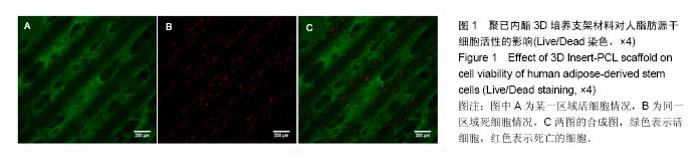
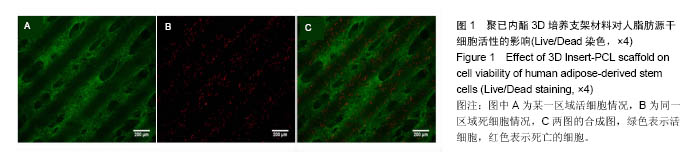
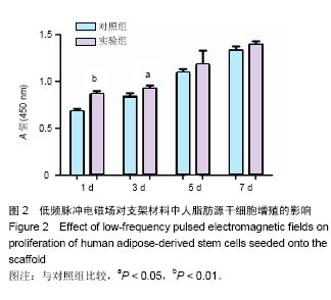
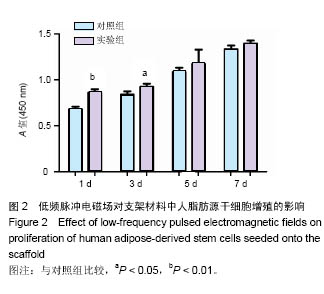
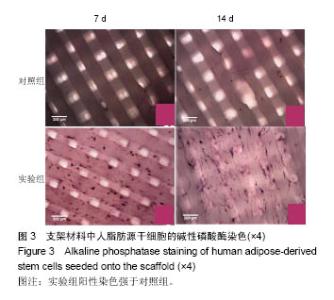
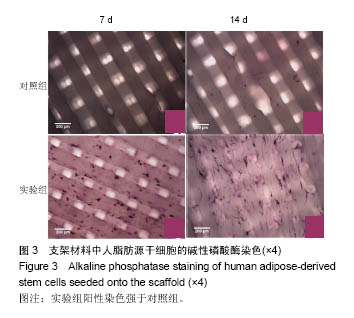
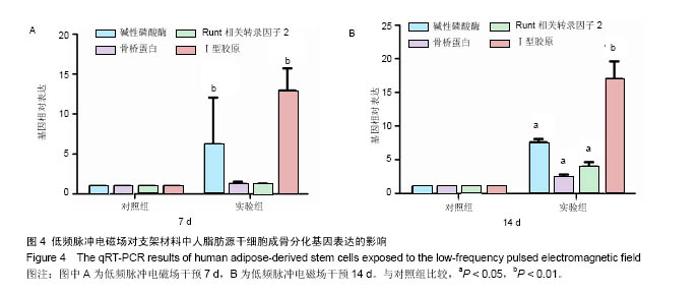
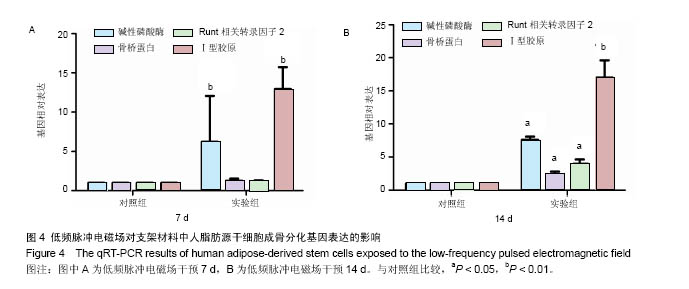
| [1]郭颖,李玉宝. 骨修复材料的研究进展[J].世界科技研究与发展, 2001,23(1):33-37.[2]郝建原,邓先模.复合生物材料的研究进展[J].高分子通报,2002, 15(5):1-8.[3]胡金龙,王静成,颜连启.组织工程学技术治疗骨缺损的最新研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(2):150-153.[4]Hutmacher DW.Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials.2001;21(24):2529-2543.[5]赵娜.脂肪干细胞诱导分化的现状及前景[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(6):969-974.[6]Minear S,Leucht P,Miller S,et al. rBMP Represses Wnt Signaling and Influences Skeletal Progenitor Cell Fate Specification During Bone Repair.J Bone Miner Res.2010; 25(6):1196-1207.[7]张志达,江晓兵,沈耿杨,等.磷酸钙及硫酸钙支架在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(8):1203-1209.[8]刘越,赵艳梅,田学忠,等.明胶/纳米羟基磷灰石三维多孔骨支架的制备及其生物安全性评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(16):1634-1640.[9]Flautre B,Descamps M,Delecourt C,et al.Porous HA ceramic for bone replacement: Role of the pores and interconnections -experimental study in the rabbit.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2001; 12(8):679-682.[10]Murugan R,Ramakrishna S.Bioresorbable composite bone paste using polysaccharide based nano hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials.2004;25(17):3829-3835.[11]赵文婧,刘玲珑,吴丽情,等.骨髓间充质干细胞的二维及三维培养实验研究[J].右江民族医学院学报,2014,36(3):355-356.[12]滕伟,郭志坤.细胞三维培养的研究进展[J].医学综述,2008, 14(12):1767-1770.[13]胡康洪,姚颖. 三维细胞培养技术的研究与应用[J].医学分子生物学杂志,2008,5(2):185-188.[14]肖登.低频脉冲电磁场的生物学作用[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2010,32(11):871-873.[15]宋先舟,陈继革,吴华,等.低频脉冲电磁场诱导成骨的研究进展[J].中华实验外科杂志,2008,25(10):1359-1360.[16]许伟东,刘家富,钱红,等.脉冲电磁场治疗骨延迟愈合的临床分析[J].中国康复医学杂志,2006,21(5):440-441.[17]许伟东.脉冲电磁场治疗骨不连的研究进展[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2009,31(10):707-708.[18]Zuk PA,Zhu M,Ashjian P,et al. Human Adipose Tissue Is a Source of Multipotent Stem Cells.MolBiol Cell.2003; 13(12): 4279-4295.[19]Frese L,Dijkman PE,Hoerstrup SP.Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine. Transfus Med Hemother. 2016;43(4):268-274.[20]Beane OS,Fonseca VC,Cooper LL,et al.Impact of aging on the regenerative properties of bone marrow-, muscle-, and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells.Plos One. 2014;9(12):e115963.[21]Zuk PA,Zhu M,Mizuno H,et al.Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng.2001;7(2):211-228.[22]Zuk PA,Zhu M,Ashjian P,et al.Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells.Mol Biol Cell.2002;13(12): 4279-4295.[23]Lyu CQ,Lu JY,Cao CH,et al.Induction of Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by a Novel Self-Supporting Graphene Hydrogel Film and the Possible Underlying Mechanism. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(36):20245-20254.[24]陈犹白,陈聪慧,Qixu Zhang,等.脂肪干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志电子版,2016,11(2):126-134.[25]Cheng G,Chen K,Li Z,et al. Enhancement of osteoblastic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rats by sinusoidal electromagnetic fields.Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi.2011;28(4):683-688.[26]Luo F,Hou T,Zhang Z,et al.Effects of pulsed electromagnetic field frequencies on the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.Orthopedics.2012;35(4):e526-e531.[27]Liu C,Yu J,Yang Y,et al. Effect of 1 mT sinusoidal electromagnetic fields on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.Bioelectromagnetics.2013;34(6):453-464.[28]Jansen JH,Op VDJ,Punt BJ,et al.Stimulation of osteogenic differentiation in human osteoprogenitor cells by pulsed electromagnetic fields: an in vitro study.Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders.2010;11(1):1-11.[29]Yang Y,Tao C,Zhao D,et al.EMF acts on rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to promote differentiation to osteoblasts and to inhibit differentiation to adipocytes. Bioelectromagnetics.2010;31(4):277-285.[30]Tsai MT,Li WJ,Tuan RS,et al. Modulation of osteogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells by specific pulsed electromagnetic field stimulation.J Orthop Res.2009;27(9): 1169-1174.[31]Lin CC,Lin RW,Chang CW,et al.Single-pulsed electromagnetic field therapy increases osteogenic differentiationthrough Wnt signaling pathway and sclerostin downregulation. Bioelectromagnetics.2015;36(7):494-505.[32]Zhou YJ,Wang P,Chen HY,et al.Effect of Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields on Osteogenic Differentiation and Wnt/beta-catenin Signaling Pathway in Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.2015;46(3):347-353.[33]Garg P,Mazur MM,Buck AC,et al.Prospective Review of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation into Osteoblasts. Orthop Surg.2017;9(1):13-19.[34]Petecchia L,Sbrana F,Utzeri R,et al. Electro-magnetic field promotes osteogenic differentiation of BM-hMSCs through a selective action on Ca(2+)-related mechanisms.Sci Rep.2015; 5:13856.[35]Roskies M,Jordan JO,Fang D,et al.Improving PEEK bioactivity for craniofacial reconstruction using a 3D printed scaffold embedded with mesenchymal stem cells.J Biomater Appl.2016;31(1):132-139.[36]Wang Z,Tian X,Bai S.Research progress of adipose-derived stem cells compound with three dimensional printing scaffold for engineered tissue.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2016;30(3):320-322. |