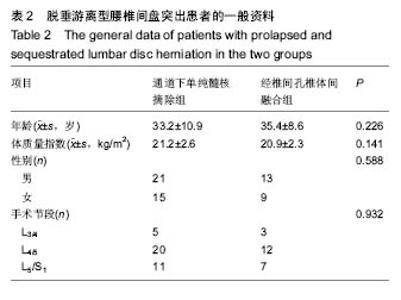
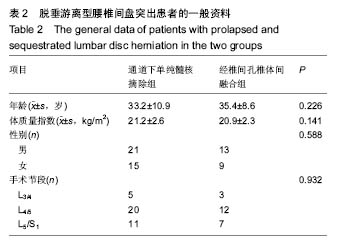
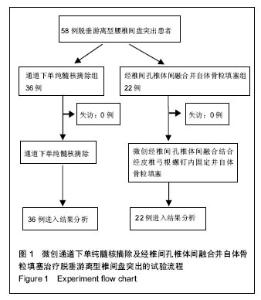
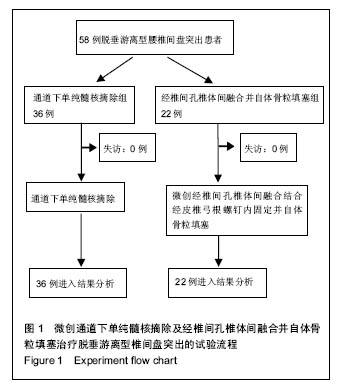
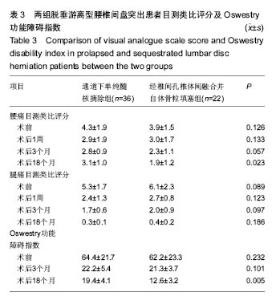
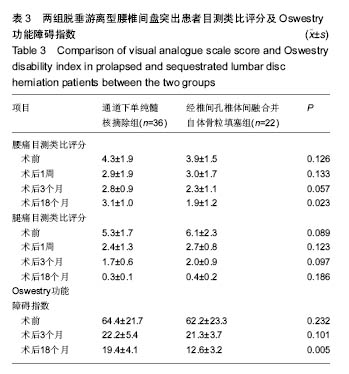
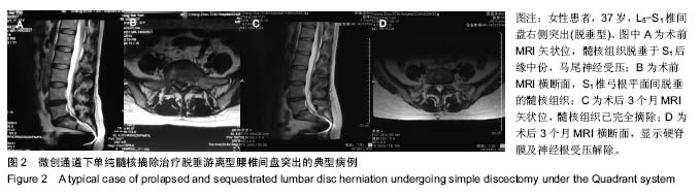
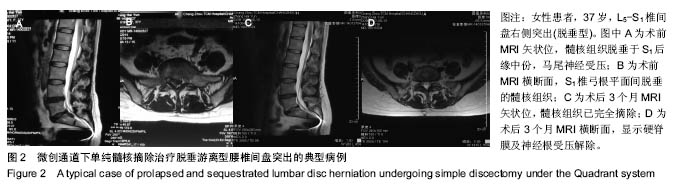
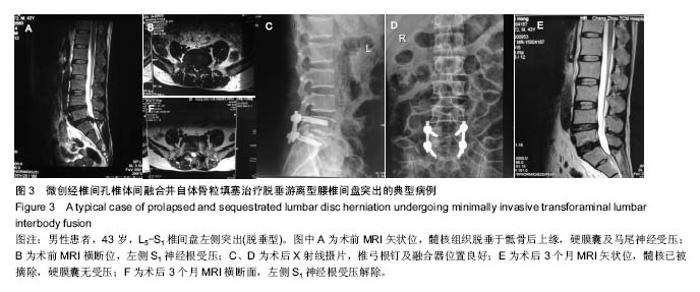
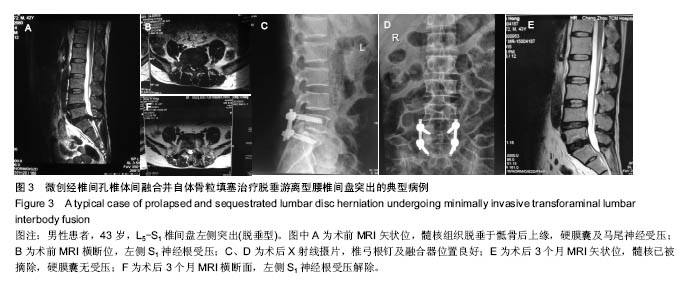
| [1]严小虎,杨红胜,曹宗锐,等. 6例椎间孔内游离型腰椎间盘突出症的临床治疗效果分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2015(12):1102-1104. [2]许真.手术治疗脱垂游离型腰椎间盘突出症21例[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2004,25(3):182-183. [3]袁正兵,高梁斌,李健,等.小切口椎板开窗髓核摘除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症142例[J].实用医学杂志,2007,23(12):1861-1863.[4]宋世江,宋瑞芳,张玉岩,等.小切口椎板开窗髓核摘除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效观察[J].山东医药,2008,48(17):49-50.[5]行军,陈俞涛,杨江伟,等.小切口椎板开窗髓核摘除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症38例[J].陕西医学杂志,2012,41(8):1089-1090.[6]周广勇,尹磊,王毅,等.小切口椎板开窗髓核摘除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症(附298例报告)[J].山东医药,2009,49(14):47-48.[7]郭继东,侯树勋,李利,等.椎板开窗髓核摘除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症10年以上随访的疗效评价[J].中国骨伤,2013,26(1):24-28.[8]Watanabe K, Yamazaki A, Morita O, et al. Clinical outcomes of posterior lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar foraminal stenosis: preoperative diagnosis and surgical strategy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24(3):137-141. [9]冯皓宇,马迅,何李明,等.后路椎间植骨融合与椎弓根钉内固定修复复发性腰椎间盘突出症:6个月随访[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(9):1371-1376.[10]Rouben D, Casnellie M, Ferguson M. Long-term durability of minimal invasive posterior transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a clinical and radiographic follow-up. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24(5):288-296. [11]高益,王斌,彭立波,等.微创经椎间孔椎体间融合术治疗腰椎间盘突出症伴腰椎不稳[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(2):227-230.[12]徐晖,肖立军,陈文贵.微创经椎间孔椎体间融合术与开放手术治疗腰椎滑脱症临床分析[J].河北医学,2013,19(1):48-51.[13]张伟彬,陈扬,杨欣建,等.微创经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合术与PLIF治疗单节段腰椎间盘突出症的临床疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2016,31(1):13-15.[14]毛克亚,王岩,肖嵩华,等.微创下腰椎经椎间孔椎体间融合术混合内固定治疗复发性腰椎间盘突出症的可行性研究[J].中华外科杂志,2013,51(8):723-727.[15]Tsou PM, Yeung AT. Transforaminal endoscopic decompression for radiculopathy secondary to intracanal noncontained lumbar disc herniations: outcome and technique. Spine J. 2002;2(1):41-48. [16]Milette PC. Classification, diagnostic imaging, and imaging characterization of a lumbar herniated disk. Radiol Clin North Am. 2000;38(6):1267-1292.[17]Stubbs DF. Visual analogue scales. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979;7(1):124. [18]Fairbank J, Pynsent P. The Oswestry disablility index. Spine 2000;25:2490-2453. [19]Macnab I. Negative disc exploration. An analysis of the causes of nerve-root involvement in sixty-eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971;53(5):891-903. [20]朱文虎,陈国平,洪天禄,等.改良微创经椎间孔椎体间融合术治疗腰椎退行性疾病的融合率[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(5):450-453.[21]孙根文,塔依尔•阿不都哈德尔.经皮椎间孔镜技术治疗腰椎病变的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(5):422-425. [22]黄炎,孔雷,孔荣,等.经皮椎间孔镜技术在脊柱微创手术中应用的研究进展[J].中华解剖与临床杂志,2015,20(5):469-472.[23]Choi G, Lee SH, Lokhande P, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic approach for highly migrated intracanal disc herniations by foraminoplastic technique using rigid working channel endoscope. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(15):E508-515. [24]Lee S, Kim SK, Lee SH, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for migrated disc herniation: classification of disc migration and surgical approaches. Eur Spine J. 2007; 16(3):431-437. [25]Kim CH, Chung CK, Jahng TA, et al. Surgical outcome of percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar lumbar diskectomy for recurrent disk herniation after open diskectomy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(5):E125-133. [26]刘丰平,赵红卫,陈海丹,等. TESSYS椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出症的学习曲线及经验[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(3): 235-241.[27]McGirt MJ, Ambrossi GL, Datoo G, et al. Recurrent disc herniation and long-term back pain after primary lumbar discectomy: review of outcomes reported for limited versus aggressive disc removal. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(2):338-344; discussion 344-345. [28]吴洁石,包聚良,徐瑞生,等.腰椎后路椎间融合术治疗原位复发性椎间盘突出症[J].江苏医药,2010,36(2):154-156.[29]Takeshima T, Kambara K, Miyata S, et al. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of disc excision for lumbar disc herniation with and without posterolateral fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(4):450-456.[30]Chrastil J, Patel AA. Complications associated with posterior and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(5):283-291. [31]Cao P, Chen Z, Zheng Y, et al. Comparison of simple discectomy and instrumented posterior lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of lumbar disc herniation combined with Modic endplate changes. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(15): 2789-2794.[32]郭鑫,皮国富,刘宏建,等.通道下经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合术治疗单节段腰椎间盘突出症[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2015,32(3):650-652.[33]丁文彬,郑召民,王建儒,等.微创与开放经椎间孔椎体间融合术治疗单节段腰椎病变的Meta分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25 (1):45-53.[34]匡凌浩,徐冬,李广庆,等.经椎间孔椎体间融合术治疗腰椎滑脱症的疗效观察[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(29):2293-2296.[35]陈晓涛,谢守宁,王凯.微创经椎间孔植入物置入腰椎体间融合:螺钉位置不良及cage移位特点[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(13): 2057-2062.[36]Carragee EJ, Spinnickie AO, Alamin TF, et al. A prospective controlled study of limited versus subtotal posterior discectomy short -term outcomes in patients with herniated lumbar intervertebral discs and large posterior annular defect. Spine. 2006;31(6):653-657. [37]Huang W, Han Z, Liu J, et al. Risk Factors for Recurrent Lumbar Disc Herniation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(2):e2378. [38]Cinotti G, Roysam GS, Eisenstein SM, et al. Ipsilateral recurrent lumbar disc herniation. A prospective, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80(5):825-832. |