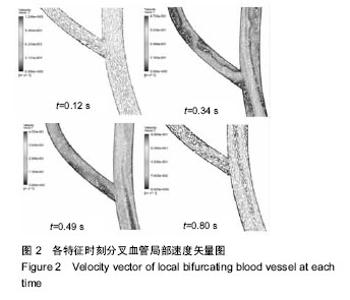
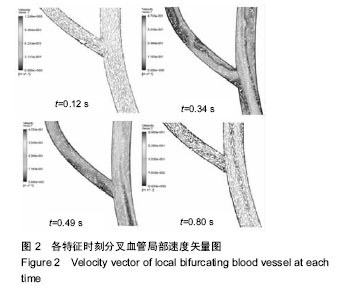
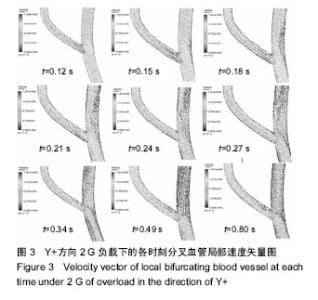
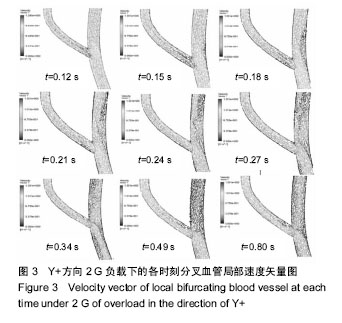
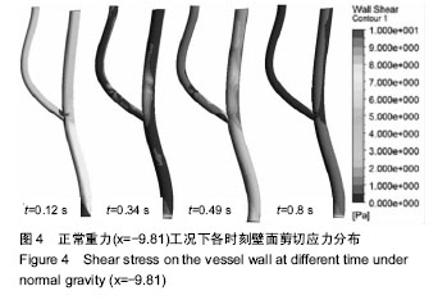
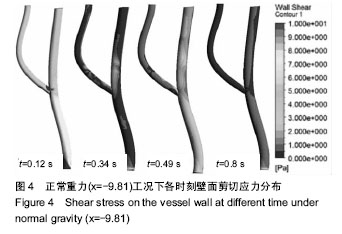
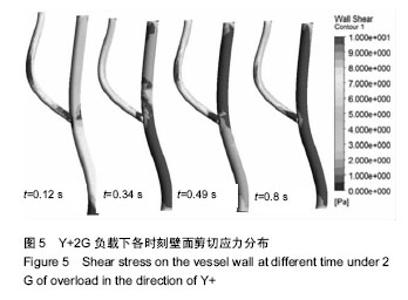
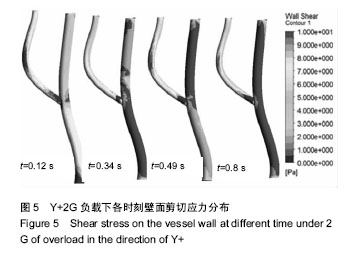
| [1] 肖国强.宇宙环境对人体机能及运动能力的影响[J].体育科学, 2005,25(1):71-73.[2] 钟国徽,李玉恒,凌树宽,等.太空微重力环境对人体的影响及防护措施[J].生物学通报,2016,51(10):1-4.[3] 孙联文,庄逢源.微重力导致航天员骨质疏松的研究进展[J].中华航空航天医学杂志. 2004,15(1):54-58.[4] 刘洋,冯娜,张曦,等.失重环境下人体心血管功能失调及对抗措施的仿真设计研究[J].医疗卫生装备,2015,36(7):16-19,33.[5] 张昭.冲击过程中脑组织力学行为的数值模拟[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2008,27(6):882-886,893.[6] 张立辉,金朝,徐艳,等.持续性加速度生理与防护研究进展[J].中华航空航天医学杂志,2014,25(4):299-307.[7] 金朝,耿喜臣,李茜,等.重复+Gz暴露后血清心肌损伤标志物浓度的变化[J].解放军预防医学杂志,2005,23(2):82-85.[8] 金朝,耿喜臣,苏迅,等.高+Gz暴露时血小板功能的变化[J].中华航空航天医学杂志,2004,15(1): 8-10. [9] 赵金萍.重力改变对人体心血管循环系统影响的仿真研究[D]. 株洲:湖南工业大学,2014. [10] 王汉青,赵金萍,陈娟.重力应激下心血管循环系统建模仿真研究进展[J].湖南工业大学学报,2014,28(3):99-102.[11] Fry DL.Acute vascular endothelial changes associated with increased blood velocity gradients.Circ Res.1968;22(2): 165-197.[12] 邓小燕.动脉狭窄内低密度脂蛋白传输的数值研究:LDL的浓度极化现象[J].计算力学学报,2002,19(3):253.[13] Malek AM,Alper SL,Izumo S.Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis.JAMA. 1999;282(21):2035-2042.[14] Fry DL.Certain histological and chemical responses of the vascular interface to acutely induced mechanical stress in the aorta of the dog.Circ Res.1969;24(1):93-108.[15] 徐跃平,杨金有,俞航,等.应用计算流体力学方法分析人体腹主动脉分叉内血液流动[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2012,22(8): 36-40.[16] Iyer EM,Malik WCH,Dikshit GCM.Serum creatine phosphokinase isoenzyme changes in pilots during +Gz training in human centrifuge.Ind J Aerospace Med. 2000; 44(1):12-15.[17] Ozturk C,Ilbasmis S,Dulkadir Z,et al.Cardiac effects of chronic +Gz exposure on military pilots. Aviat Space Environ Med. 2011;82(3):218-219.[18] Tetsuya H, Kimura M, Inui T, et al. Patterns of premature ventricular contractions occurrence during high Gz training. Aviat Space Environ Med.201.82(3):219.[19] 罗惠兰,李茜,耿喜臣,等.正加速度暴露对兔动脉粥样硬化过程中的内源性一氧化碳及血清脂质代谢的影响[J].中华航空航天医学杂志,2006,20(3):206-211.[20] 李茜,耿喜臣,金朝,等.在高+Gz应激下人体血清睾酮和皮质醇水平的变化[J].中华航空航天医学杂志, 2003,14(1):22-25. |