Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (22): 3501-3506.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.22.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Three-dimensional finite element analysis on the stress of mandibular first molar restored with different locations and numbers of gold alloy posts and cores
- Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining 272100, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2017-06-01Online:2017-08-08Published:2017-09-01 -
About author:Liu Tao, Master, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining 272100, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Development Plan of Jining City, No. [2015]57-43, [2011]57; the Medical and Health Science Development Project of Shandong Province, No. 2015WS0411
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Tao, Geng Hai-xia.
share this article
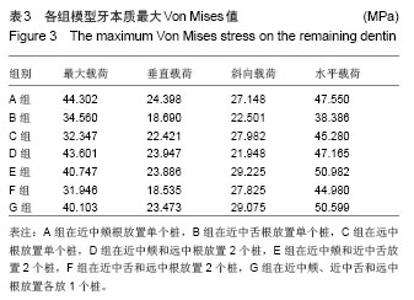
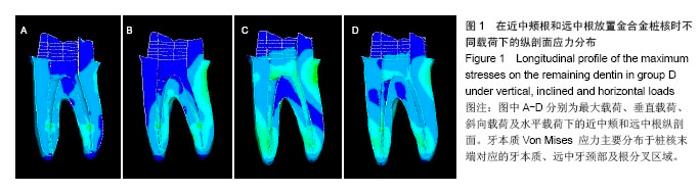
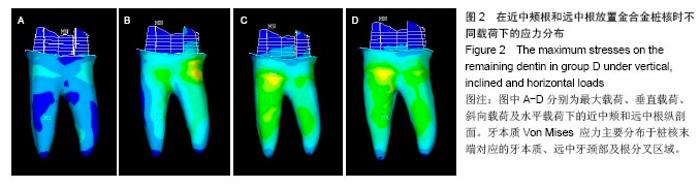
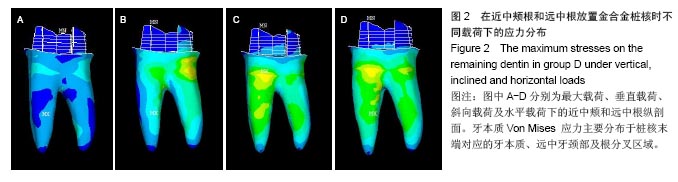
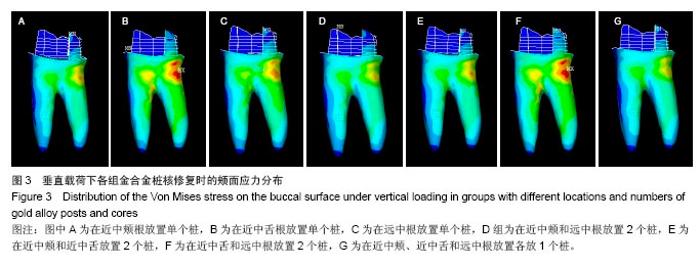
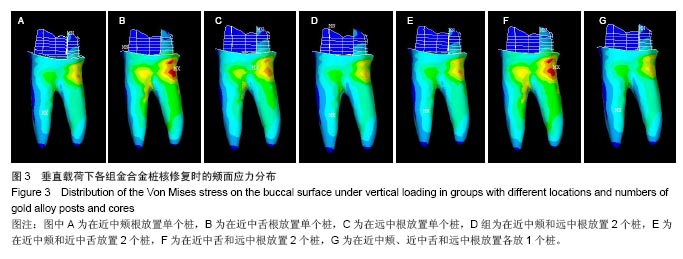
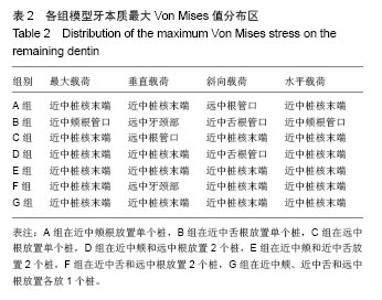
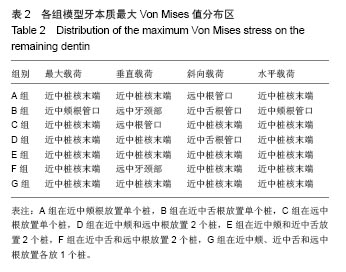
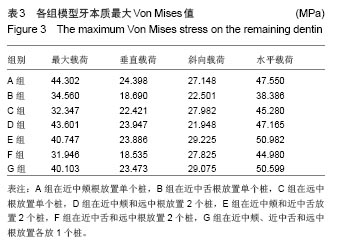
2.2 桩核数目、位置及载荷对基牙Von Mises 应力最大值的影响 桩核数目和位置:下颌第一磨牙近中颊壁缺损金合金桩核全瓷冠修复时,不同数目和位置桩修复时牙本质的Von Mises 应力峰值,见表3。当放置单个桩时,在垂直载荷、斜向载荷和水平载荷作用下,远中根内放置桩较近中颊根和近中舌根放置桩,牙本质最大Von Mises值小,随着桩的数目和位置变化,剩余牙本质上Von Mises 应力峰值呈现出不规律变化。 载荷:在相同修复方式下,随着载荷侧向力增加,基牙Von Mises 应力最大值逐渐增加;在水平载荷下,近中颊根和近中舌根放置桩时,基牙最大Von Mises应力值最大,为50.982 MPa。"
| [1]Olsburgh S,Jacoby T,Kerjci I.Crown fractures in the permanent dentition:pulpal and restorative considerations.Dent Traumatol.2002;18(3):103-115.[2]Aquilino SA,Caplan DJ.Relationship between crown placement andthe survival of endodontically treated teeth.J Prodent Dent.2001;87(3):256-263.[3]Watanabe MU,Anchieta RB,Rocha EP,et al.Influence of crown ferrule heights and dowel material selection on the mechanical behavior of root- filled teeth: a finite element analysis. J Prosthodont. 2012;21(4):304-311.[4]Roscoe MG,Noritomi PY,Novais VR,et al.Influence of alveolar bone loss, post type, and ferrule presence on the biomechanical behavior of endodontically treated maxillary canines: strain measurement and stress distribution.J Prosthet Dent.2013;110(2):116-126.[5]Sturdevant JR,Bader JD,Shugars DA,et al.A simple method to estimate restoration volume as a possible predictor for tooth fracture.J Prosthet Dent.2003;90(2):162-167.[6]Dejak B,Mlotkowski A.The influence of ferrule effect and length of cast and FRC posts on the stresses in anterior teeth.Dent Mater.2013;29(9):e227-e237.[7]Chen D,Wang N,Gao Y,et al.A 3-dimensional finite element analysis of the restoration of the maxillary canine with a complex zirconia post system.J Prosthet Dent.2014;112(6): 1406-1415.[8]唐昊喆,刘伟,许方文,等.牙本质肩领形态及纤维桩的长度对患牙抗折强度影响的研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2013,14(4): 243-246.[9]刘畅,薛莉,张玉.纤维桩修复严重缺损后牙的临床疗效评价[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2013,1(40):24-27.[10]马洪学,申丽丽,刘琨,等.玻璃纤维桩核与铸造金属桩核修复残根残冠及无桩修复牙体的临床效果评价[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2013,2(1):45-48.[11]Zhang Y,Ayiguli A,Li Q,et al.The influence of ferrule effect on post-restored restoration using extended finite element method.Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi.2014;49(6): 357-361.[12]康成容,魏素华,周折冲,等.牙本质肩领高度对上颌中切牙应力影响的三维有限元研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2016,17(1): 31-36.[13]苏恩典,吴凤鸣.不同位置和高度的单壁箍结构对牙根抗力影响的实验研究[J].口腔医学,2013,5(5):303-306.[14]王惠芸.我国人牙的测量与统计[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 1959, 7(3):149-154.[15]赵铱民,陈吉华.口腔修复学[M].6 版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2008:99-103.[16]Ho MH,Lee SY,Chen HH,et al.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effects of posts on stress distribution in dentin.J Prosthet Dent.1994;72(4):367-372.[17]Ashman RB,Van Buskirk WC.The elastic properties of a human mandible.Adv Dent Res.1987;1(1):64-67.[18]Fischer H,Weber M,Marx R.Lifetime prediction of all-ceramic bridges by computational methods. J Dent Res.2003;82(3): 238-242.[19]Imanishi A,Nakamura T,Ohyama T,et al.3-D Finite element analysis of all-Ceramic posterior crowns. J Oral Rehabil. 2003;30(8):818-822.[20]Lanza A,Aversa R,Rengo S,et al.3D FEA of cemented steel, glass and carbon posts in a maxillary incisor.Dent Mater. 2005;21(8):709-715.[21]翁维民,李玲,张富强,等.不同材料桩核冠系统修复上中切牙后的三维有限元分析[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2004,13(2):79-82.[22]于海洋,巢永烈,杜传诗.不同弹性模量的粘接剂对三型瓷贴面复合体应力的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 1999,15(5):335- 338[23]Takash N,Aogu I,Hisatsugu K,et al.Stress analysis of metalfree polymer crows using the three-dimensional finite element method.Int J Prosthodont.2001;14(5):401-405.[24]Magne P.Efficient 3D finite element analysis of dental restorative procedures using micro-CT data.Dent Mater. 2007;23(5):539-548.[25]Matsukawa K,Yato Y,Hynes RA,et al.Comparison of Pedicle Screw Fixation Strength Among Different Transpedicular Trajectories: A Finite Element Study.Clin Spine Surg.2017; 30(7):301-307. [26]Toniollo MB,Macedo AP,Pupim D,et al.Finite Element Analysis of Bone Stress in the Posterior Mandible Using Regular and Short Implants, in the Same Context, with Splinted and Nonsplinted Prostheses.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2017;32(4):e199-e206. [27]Verri FR,Santiago JF Jr,Almeida DA,et al.Biomechanical Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Single Implant-Supported Prostheses in the Anterior Maxilla, with Different Surgical Techniques and Implant Types.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2017;32(4):e191-e198. [28]Pegoretti A,Fambri L,Zappini G,et al.Finite element analysis of a glass fibre reinforced composite endodontic post. Biomaterials.2002;23:2667-2682.[29]Su C,Su Y,Li Z,et al.In situ synthesis of bilayered gradient poly(vinyl alcohol)/hydroxyapatite composite hydrogel by directional freezing-thawing and electrophoresis method.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;77:76-83.[30]Han SH,Sadr A,Tagami J,et al.Internal adaptation of resin composites at two configurations: Influence of polymerization shrinkage and stress.Dent Mater.2016; 32(9):1085-1094.[31]Fronza BM,Rueggeberg FA,Braga RR,et al.Monomer conversion, microhardness, internal marginal adaptation, and shrinkage stress of bulk-fill resin composites.Dent Mater.2015;31(12):1542-1551. [32]Kishen A,Kumar GV,Chen NN.Stress-strain response in human dentine: Rethinking fracture predilection in postcore restored teeth.Dent Traumatol.2004;20(2):90-100.[33]Asmussen E,Peutzfeldt A,Sahafi A.Finite element analysis of stresses in endodontically treated, dowel -restored teeth.J Prosthet Dent.2005;94(4):321-329.[34]Zhen M,Wei YP,Hu WJ,et al.Finite element analysis of the maxillary central incisor with traditional and modified crown lengthening surgery and post-core restoration in management of crown-root fracture.Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016;51(6):362-367. [35]Zhen M,Hu WJ,Rong QG.Finite element analysis of the maxillary central incisor with crown lengthening surgery and post-core restoration in management of crown-root fracture.Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao.2015;47(6):1015-1021. [36]Minamino T,Mine A,Matsumoto M,et al.Nondestructive observation of teeth post core-space using optical coherence tomography: comparison with microcomputed tomography and live images.J Biomed Opt.2015;20(10):107001. [37]Qian YM,Zhong Q,Chen S.Comparison of clinical effects of Co-Cr alloy cast post-core and everStick fiber post in restoration of labially or lingually inclined maxillary central incisor.Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue.2017;26(1):89-93. [38]Lee KS,Shin JH,Kim JE,et al.Biomechanical Evaluation of a Tooth Restored with High Performance Polymer PEKK Post-Core System: A 3D Finite Element Analysis.Biomed Res Int.2017;2017:1373127. [39]Huang SF,Chen WR,Lin CL.Biomechanical interactions of endodontically treated tooth implant-supported prosthesis under fatigue test with acoustic emission monitoring.Biomed Eng Online.2016;15:23. [40]Yang A,Lamichhane A,Xu C.Remaining coronal dentin and risk of fiber-reinforced composite post-core restoration failure: a meta-analysis.Int J Prosthodont.2015;28(3):258-264. [41]Durmu? G,Oyar P.Effects of post core materials on stress distribution in the restoration of mandibular second premolars: a finite element analysis.J Prosthet Dent.2014;112(3): 547-554. [42]Nie EM,Chen XY,Zhang CY, et al.Influence of masticatory fatigue on the fracture resistance of the pulpless teeth restored with quartz-fiber post-core and crown.Int J Oral Sci.2012 Dec;4(4):218-220. [43]Mahmoudi M,Saidi A,Gandjalikhan Nassab SA,et al.A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effects of restorative materials and post geometry on stress distribution in mandibular molar tooth restored with post-core crown.Dent Mater J.2012;31(2):171-179. [44]赵莉,李丽君,赵克,等.不同桩核系统修复上颌第一磨牙的有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(6):607-612.[45]付钢,杜莉,任嫒姝,等.不同设计桩核的后牙残根核桩冠修复体的三维有限元应力分析[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(1):24-28. |
| [1] | Wei Guoqiang, Li Yunfeng, Wang Yi, Niu Xiaofen, Che Lifang, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Shi Guopeng, Bai Ling, Mo Kai, Zhang Chenchen, Xu Yangyang, Li Xiaohe. Biomechanical analysis of non-uniform material femur under different loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [2] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [3] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [4] | Wen Mingtao, Liang Xuezhen, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Mechanical stability of Sanders II type calcaneal fractures fixed by two internal fixation methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 838-842. |
| [5] | Wang Hailong, Li Long, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yilihamu·Tuoheti. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of acetabular prosthesis in the Lewinnek safety zone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 843-847. |
| [6] | Wei Bing, Chang Shan. Finite element analysis of different angles of nail placement in sagittal plane of spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 864-869. |
| [7] | Li Guijun, Fang Xiaohui, Kong Weifeng, Yuan Xiaoqing, Jin Rongzhong, Yang Jun. Finite element analysis of the treatment of hallux valgus deformity by microplate combined with super strong suture elastic fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 938-942. |
| [8] | Zhang Jianguo, Chen Chen, Hu Fengling, Huang Daoyu, Song Liang. Design and biomechanical properties of dental implant pore structure based on three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 585-590. |
| [9] | Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Renaguli·Maihemuti, Aizimaitijiang·Saiyiti, Wang Junxiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Stress analysis of maxillary central incisor crown implant restoration in different occlusal modes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 567-572. |
| [10] | Wang Can, Gu Weiping, Jiang Yubin, Zhu Lin, Chen Gang. Finite element analysis of the influence of different implant designs on the stress of mandibular edentulous jaw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 573-578. |
| [11] | Lin Boying, Shen Mao. Biomechanical stability of endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw combined with contralateral translaminar facet screw fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 329-333. |
| [12] | Nie Wenzhong, Li Xiaoxuan, Zeng Jiayi, Shi Changqiang. Biomechanical changes in different implantation and fixation methods of lumbar fusion cage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(10): 1505-1509. |
| [13] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [14] | Song Chengjie, Chang Hengrui, Shi Mingxin, Meng Xianzhong. Research progress in biomechanical stability of lateral lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 923-928. |
| [15] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||