2018, 39(10): 36-41[25] 刘冬梅,何文,杨敏.彩色多普勒超声评价脑卒中患者颈动脉血流剪切力[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2014, 48(1):55-57.[26] 李晓,刘晓晟.局部血流动力学与颈动脉斑块相关性的影像技术研究[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志,2016, 39(5):535-538. |