Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (31): 5060-5065.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.31.024
Previous Articles Next Articles
Transpedicular screw fixation for thoracolumbar fracture based on finite element analysis
Hao Shen-shen, Zhao Ru-yuan, Liu Zhi-bin, Wang Bo-wen, Cao Xin-hao, Xue Xiao-wei
- Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Online:2017-11-08Published:2017-12-01 -
Contact:Liu Zhi-bin, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Hao Shen-shen, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’ an University, Yan ’an 716000, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Social Development and Technology Research & Development Project of Shaanxi Province, No. 2015SF115; the Technology Huimin Project of Yan’an, No. 2016HM-10-03.
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hao Shen-shen, Zhao Ru-yuan, Liu Zhi-bin, Wang Bo-wen, Cao Xin-hao, Xue Xiao-wei. Transpedicular screw fixation for thoracolumbar fracture based on finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(31): 5060-5065.
share this article
2.1 骨折损伤机制的有限元分析 胸腰段脊柱泛指T11-L2脊柱节段,因其处于胸椎后凸和腰椎前凸的交界处,当肩背承受外伤时,则胸腰段位置承受应力最大,在外伤时容易因传导暴力致损伤。同时脊髓圆锥与马尾在该部位的移行区,椎管相对狭窄,硬膜囊周围有效间隙较小,损伤后产生并发症较多见。鉴于此,必需对胸腰段脊柱骨折的损伤机制有清晰的了解,方能有效地进行合理的治疗。 研究胸腰段脊柱骨折的损伤机制离不开生物力学。传统的生物力学研究多以尸体或动物脊柱标本作为研究对象,模拟损伤过程,分析其可能的发生机制,并对不同治疗方法进行比较。尸体标本因在结构形状、材料特性方面与正常人体相似,故结果直接、可靠,可有效的指导临床诊疗。然而尸体标本获取困难、费用高、可重复性较差,其实际应用也受到限制;而动物标本虽容易获得,但与正常生理状态下的人体有较大的差别,实验结果并非十分可靠。 近年来,有限元分析法(finite element method,FEM)逐渐应用于胸腰段脊柱骨折损伤及固定的生物力学研究中,并得到研究者的青睐。有限元分析法是数值计算中的一种离散化方法,是矩阵方法在结构力学和弹性力学等领域中的发展和应用。将一个由无数个质点组成且有无限个自由度的连续体,近似为由有限个且按一定方式相互联结在一起的单元所组成的集合体,来模拟或逼近原来的物体。从而将一个连续的无限自由度问题简化为离散的有限自由度问题进行求解的分析方法。通过对离散后的物体中的各个单元进行单元分析,最终得到对整个物体的分析。 与以往的数值计算方法不同,有限元分析法能用不同形态、不同大小、不同类型的单元任意划分载荷,并且能模拟由不同材料组成的复合结构,整个计算过程已程序化。 Brekelmans等[3]于1972年首次报道了将有限元分析法应用于脊柱生物力学研究。此后有限元分析法在脊柱生物力学领域的研究、应用愈加成熟和广泛。该研究方法具有费用低、耗时短、可重复性强等优点。 Qiu等[4]通过建立T12-L1脊柱有限元模型,分析椎体在轴向载荷下应力分布及终板位移情况,得出临近髓核的终板中心是椎体最高应力(93.7 MPa)集中处,证明骨折起始于终板,终板将后应力传递至椎体中心的网状松质骨,挤压脂肪、骨髓,进而引起椎体前后缘皮质发生断裂,形成爆裂骨折,与临床上椎体终板骨折多见的现象相符合。 Zeng等[5]报道通过有限元分析法建立胸腰段脊柱模型,L1椎体在加载100 J能量负荷时,测量轴向、前屈15°、后伸15°运动时各部位应力分布情况,发现模型载荷应力主要集中在L1椎体后上缘并随时间出现应力峰值;而去除L1上关节突后伸15°时,椎体应力较前明显较小、峰值消失,证明引起椎管内骨折形成的原因是骨折过程中关节突关节应力转移至椎体后上缘结果。 闫家智等[6]通过有限元分析法研究表明应力分布在退变的椎间盘发生了改变,较大应力施加在纤维环周边时,而应力在髓核明显降低,致使应力集中在软骨终板外周偏后,应力在关节突关节面明显增大,从而阐明了高龄、伴有椎间盘退变患者的高骨折风险及常见骨折部位的生物力学原因。 Yan等[7]通过有限元分析法建立T12-L1脊柱有限元模型研究骨折导致脊髓损伤的机制,证明了脊髓腹侧更易损伤。 王健等[8]通过有限元分析法建立不同压缩程度的胸腰段脊柱压缩骨折模型,分析不同运动工况下脊柱的活动度,证明了椎体压缩程度越大活动度越大。 然而,有限元分析法并非十分完美,建立的模型假定为均质、连续、个体同性材料,与实际生物材料特性有一定的误差[9]。人体胸腰段脊柱承重较大、活动范围大、力学性质复杂,还受体质量、周围肌肉力及韧带、腹压、双下肢姿势影响;有限元模型反映的是某一个体,某一刻,某一点的力学特性,现实中胸腰段脊柱骨折的分型较多、程度差异、软组织损伤程度不同,目前条件下完全模拟实际情况尚难以做到[8]。有限元分析法学习曲线长、建模耗时长、分析数据运算量大,因此临床应用受到一定的限制。 2.2 骨折的分型 (1)1930年,Boehler[10]首先分析了胸腰段脊柱骨折损伤机制的形态学特点,首次将胸腰段脊柱骨折分为剪力型骨折、压缩型骨折、牵拉伸展型骨折、牵拉屈曲型骨折和旋转型骨折5个类型。 (2)1983年,Denis[11]完善了 Holdsworth[12]的“二柱”理论,提出了著名的“三柱”理论。将胸腰段脊柱骨折分为4大类型及16个亚型。认为中柱是维持脊柱稳定最重要的结构并首次重点阐述了神经功能的重要性,将其列入不稳定程度的评估标准当中,其中I度不稳为单纯力学不稳,Ⅱ度不稳为神经功能有损害但未出现力学不稳,Ⅲ度不稳为同时存在神经功能损害和力学不稳。 (3)1994 年,McCormack等[13]对前中柱的骨折解剖情况严重程度进行评分,提出了载荷分享分类(load sharing classification,LSC )。该评分与后路内固定失败呈一定的相关性,载荷分享分类评分> 7,显示短节段固定失败率高;载荷分享分类评分≤ 6显示短节段固定鲜有失败。载荷分享分类以量化的方法,依据影像学资料、椎体受损程度、后凸畸形矫正程度等综合评分。该评分有助于临床治疗时手术入路的选择,当载荷分享分类> 7时,建议前路手术;当载荷分享分类≤6时,建议后路手术。 (4)1994年,Magerl等[14]进一步完善了Holdsworth[12]的理论,依据脊柱损伤的病理形态学特点,提出了AO分类。将胸腰段脊柱骨折分为3类9组27型,即A类:压缩型,B类:牵张型,C类:旋转型3 大类,再依据骨折形态、骨折部位、移位方向、韧带损伤等再细分为不同亚型,共多达55种。该分类目前临床应用较广泛。并概述了与分型有关的3种主要作用于脊柱的外力,即①压缩外力,可引起压缩性或爆裂性骨折;②牵张外力:可引起横向结构的损伤;③轴向扭转外力:可引起旋转性损伤。 (5)2005年,美国的脊柱创伤研究学组综合分析神经功能损伤情况和影像学资料,提出了胸腰段脊柱损伤评分系统(thoracolumbar injury severity score,TLISS)/胸腰段脊柱损伤分型及评分系统(thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score,TLICS)[15]。TLISS评分系统的主要参考因素包括骨折机制、神经系统功能状态和椎体后方韧带复合结构(posterior ligamentous complex,PLC)完整性。TLICS 评分系统的主要参考因素包括影像学资料、PLC损伤程度和神经功能损伤情况。该分类对损伤程度评估和治疗选择具有高度的关联性、同一性、重复性、可靠性,在指导非手术治疗上同样具有高度同一性。 (6)2015年,Park等[16]提出了一种改进的胸腰段脊柱损伤分型及评分系统(modified thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score,mTLICS),mTLICS改进了TLICS在放射诊断标准模糊的缺陷,可更准确地预测手术治疗,是一种更合适的评分系统。 (7)国内也有学者提出了自己的胸腰段脊柱损伤分类方案。金大地等[17]采用“类-型-亚型”体系,将胸腰段脊柱骨折分为3类2型3亚型,达18种之多。李利等[18]依据椎管中突入的爆裂性椎体的多少,将胸腰段脊柱骨折分为3个类型。 每一次分类的进步,都凝聚着无数研究者的辛勤劳动。随着对胸腰段脊柱损伤机制了解的深入和影像技术的发展,部分分类经过临床检验得以保存(表1),部分分类因其敝端过大,不适于临床应用。因此,目前尚无一种完美的分类方法。"
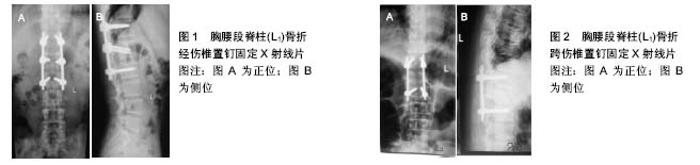
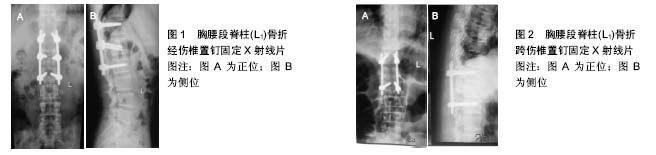
2.3 经伤椎置钉固定的应用 经伤椎置钉固定与跨伤椎置钉固定在治疗胸腰段脊柱骨折时均能获得良好的临床固定效果。随着置入螺钉数目的增加,相应手术风险和医疗费用也会增加,因此许多研究者对不同固定方法的生物力学和临床效果进行了研究报道。 Li等[19]应用有限元分析法建立胸腰段脊柱压缩骨折模型比较经伤椎和跨伤椎置钉固定的生物力学特性,发现螺钉根部为应力集中处,而且在不同运动工况如轴向、屈伸、侧弯及旋转负荷时,前者的各螺钉应力较后者明显减小,从而可减少术后螺钉断裂等发生。王洪伟等[20]动物生物力学测试证实经伤椎置钉标本在屈曲、后伸、旋转等各个运动方向的即时稳定性均较跨伤椎置钉标本好;且长期的病例随防也证实前者在保持矫正效果方向优于后者。谢申等[21]对比在压缩骨折中经伤椎置钉与跨伤椎置钉的疗效,认为后者的优点是明显缩短手术时间、减少术中出血及输血,而前者的优点是明显缩短住院卧床时间,减少术后6个月Cobb角及伤椎前缘高度丢失、降低目测类比评分得分等。刘潮坚等[22]报道对比爆裂骨折中经伤椎置钉与跨伤椎置钉的疗效,认为两者手术时间、出血量及住院时间方面无明显差异,但在术后2年随防时前者Cobb角及伤椎前缘高度丢失率方面明显小于后者。刘上楼等[23]的经伤椎与跨伤椎固定的生物力学实验结果认为,前者在生物力学强度、轴向刚度、抗扭力、脊柱稳定性等方面均优于后者。袁强等[24]也认为经伤椎置钉比跨伤椎置钉固定承受的应力少,并且利用螺钉的向腹侧加压作用克服骨折产生的后凸应力,防止骨折椎后移压迫椎管及椎体高度的丢失。Dick等[25]报道了在牛腰椎模型上进行生物力学研究,证明经伤椎固定能降低跨伤椎固定的平行四边形效应,增加稳定性,减少断钉断棒发生等。 邓海棠[26]应用有限元分析法分析了不同椎弓根螺钉置入内固定的应力分布,在不同运动状态下的前屈、侧弯、轴向旋转上的三维运动范围方面,经伤椎6钉固定最小;其次为经伤椎5钉固定;而跨伤椎4钉固定最大,生物力学稳定性最差。Li等[27]的研究也得出了相似的结论,应用有限元分析法对比分析经伤椎伤椎双侧与单侧置钉、跨伤椎置钉和单节段置钉的生物力学特性,最终认为经椎双侧置钉后脊柱的刚度和内固定装置的应力最为合适,生物力学稳定性最好。但是魏富鑫等[28]的生物力学测试得出了不同的结果,6钉经伤椎固定与4钉跨伤椎固定在前屈、后伸、左右侧弯、左右轴向扭转各运动范围及刚度值等方面,差异均无统计学意义。 马立敏等[29]应用有限元分析法分析了经伤椎置钉固定时钉棒系统有无横连杆时在不同运动工况下的生物力学变化,在轴向压缩工况下,由于应力主要集中在钉棒系统,故横连杆的存在与否无统计学差异;但在扭转及屈曲工况下,由于横连杆的存在可分担集中于钉棒系统下段的应力,从而起到优化钉棒系统的载荷,达到减少断钉发生的效果。 漆伟等[30]利用有限元分析法研究不同长度的椎弓根螺钉-骨复合体模型的应力变化,认为生理载荷下螺钉长度在30-50 mm范围内,螺钉长度的增加伴随螺钉上的平均应力逐渐增大,而皮质骨及松质骨上的平均应力逐渐减小。 Hsu等[31]运用机械测试和有限元分析法对比同一长度不同直径的椎弓根螺钉的固定效果,发现螺钉外径越大,则骨-螺钉界面的刚度、拔出力也越大。由于椎弓根较细且毗邻重要神经、血管和脏器等组织,一旦螺钉置入过程中发生偏移并突破骨皮质,可能会损伤这些结构。 谭磊等[32]应用有限元分析法对比分析经伤椎置钉时不同方式的伤椎置钉对腰椎和螺钉的影响,认为经伤椎斜向下置钉固定可以避免应力集中,从而能更有效地预防内固定断裂、退钉等内固定失效的发生;伤椎螺钉长度以仅限于椎弓根内或达椎体后1/3即可提供足够的把持固定和矫正效果,又能避免伤椎螺钉过度向前推挤而影响伤椎内骨折块复位。 6钉经伤椎固定(见图1)与4钉跨伤椎固定(见图2)相比,分散了钉棒连接应力,降低了各钉的聚中应力,缩短了椎间固定点的距离,提供三平面固定,避免了4钉跨伤椎固定的“平行四边形效应”和“悬挂效应”[32]。直接对骨折椎体进行固定,降低了正常椎间盘的牵张,增加了固定稳定性。同时伤椎螺钉可对伤椎起到一定的复位和向前推顶作用。 李晶等[33]对6钉经伤椎固定的合理性提出怀疑,认为伤椎置钉可导致骨折块进一步分离,而且在纵向撑开时伤椎内的螺钉可产生移动切割椎体作用。经伤椎置钉固定的适应证相对较严格,如要求上下两侧椎弓根完整且椎体粉碎程度相对较轻,伤椎至少有一侧终板保持完整,选择合适的螺钉进钉位置、角度,保证伤椎内钉道完整、骨质完整等,方能确保内固定的成功,并且伤椎螺钉置是否会增加手术风险、影响伤椎骨折愈合等问题还需进一步研究。 经伤椎单节段置钉固定近年来在临床上应用较多,其置钉固定于伤椎及其相临的一个上位椎或下位椎,即将2对椎弓根钉分别固定于伤椎与相邻的正常椎体中,此种4钉两棒的手术方法可减小后柱力矩,降低钉-棒应力负荷,减少内固定疲劳折断率。由于仅融合一个节段,可将脊柱运动节段的丢失减到最低,减少邻节段椎体退变率[34]。Xu等[35]报道经伤椎单节段4钉和跨伤椎4钉固定的生物力学特性相似,认为特定的胸腰段脊柱骨折可选择经伤椎单节段4钉固定。鲁世保等[36]报道经伤椎单节段与经伤椎置钉固定两种术式的疗效之间无明显差异,但经伤椎单节段置钉固定节段少、出血量少、手术时间短、费用低,并且对椎体活动度与邻近椎体的影响较小,认为此种术式有较好的推广应用价值。 伤椎植骨可以促进骨折愈合及减少术后矫正丢失。植骨的方法包括椎间植骨法、经椎管椎体植骨法、经伤椎椎弓根椎体植骨法。椎间植骨由于显露较好、操作方便、减压充分、出血较少、对脊髓刺激较轻。然而植骨块未进行直接固定,可能存在滑移,一旦突入椎管将压迫脊髓或神经。而且髓核组织通常清除不彻底,残留潜在致压物。经椎管椎体植骨在直视下进行,植骨充分,支撑可靠,植骨口易于封闭,避免了小植骨粒进入椎管的可能性,且不受伤椎椎弓骨折的影响。经伤椎椎弓根椎体植骨无需椎板减压、不经过椎管、脊髓和神经根干扰小,保存了脊柱后柱结构的完整性。然而此法植骨量有限、充填不确定,当存在较大空洞时,植骨效果欠佳。 宋元进等[37]应用有限元分析法建模验证了经伤椎椎弓椎植骨较不植骨在生物力学稳定性更优越。亦有学者研究骨水泥强化替代植骨的效果。Xu等[38]通过有限元分析法模拟两种不同程度T12椎体骨折,研究单纯内固定与是否行骨水泥强化效果,结果认为重度脊柱骨折的内固定钉棒系统和脊柱的应力在骨水泥强化后明显减小,还可预防脊柱矫正度的丢失及内固定失效。此方法操作过程中对脊髓、神经根有一定的干扰,要求操作者熟悉脊柱解剖结构,对临床经验、技巧要求较高。Oken等[39]研究认为术后患者运动功能与植骨节段长短没有关系。Chou等[40]通过回顾性分析发现椎体内植骨不能防止内固定的失败与矫正度的丢失,因此不推荐伤椎植骨。Jindal等[41]发现椎体内植骨后出现骨纤维化而影响骨愈合。 "
| [1] Bensch FV, Koivikko MP, Kiuru MJ, et al. The incidence and distribution of burst fractures. Emergency Radiology.2006;12(3):124-129.[2] 徐少汀,葛宝丰,徐印钦.实用骨科学[M],4版.北京:人民军医出版社, 2015:780-781.[3] Brekelmans WA, Poort HW, Slooff TJ. A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts. Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317.[4] Qiu TX, Tan KW, Lee VS,et al.Investigation of thoracolumbar T12-L1 burst fracture mechanism using finite element method. Med Eng Phys. 2006; 28(7):656-664.[5] Zeng ZL, Zhu R, Li SZ, et al. Formative mechanism of intracanal fracture fragments in thoracolumbar burst fractures: a finite element study.中华医学杂志(英文版), 2013;126(15):2852-2858.[6] 闫家智,吴志宏,汪学松,等. 腰椎间盘退变后应力变化的有限元分析[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2009, 31(4):464-467.[7] Yan Y, Qi W, Wu Z, et al.Correction: Finite Element Study of the Mechanical Response in Spinal Cord during the Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture.Plos One.2012; 7(9):e41397.[8] 王健,李凯,陈博,等.胸腰椎体压缩性骨折三维有限元模型的建立和分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(16):1498-1503.[9] 陈浩,张锦洪,贺增良. 脊柱胸腰段三维有限元模型的建立与验证[J]. 江苏大学学报: 医学版,2014,24(1):72-75.[10] Boehler L. Die Techniek der KnochenbruchbehandlungimGrieden und imKriege. Vienna, Austria: Verlag Von WilheimMaudrich.1930: 9-11.[11] Denis F.The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine. 1983;8(8):817-831.[12] Holdsworth F. Fractures, dislocations, and fracture-dislocations of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1970;52(8):1534-1551.[13] Mccormack T,Karaikovic E,Gaines RW.The load sharing classification of spinefractures.Spine.1994;19(15):1741-1744.[14] Magerl F, Aebi M,Gertzbein SD, et al. A comprehensive classification of thoracic and lumbar injuries.Eur Spine J.1994; 3(4):184-201.[15] Vaccaro AR, Jr LR, Hurlbert RJ, et al.A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries: the importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status. Spine.2005;30(20):2325-2533.[16] Park HJ, Lee SY, Park NH, et al. Modified thoracolumbar injury classification and severity score (TLICS) and its clinical usefulness. Acta Radiologica.2015; 57(1):74-81.[17] 金大地, 杨守铭, 于娜沙,等. 胸腰椎骨折分类及其病理形态特点[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2000, 38(11):811-814.[18] 李利, 史亚民, 王华东,等. 胸腰椎爆裂骨折椎管内骨折块CT分型及对后路减压方式的意义[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2006, 8(3):215-217.[19] Li QL, Li XZ,Liu Y,et al.Treatment of thoracolumbar fracture withpedicle screws at injury level: a biomechanical study based on threedimensional finite element analysis. Eur J OrthopSurg Traumatol.2013;23:775-780.[20] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.伤椎置钉技术治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学及临床随访研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(16):1356-1360.[21] 谢申,祝少博.经伤椎和跨伤椎螺钉置入固定胸腰椎压缩性骨折:脊柱稳定性长期随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20:522-528.[22] 刘潮坚,蔡拉加,石昭宏,等.伤椎置钉与不置钉短节段内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(6):531-535.[23] 刘上楼,徐军,倪卓民,等.经胸腰段伤椎单节段椎弓根螺钉固定后的生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(39):6908-6913.[24] 袁强,田伟,张贵林,等.骨折椎垂直应力螺钉在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(4):217-222.[25] Dick JC, Jones MP, Zdeblick TA, et al.A biomechanical comparison evaluating the use of intermediate screws and cross-linkage in lumbar pedicle fixation. J Spinal Disord.1994; 7(5):402-407.[26] 邓海棠.有限元法分析胸腰椎骨折椎弓根钉置入内固定的应力分布[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(17):2533-2539.[27] Li C, Zhou Y, Wang H, et al. Treatment of unstable thoracolumbarfractures through short segment pedicle screw fixation techniquesusing pedicle fixation at the level of the fracture: A finite elementanalysis. PLoS One.2014;9:e99156.[28] 魏富鑫,刘少喻.后路短节段椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的进展[J].脊柱外科杂志, 2006, 4(2):112- 115.[29] 马立敏,周烨,张余,等.伤椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰段椎体压缩骨折的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国数字医学, 2013,8(10):54-57.[30] 漆伟, 雷伟, 严亚波. 椎弓根螺钉长度变化对螺钉-骨复合体模型应力影响的三维有限元分析研究[J]. 医用生物力学, 2010, 25(3): 206-211.[31] Hsu CC, Chao CK, Wang JL, et al.Increase of pullout strength of spinal pedicle screws with conical core: biomechanical tests and finite element analyses. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(4):788-794.[32] 谭磊,李彦慧,于铁成,等.六钉系统中伤椎不同置钉方式治疗腰椎骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2015(19):66-69.[33] 李晶,吕国华,王冰,等.胸腰椎骨折脱位伤椎固定的可行性研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2005, 25(5):293-296.[34] Junge A,Gotzen L, Von GT, et al. Monosegmental internal fixator instrumentation and fusion in treatment of fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. Indications, technique and results. Der Unfallchirurg.1997;100(11):880-887.[35] Xu G, Fu X, Du C, et al. Biomechanical comparison of mono-segment transpedicular fixation with short-segment fixation for treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: a finite element analysis. ProcInstMech Eng H.2014;228:1005-1013.[36] 鲁世保, 孔超, 海涌,等.单节段与双节段经伤椎椎弓根钉固定治疗轻中度不稳定胸腰椎骨折的疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2013, 33(6):615-620.[37] 宋元进,蔡锦方.胸腰段骨折不同固定方式的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(52):10269-10273.[38] Xu G, Fu X, Du C, et al. Biomechanical effects of vertebroplasty on thoracolumbar burst fracture with transpedicular fixation: a finite element model analysis.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;10:379-383.[39] Oken F, Yildirim O, Oken O, et al.Short or long fusion after thoracolumbar burst fractures does not alter selected gait parameters: a preliminary study. J Orthop Res.2011;29(6): 915-918.[40] Chou PH,MaHL,WangST,et al.Fusion may not be a necessaryprocedure for surgically treated burst fractures of the thoracolumbarand lumbar spines: a follow-up of at least ten years.J BoneJointSurg Am.2014;96(20):1724-1731.[41] Jindal N, Sankhala S S, Bachhal V. The role of fusion in the management of burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine treated by short segment pedicle screw fixation: a prospective randomisedtrial. Macromolecules. 2012;10(6):1177-1181.[42] 孙涛, 西永明, 汪贯习,等. 椎间盘镜下微创治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2005,13(8):634-635. |
| [1] | Wei Guoqiang, Li Yunfeng, Wang Yi, Niu Xiaofen, Che Lifang, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Shi Guopeng, Bai Ling, Mo Kai, Zhang Chenchen, Xu Yangyang, Li Xiaohe. Biomechanical analysis of non-uniform material femur under different loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [2] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [3] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [4] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [5] | Wen Mingtao, Liang Xuezhen, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Mechanical stability of Sanders II type calcaneal fractures fixed by two internal fixation methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 838-842. |
| [6] | Wang Hailong, Li Long, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yilihamu·Tuoheti. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of acetabular prosthesis in the Lewinnek safety zone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 843-847. |
| [7] | Wei Bing, Chang Shan. Finite element analysis of different angles of nail placement in sagittal plane of spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 864-869. |
| [8] | Li Guijun, Fang Xiaohui, Kong Weifeng, Yuan Xiaoqing, Jin Rongzhong, Yang Jun. Finite element analysis of the treatment of hallux valgus deformity by microplate combined with super strong suture elastic fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 938-942. |
| [9] | Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Renaguli·Maihemuti, Aizimaitijiang·Saiyiti, Wang Junxiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Stress analysis of maxillary central incisor crown implant restoration in different occlusal modes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 567-572. |
| [10] | Wang Can, Gu Weiping, Jiang Yubin, Zhu Lin, Chen Gang. Finite element analysis of the influence of different implant designs on the stress of mandibular edentulous jaw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 573-578. |
| [11] | Zhang Jianguo, Chen Chen, Hu Fengling, Huang Daoyu, Song Liang. Design and biomechanical properties of dental implant pore structure based on three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 585-590. |
| [12] | Lin Boying, Shen Mao. Biomechanical stability of endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw combined with contralateral translaminar facet screw fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 329-333. |
| [13] | Nie Wenzhong, Li Xiaoxuan, Zeng Jiayi, Shi Changqiang. Biomechanical changes in different implantation and fixation methods of lumbar fusion cage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1505-1509. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Cai Qunbin, Zou Xia, Hu Jiantao, Chen Xinmin, Zheng Liqin, Huang Peizhen, Lin Ziling, Jiang Ziwei. Relationship between tip-apex distance and stability of intertrochanteric femoral fractures with proximal femoral anti-rotation nail: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 831-836. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||