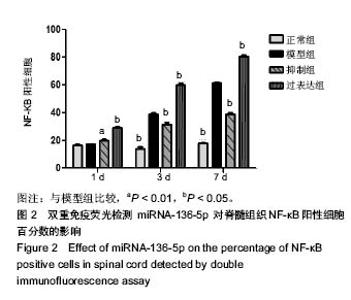
| [1] 杨俊松,郝定均,刘团江,等.急性脊髓损伤的临床治疗进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(4):368-373. [2] Böthig R, Fiebag K, Thietje R,et al. Morbidity of urinary tract infection after urodynamic examination of hospitalized SCI patients: the impact of bladder management. Spinal cord. 2013;51(1):70-73.[3] 梁锦前,沈建雄,邱贵兴.干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2008, 18(6): 475478.[4] Kwon BK,Dyomk MF,Fisher CG,et al.Spinal cord injury regene rative strategies and obstacles.Curr 0pin 0rthop.2004;15(3): 196-201.[5] Zhao T, Zhang ZN, Rong Z, et al. Immunogenicity of induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature.2011;474(7350): 212-215.[6] van Solingen C, Seghers L, Bijkerk R,et al. Antagomir- mediated silencing of endothelial cell specific microRNA-126 impairs ischemia-induced angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(8A):1577-1585. [7] Ma X,Zhou J,Zhong Y,et al.Expression, regulation and function of microRNAs in multiple sclerosis.Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(8):810-818.[8] Ksiazekwiniarek DJ, Kacperska MJ, Glabinski A.MicroRNAs as Novel Regulators of Neuroinflammation. Mediators Inflamm 2013;2013:519-530.[9] Lee HK,Bier A, Cazacu S, et al.MicroRNA-145 is downregulated in glial tumorsand and regulates glioma cell migration by targeting connective tissue growth factor. Plos One.2013;8:e54652.[10] Wang XH, Wang TL.MicroRNAs of microglia: Wrestling with central nervous system disease.Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(12):2067-2072. [11] Nishida N, Nagahara M, Sato T, et al. Microarray analysis of colorectal cancer stromal tissue reveals upregulation of two oncogenic miRNA clusters. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(11): 3054-3070.[12] Visone R, Russo L, Pallante P,et al. MicroRNAs miR-221 and miR-222, both overexpressed in human thyroid papillary carcinomas, regulate p27Kip1 protein levels and cell cycle.Endocrine-Related Cancer. 2007; 14(3): 791-798.[13] Chen HY, Lin YM, Chung HC, et al. miR-103/107 promote metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting the metastasis suppressors DAPK and KLF4. Cancer Res. 2012;72(14): 3631-3641.[14] Schulte LN, Westermann AJ, Vogel J. Differential activation and functional specialization of miR-146 and miR-155 in innate immune sensing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(1): 542-553.[15] Psathas JN, Doonan PJ, Raman P, et al. The Myc-miR-1792 axis amplifies B-cell receptor signaling via inhibition of ITIM proteins: a novel lymphomagenic feed-forward loop. Blood. 2013; 122(26): 4220-4229.[16] Zardo G, Ciolfi A, Vian L, et al. Polycombs and microRNA-223 regulate human granulopoiesis by transcriptional control of target gene expression. Blood. 2012; 119(17): 4034-4046.[17] Siddle KJ, Deschamps M, Tailleux L, et al. A genomic portrait of the genetic architecture and regulatory impact of microRNA expression in response to infection. Genome research. 2014; 24(5): 850-859.[18] 程素利,徐家淳,王剑歌,等.急性脊髓损伤大鼠Allen's造模方法的改良及行为学评价[J].四川中医,2015,33(10):43-45.[19] Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S. mi RBase: integrating micro RNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res.2011;39(Database issue): D152-157.[20] Zhou X, Jeker LT, Fife BT. Selective mi RNA disruption in T reg cells leads to uncontrolled autoimmunity. J Exp Med. 2008; 205(9): 1983-1991.[21] Bak M, Silahtaroglu A, Møller M, et al. MicroRNA expression in the adult mouse central nervous system.RNA (New York, N.Y.).2008;14(3): 432-444.[22] Bartel DP.MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function.Cell. 2004; 116(2):281-297.[23] Pauley KM,Cha S,Chan EK.MicroRNA in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases.(New York, N.Y.)J Autoimmun.2009; 32(3-4):189-194.[24] 杨俊娜,何丽,徐陶,等.miR-124在神经系统发育、损伤及修复中作用的研究进展[J].山东医药,2018,58(20):100-103.[25] 田密,丁宇,侯德仁,等.实时荧光定量PCR检测转基因阿尔茨海默病小鼠脑组织中miRNAs的差异表达[J].南方医科大学学报, 2013,33(2):262-266.[26] 孔程程,杨文平,华建,等.血清miRNA-181a在帕金森病中神经保护作用及机制分析[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 37(9):1081-1085.[27] Shi XZ,Zong SH,He JC,et al. miR-136-5p effect on A20 expression in interleukin-17-stimulated astrocytes. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2017;21(16):2587-2592.[28] Bortolotto V, Grilli M.Novel insights into the role of NF-κB p50 in astrocyte-mediated fate specification of adult neural progenitor cells.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(3):354-357.[29] Strickland ER, Hook MA, Balaraman S, et al.MicroRNA dysregulation following spinal cord contusion: implications for neural plasticity and repair. Neuroscience. 2011;186:146-160.[30] Aoki E,Yano R,Yokoyama H,et al.Role of nuclear transcription factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) for MPTP-induced apoptosis in nigral neurons of mice. Experimental and Molecular Pathlogy 2009;86:57-64.[31] Ahn KS, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappa B: from clone to clinic. Current Mol Med 2007;7:619-637[32] Sohn KH, Jo JM, Cho WJ, et al. Bojesodok-eum, a herbal prescription, ameliorates acute inflammation in association with the inhibition of NF-κB-mediated nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokine production.Evid-Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012: 457370.[33] Cortez M, Carmo LS, Rogero MM, et al. A high-fat diet increases IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α production by increasing NF-κB and attenuating PPAR-γ expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Inflammation.2013;36: 379−386.[34] Jobin C, Sartor RB. NF-κB signaling proteins as therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2000; 6: 206−213.[35] He J, Zhao J, Peng X,et al. Molecular Mechanism of MiR-136-5p Targeting NF-κB/A20 in the IL-17-Mediated Inflammatory Response after Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(3):1224-1241. |