Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (14): 2259-2264.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0734
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biocompatibility of fully biodegradable polylactic acid and its copolymers: present and future applications
Shen Xin1, Liu Xue2, Su Feng2, Chen Zuo-sheng3, Li Su-ming4
- 1College of Polymer Science and Engineering, 2College of Chemical Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266042, Shandong Province, China; 3College of the Environmental Science and Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China; 4Institut Europeen des Membranes, UMR CNRS 5635, Universite Montpellier II, Montpellier 34095, France
-
Received:2017-12-27Online:2018-05-18Published:2018-05-18 -
Contact:Chen Zuo-sheng, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, College of the Environmental Science and Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China -
About author:Shen Xin, Doctoral candidate, College of Polymer Science and Engineering, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266042, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81570287; the Science and Technology Development Plan of Shandong Province, No. 2015GGX102017; the Achievement Transformation Plan of Qingdao, No. 16-6-2-17-nsh, 16-6-2-9-nsh
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shen Xin, Liu Xue, Su Feng, Chen Zuo-sheng, Li Su-ming. Biocompatibility of fully biodegradable polylactic acid and its copolymers: present and future applications[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(14): 2259-2264.
share this article
2.1 聚乳酸及其共聚物作为药物传输载体的生物相容性 作为药物传输载体,聚乳酸的疏水性增强了单核吞噬细胞系统摄取载药纳米颗粒的作用,导致体内循环停留时间缩短,造成药物效率降低。实现体内长循环的有效方法是通过聚乳酸与PEG等形成两亲性嵌段共聚物,在水中自组装形成核/壳结构的纳米胶束。在评价聚乳酸类生物材料的生物相容性时,也需考察载药治疗剂的生物相容性。包载顺铂的聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物微球也会由于药物的存在使大鼠体内出现炎症反 应[8],炎症反应和异物反应的程度较没有包载顺铂时增强(表1)。包载纳曲酮的聚丙交酯乙交酯缓释制剂在大鼠和兔子体内也会造成慢性炎症反应,而共聚物没有包载药物时在实验动物体内则没有发现相应症状[9]。也存在相反的情况,Anderson等[10]发现可生物降解材料载药时也会具有抗炎作用,将包载醋酸氢化可的松的聚乳酸膜植入大鼠皮下后,炎症部位所有类型的白细胞数量都显著降低,同时还减少了纤维包膜的形成。包载氢化泼尼松的聚乳酸微球可减少乳酸脱氢酶和溶酶体酶β-葡萄糖醛酸酶的释放,抑制小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞的活性。这些研究表明评价可生物降解药物递送系统的生物相容性时必须考虑治疗剂的毒性作用,并需要设置没有载药的可生物降解材料对照组。"

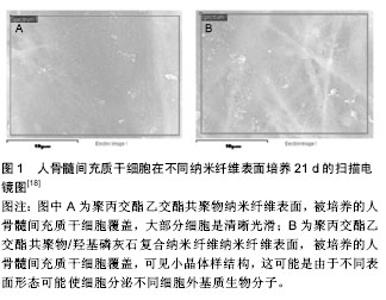
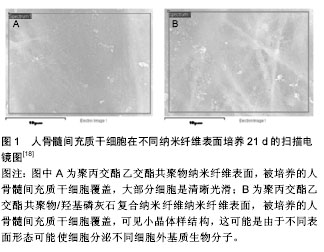
2.2 聚乳酸及其共聚物应用于骨科的生物相容性 临床上,骨科植入物导致的延迟炎症反应会在愈合伤口周围出现疼痛、红斑和肿胀等症状。这种反应显然与植入物的降解速率有关,例如聚乙交酯植入后12周可观察到炎症反应,然而聚乳酸的降解速率要慢得多,会在手术植入两到三年后才会出现反应[11]。除了材料本身,其降解速率也可能影响不良反应的形成。降解速率不仅取决于植入物的尺寸、设计和表面结构,还与植入部位、血流和患者的年龄等因素有关。植入物承受的压力增大会导致其断裂,这会增加表面积,使其降解加快。这反过来可能导致局部组织中的结晶物质浓度过高,并增强巨噬细胞介导的FBRs[12-13]。 报道显示左旋聚乳酸可吸收螺钉在多种情况下以胫骨和胫前黏液性囊肿、溶骨性股骨隧道变宽、侧股骨上髁异物反应以及关节内炎症反应延迟等形式引起异物反应,异物反应主要发生在螺钉断裂后,并且囊肿和螺钉碎片的消除会使症状得到缓解[14]。左旋聚乳酸颗粒仅造成了轻微的细胞损伤,不会引起严重的细胞损伤或细胞死亡。然而,这些组织病理学观察却不能完全解释患者中出现的组织肿胀现象,其可能是由多种因素共同造成的,例如左旋聚乳酸降解成较小的颗粒,导致渗透压增加,同时皮下组织的阻力相对于骨更小。组织病理学结果还显示左旋聚乳酸颗粒从纤维基质中的吞噬细胞外进入细胞内,这会导致成纤维样细胞的活化。囊肿本身由非细胞液体组成,且机体无疼痛感。囊肿的形成伴随着聚合物器械的降解和清除,这表明炎症反应与聚合物的降解产物密切相关。 生物可降解材料也被应用于上唇或肩袖损伤的治疗。有报道显示使用左旋聚乳酸类生物材料出现了并发症。例如4例患者的关节窝骨溶解和盂肱关节病进一步恶化,这不仅是由于软骨细胞的机械损伤,还可能是细胞介导的反应造成的[15]。在另一项研究中,22例患者中有3例出现软骨溶解症状,这可能是由与降解材料相关的炎症反应引起的[16]。最近的一项大型调查分析表明,植入左旋聚乳酸材料后有44例出现了并发症,84%的病例出现巨细胞反应。在所有病例中都观察到了晶体材料的存在,而分别有79%和70%的病例出现了乳头状滑膜炎和软骨损伤[17]。 目前主要通过对聚乳酸改性,制备复合材料来克服其在骨科应用时产生的不良生物医学反应。将羟基磷灰石[18]、β-磷酸三钙和珍珠层等与聚乳酸复合,中和聚乳酸降解的酸性微环境,提高材料的骨诱导性和骨传导性,达到减少非炎症反应的目的,并辅以血小板衍生生长因子等生物活性因子构建骨修复材料(图1)[19-20]。 2.3 聚乳酸及其共聚物应用于皮肤的生物相容性 聚乳酸在欧洲和美国被广泛用于软组织填充。皮肤治疗时由于炎症反应,会形成纤维结缔组织和胶原纤维再生组织,这反而有益于脂肪萎缩或面部老年性改变的患 者[21]。值得注意的是在治疗早期不良反应的发生率很高,主要表现为丘疹和结节。材料分布不均匀和不恰当重构都会引起这些不良反应[22]。在一项研究中,Vleggaar等[23]发现在接受7 185个疗程的2 131例患者中,大约3.2%的患者在面部发现了肉眼看不见的皮下丘疹,其中26.9%的患者丘疹在3个月内会自发消退,26例(1.2%)患者出现可见的皮下丘疹,组织学检查显示3例(0.1%)患者出现了肉芽肿瘤。 12例患者用聚乳酸制成的填充剂进行面部注射5-36个月后,出现了口内病变[24]。大剂量和高压力注射、肌肉运动或重力都能造成例如移位或错位等现象。病理组织学检查这些口内病变发现包括卵形、米粒状或纺锤状折射结构组成的边缘清晰小叶,具有非坏死性肉芽肿反应的巨细胞细胞质中也经常能观察到这些结构。所有病例都伴随着极微到中等程度的慢性炎症浸润和纤维变性,其中2例患者出现细胞坏死,2例患者观察到肌肉炎。正如其他报告中观察到的,在5个病例的肉芽肿处也发现了星状小体[25]。注射填充剂的体积较大,反复注入微液滴,填料中含有杂质,注射深度不当和粒子粒径大等因素都可能引发炎症形成。 聚乳酸是牛津循证医学中心(the Oxford Centre for Evidence-based Medicine)惟一推荐等级为B的填充剂,其他填充剂均为C或D[26]。在聚乳酸类填充剂得到广泛使用的同时,注射技术的提高显著降低了不良反应发生的数量。No等[27]通过将聚乳酸注入58例患者的鼻唇沟来研究提高注射技术的安全性,其中30例患者持续观察了24个月,仅有4例患者在注射部位出现了轻微的不良反应,但均在2个月后恢复,并且24个月后没有观察到与聚乳酸有关的不良反应。因此,聚乳酸填充剂能够安全有效地修复鼻唇沟。 2.4 聚乳酸及其共聚物在其他应用中的生物相容性 生物可降解材料可应用于中枢神经系统。Lewitus等[28]评价了将聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物植入SD大鼠脑实质内1-4周后对中枢神经系统的影响,结果表明聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物植入导致神经胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞的持续活化,并伴随持续的神经衰退。但聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物比降解速度较快材料产生的影响更为轻微。 在一项关于鼠气管滴注聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物后的影响研究中,观察到了炎症反应[29]。但从多核中性粒细胞聚集的数量来看,聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物比聚苯乙烯纳米微球所引发的炎症反应要轻微得多。同时新型聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物衍生物——二乙基氨基丙胺-聚乙烯醇-聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物会明显减少炎性递质。 Cantin等[30]评估了聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物对薄壁组织的影响,将聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物微粒注入SD大鼠的腮腺,随后进行了14 d的组织学检测。结果显示,薄壁组织的导管内腔和腺泡厚度等几项形态学参数发生改变。然而,这些变化都是轻微的,并且无明显的炎症反应。 聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物/聚乳酸微球可用作玻璃体内的药物递送系统。Rong等[31]通过将聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物/聚乳酸微球注入新西兰兔玻璃体内,来评价这些生物可降解材料的生物相容性,并在注射后12周内进行了详尽地检查。结果表明,在视网膜中没有发现细胞死亡、神经胶质细胞活化或炎症反应,并且也没有观察到组织或细胞超微结构的变化。更重要的是,通过评估双眼视网膜电图没有发现视网膜功能损坏。因此,聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物/聚乳酸微球是一种安全的药物递送系统,可用于玻璃体内注射来治疗眼后段疾病。类似的,Manna等[32]将包载甲氨蝶呤的聚乳酸微种植体植入到新西兰兔玻璃体内,未发现任何毒性迹象。并且在临床前和临床研究中,聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物在眼内转运也是安全的。值得注意的是,左旋聚乳酸植入兔玻璃体内会导致眼内压大幅下降并伴随CD11b+炎性细胞在小梁网的累积。但左旋聚乳酸比聚苯乙烯和聚-N-异丙基丙烯酰胺等材料引起的炎症反应更小。 聚乳酸可用作治疗粘连性中耳炎。在分别以豚鼠和南美栗鼠类啮齿动物为对象的两项研究中,聚乳酸对耳部没有明确的炎症反应[33-34]。而且,没有发现对听阈和波潜伏期等功能的影响。此外,将聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物植入豚鼠的中耳时,主要在30 d后出现了中性粒细胞等一些急性炎症反应[35]。这些研究结果与阴性对照差异均统计学意义。 在泌尿学领域,聚乳酸作为膨胀剂治疗膀胱输尿管回流和小便失禁。一些研究评价了聚乳酸和聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物在小鼠、大鼠和兔体内的短期和长期影响,在这些研究中都未发现炎症反应[36-37]。 生物可降解材料可用作血管支架,Pan等[38]在体外研究了左旋聚乳酸和聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物的血液相容性。研究表明两种材料均不影响红细胞形态,而且溶血率正常。凝血活性测试表明左旋聚乳酸和聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物会激活凝血途径,但引起的变化都在正常参考范围之内。因此,左旋聚乳酸和聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物的生物相容性符合在循环系统中使用的要求。 通过将聚乳酸及其共聚物与其他材料复合,负载药物和生物活性因子,并利用3D生物打印等技术手段,减少了不良反应的发生[39-42]。 2.5 聚乳酸及其共聚物的遗传毒性和致癌性 由于大部分致癌物都有遗传毒性,因此在评价生物材料的生物相容性时必须进行适当的遗传毒性评估。Uzun等[43]通过中国仓鼠卵巢细胞株和胞质分裂阻滞微核测试法评价聚乳酸对DNA的潜在损伤,发现无遗传毒性。Setyawati等[44]在人类皮肤成纤维细胞系BJ的基础上,通过观察γH2AX的表达,从分子水平研究聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物的潜在遗传毒性,证明聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物纳米粒无遗传毒性。Kazimirova等[45]用TK6类淋巴母细胞系证明聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物-聚氧化乙烯纳米粒没有遗传毒性。另外,用单核细胞检测聚丙交酯乙交酯共聚物-聚氧化乙烯纳米粒时会观察到微核数量增加。 可降解材料植入啮齿动物体内较长时间后,会在植入部位附近形成肉瘤,鼠的发生率更可高达80%。这种在长期植入啮齿动物后形成肿瘤的现象,通常被归结为由于固态致癌性或者奥本海默效应[46]。聚乳酸类生物材料植入后也观察到此现象,这与在啮齿动物中植入没有毒性或致瘤性的固体材料(如惰性塑料、金属和其他材料)仍会形成肉瘤相类似[47]。将左旋聚乳酸植入70只鼠,在106周的观察期内发现3只鼠有纤维肉瘤,而植入50只雄性Wistar鼠,2年后发现22只鼠出现纤维肉瘤和恶性纤维组织细胞瘤[48]。此外,Manavitehrani等[49]将左旋聚乳酸-聚己内酯植入15只SD大鼠关节内,结果有1只鼠在植入部位出现肉瘤。在这些研究中,肿瘤都没有系统性影响。 肉瘤形成的确切机制仍不清楚。肿瘤发生可能源于长期局部轻微炎症引发的一连串与生长因子和活性氧分泌有关的反应,导致Hh和Wnt信号通路激活和多重附加突变的积累,最终形成肿瘤[50]。局部肉瘤的形成与植入物的形状尺寸、植入时间和炎症程度等有关,与生物可降解聚合物的特定化学组分无关,同时人体出现局部肉瘤形成是极其罕见的。因此可得出结论,植入物引起的肉瘤具有物种依赖性,与植入物本身无关。 "
| [1] Gupta B,Revagade N,Hilborn J.Poly(lactic acid) fiber: an overview. Prog Polym Sci.2007;32(4): 455-482.[2] Vasir JK,Labhasetwar V.Biodegradable nanoparticles for cytosolic delivery of therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2007; 59(8):718-728.[3] Gunatillake PA,Adhikari R.Biodegradable synthetic polymers for tissue engineering.Eur Cell Mater.2003;5(1):1-16.[4] Lasprilla AJR,Martinez GAR,Lunelli BH,et al.Poly-lactic acid synthesis for application in biomedical devices-A review. Biotechnol Adv.2012;30(1):321-328.[5] Rasal RM,Janorkar AV,Hirt DE.Poly(lactic acid) modifications. Prog Polym Sci.2010;35(3):338-356.[6] Anderson JM.Biological responses to materials.Ann Rev Mater Res:2001;31(1):81-110.[7] Williams DF.On the mechanisms of biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2008;29(20):2941-2953.[8] Dhar S,Kolishetti N,Lippard SJ,et al.Targeted delivery of a cisplatin prodrug for safer and more effective prostate cancer therapy in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci.2011;108(5):1850-1855.[9] Yamaguchi K,Anderson JM.Biocompatibility studies of naltrexone sustained release formulations.J Control Release. 1992;19:299-314.[10] Anderson JM,Shive MS.Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA microspheres.Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2012; 64:72-82.[11] Tyler B,Gullotti D,Mangraviti A,et al.Polylactic acid(PLA) controlled delivery carriers for biomedical applications.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;107:163-175. [12] Evans NT,Irvin CW,Safranski DL,et al.Impact of surface porosity and topography on the mechanical behavior of high strength biomedical polymers.J Mech Behav Biomed. 2016; 59:459-473.[13] Boccafoschi F,Mosca C,Cannas M.Cardiovascular biomaterials: when the inflammatory response helps to efficiently restore tissue functionality.J Tissue Eng Regen M. 2014;8(4):253-267.[14] Thompson SM,Fung S,Wood DG.The natural history of biointerference screw cyst and new bone formation in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction 16-Year follow-up.Am J Sport Med.2016;44(1):113-117.[15] Athwal GS,Shridharani SM,O'Driscoll SW.Osteolysis and arthropathy of the shoulder after use of bioabsorbable knotless suture anchors.J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88(8):1840-1845.[16] Boden RA,Burgess E,Enion D,et al.Use of bioabsorbable knotless suture anchors and associated accelerated shoulder arthropathy report of 3 cases.Am J Sport Med.2009;37(7): 1429-1433.[17] McCarty LP,Buss DD,Datta MW,et al.Complications observed following labral or rotator cuff repair with use of poly-L-lactic acid implants.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2013;95(6):507-511.[18] Lee JH,Rim NG,Jung HS,et al.Control of osteogenic differentiation and mineralization of human mesenchymal stem cells on composite nanofibers containing poly [lactic-co-(glycolic acid)] and hydroxyapatite.Macromol Biosci. 2010;10(2):173-182.[19] Lou T,Wang X,Song G,et al.Fabrication of PLLA/β-TCP nanocomposite scaffolds with hierarchical porosity for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol.2014;69:464-470.[20] Dai J,Bai J,Jin J,et al.Stimulation by pearl of mineralization and biocompatibility of PLA.Adv Eng Mater.2015;17(11):1691-1697.[21] Rotunda AM,Narins RS.Poly-L-lactic acid: a new dimension in soft tissue augmentation.Dermatol Ther.2006;19(3):151-158.[22] Jones D.Volumizing the face with soft tissue fillers.Clin Plast Surg.2011;38(3):379-390.[23] Vleggaar D.Soft-tissue augmentation and the role of poly-L-lactic acid.Plast Reconstr Surg.2006; 118(3S):46S-54S.[24] Shahrabi-Farahani S,Lerman MA,Noonan V,et al. Granulomatous foreign body reaction to dermal cosmetic fillers with intraoral migration.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014;117(1):105-110.[25] Malzone MG,Campanile AC,Gioioso A,et al.Silicone lymphadenopathy: Presentation of a further case containing asteroid bodies on fine-needle cytology sample.Diagn Cytopathol.2015;43(1):57-59.[26] Jagdeo J,Ho D,Lo A,et al.A systematic review of filler agents for aesthetic treatment of HIV facial lipoatrophy (FLA).J Am Acad Dermatol.2015;73(6):1040-1054.[27] No YA,Seok J,Hyun MY,et al.Long-Term(24-Month) Safety Evaluation of Poly-DL-Lactic Acid Filler Injection for the Nasolabial Fold: A Multicenter, Open, Randomized, Evaluator-Blind, Active-Controlled Design.Plast Reconstr Surg.2015;135(6):1074e-1075e.[28] Lewitus DY,Smith KL,Shain W,et al.The fate of ultrafast degrading polymeric implants in the brain. Biomaterials. 2011;32(24):5543-5550.[29] Hara K,Tsujimoto H,Tsukada Y,et al.Histological examination of PLGA nanospheres for intratracheal drug administration.Int J Pharmaceut.2008;356(1):267-273.[30] Cantin M,Miranda P,Galdames IS,et al.In vivo biocompatibility of the PLGA microparticles in parotid gland.Int J Clin Exp Patho. 2013;6(11):2412-2412.[31] Rong X,Yuan W,Lu Y,et al.Safety evaluation of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid)/poly (lactic-acid) microspheres through intravitreal injection in rabbits.Int J Nanomed. 2014;9: 3057-3057.[32] Manna S,Banerjee RK,Augsburger JJ,et al.Biodegradable chitosan and polylactic acid-based intraocular micro-implant for sustained release of methotrexate into vitreous: analysis of pharmacokinetics and toxicity in rabbit eyes.Graef Arch Clin Exp.2015;253(8):1297-1305.[33] Ensari N,Tutar H,Ekinci O,et al.Effects of polylactic acid film on middle ear mucosa and cochlear function in Guinea pigs.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.2015;272(5):1091-1097.[34] Peltonen LI,Jero J,Sukura A,et al.Biocompatibility of polylactides in the middle ear: an experimental animal study.Otol Neurotol.2007;28(6):850-853.[35] Garcia LB,Junior C,da Silva A,et al.Tissue response evaluation of the mucosa of the tympanic cavity of guinea pigs, when receiving biodegradable implant.Acta Cir Bras. 2014;29: 12-18.[36] Lee SH,Ko K,Choo MS,et al.The effect and safety of polylactic acid and adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cell as an injectable bulking agent in urologic field: A 24-week follow-up study. J Biomed Mater Res B.2015;103(2):440-447.[37] Kotsar A,Isotalo T,Mikkonen J,et al.A new biodegradable braided self-expandable PLGA prostatic stent: an experimental study in the rabbit.J Endourol. 2008;22(5): 1065-1070.[38] Pan CJ,Tang JJ,Weng YJ,et al.Preparation, characterization and anticoagulation of curcumin-eluting controlled biodegradable coating stents.J Control Release. 2006;116(1): 42-49.[39] Yang YL,Chang CH,Huang CC,et al.Osteogenic activity of nanonized pearl powder/poly (lactide-co-glycolide) composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Bio Med Mater Eng. 2014; 24(1): 979-985.[40] Durand E, Sharkawi T, Leclerc G, et al. Head-to-head comparison of a drug-free early programmed dismantling polylactic acid bioresorbable scaffold and a metallic stent in the porcine coronary artery six-month angiography and optical coherence tomographic follow-up study. Circ Cardiovasc Inte. 2014; 7(1): 70-79.[41] Wang Y,Wei Y,Zhang X,et al.PLGA/PDLLA core-shell submicron spheres sequential release system: Preparation, characterization and promotion of bone regeneration in vitro and in vivo.Chem Eng J. 2015; 273:490-501.[42] Cui H,Zhu W,Nowicki M,et al.Hierarchical fabrication of engineered vascularized bone biphasic constructs via dual 3D bioprinting: integrating regional bioactive factors into architectural design.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(17): 2174-2181.[43] Uzun N,Martins TD,Teixeira GM,et al.Poly(l-lactic acid) membranes: bbsence of genotoxic hazard and potential for drug delivery.Toxicol Lett.2015;232(2):513-518.[44] Setyawati MI,Khoo PKS,Eng BH,et al.Cytotoxic and genotoxic characterization of titanium dioxide, gadolinium oxide, and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles in human fibroblasts.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(3):633-640.[45] Adhikari R,Danon SJ,Bean P,et al.Evaluation of in situ curable biodegradable polyurethanes containing zwitterion components. J Mater Sci Mater M.2010;21(4):1081-1089.[46] Kazimirova A,Magdolenova Z,Barancokova M,et al. Genotoxicity testing of PLGA-PEO nanoparticles in TK6 cells by the comet assay and the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay.Mutat Res/Gen Tox En. 2012;748(1):42-47.[47] Ramot Y,Nyska A,Markovitz E,et al.Long-term local and systemic safety of poly (l-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) after subcutaneous and intra-articular implantation in rats. Toxicol Pathol.2015;43(8):1127-1140.[48] Sasaki R,Matsumine H,Matsumoto N,et al.Spontaneous fibrosarcoma in an experimental aged Lewis rat. Lab Anim. 2012;46(4):352-355.[49] Manavitehrani I,Fathi A,Wang Y,et al.Reinforced poly(propylene carbonate) composite with enhanced and tunable characteristics, an alternative for poly(lactic acid). ACS Appl Mater Inter.2015; 7(40):22421-22430.[50] Kipanyula MJ,Etet PFS,Vecchio L,et al.Signaling pathways bridging microbial-triggered inflammation and cancer.Cell Signal.2013;25(2):403-416. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||