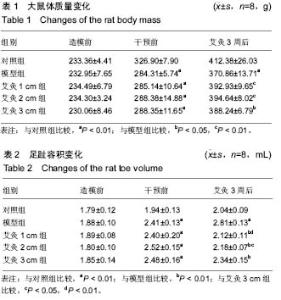
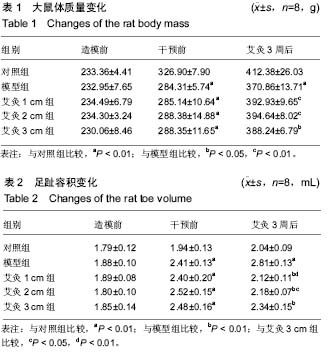
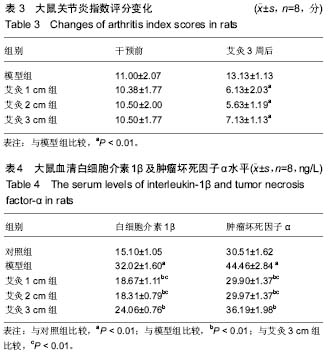
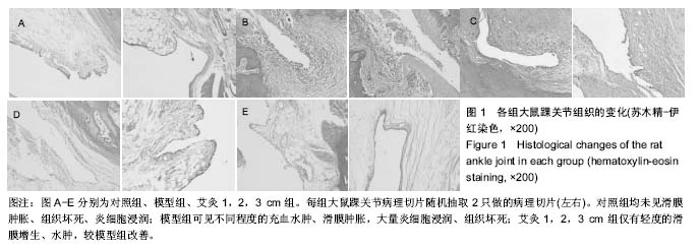
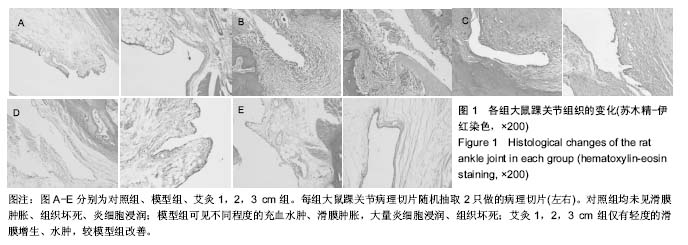
| [1] 莫选荣,罗心静.类风湿性关节炎发病机制的研究进展[J].医学临床研究,2007,24(2):336-340.[2] Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;376(9746):1094-1108.[3] 中华医学会风湿病学分会.类风湿关节炎诊治指南(草案)[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2003,7(4):250-254.[4] 种涛,巴哈尔古丽•力体甫,张继东,等.类风湿性关节炎的中西医治疗进展[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2010,16(2):176-178.[5] Joshi P, Dhaneshwar SS. An update on disease modifying antirheumatic drugs. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2014; 13(4):249-261.[6] Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(3):492-509.[7] Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012;64(5):625-639. [8] 李红娟,刘长信,庾科瀚.类风湿关节炎中医外治的临床研究进展[J].医学综述,2014,20(16):2999-3001.[9] Huang QF, Wu HG, Liu J, et al. Bibliometric analysis of diseases spectrum of moxibustion therapy. Acupunct Tuina Sci. 2012;10:342-348.[10] 俞红五,朱艳,潘喻珍,等.艾灸辅助治疗类风湿关节炎患者临床疗效观察及机制探讨[J].中国针灸,2016,36(1):17-20.[11] 张传英,蔡荣林,唐照亮.艾灸对类风湿性关节炎大鼠炎症因子和滑膜细胞凋亡的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报,2014,37(3):190-195.[12] Kim JH, Kim HK, Park YI, et al. Moxibustion at ST36 alleviates pain in complete Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritic rats. Am J Chin Med. 2006;34(1):57-67.[13] Sun Z, Xu X, Du S, et al. Moxibustion for treating rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Integr Med. 2014;6(6):621-630.[14] 郑保主,胡玲,宋小鸽,等.艾灸对类风湿关节炎大鼠下丘脑POMC mRNA和PDYN mRNA表达的影响[J].中国针灸, 2013,33(5): 433-437.[15] 高骏,刘旭光,黄迪君,等.艾灸对实验性RA大鼠类风湿性关节炎作用机制的研究[J].中国针灸,2008,28(S1):66-68.[16] Xu X, Wang MM, Sun ZL, et al. Discovery of serum proteomic biomarkers for prediction of response to moxibustion treatment in rats with collagen-induced arthritis: an exploratory analysis. Acupunct Med. 2015;34(3):1658.[17] 许培昌,李达良,崔淑丽.不同施灸距离对人体体表皮肤温度的影响-论施灸的安全距离[J].中国针灸,2012,32(7):611-614[18] 季辉,王玲玲,周攀,等.不同灸温对急性佐剂性关节炎大鼠血清IL-1β、IL-2及TNF-α含量的影响[J].上海针灸杂志,2015, 34(7): 597-599.[19] 谢波,王玲玲,季辉,等.不同灸温下穴位涂抹辣椒素对佐剂性关节炎疗效的影响[J].辽宁中医杂志,2015,42(3):600-603.[20] Courtenay JS, Dallman MJ, Dayan AD, et al. Immunisation against heterologous type II collagen induces arthritis in mice. Nature. 1980;283(5748):666-668.[21] Yi JK, Kim HJ ,Yu DH, et al. Regulation of inflammatory responses and fibroblast-like synoviocyte apoptosis by calcineurin-binding protein 1 in mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(7):2191-2200.[22] 李忠仁.实验针灸学[M].第2版.北京:中国中医药出版社,2007.[23] 刘明岭,沈鹰,陈志煌.中药熏蒸在治疗大鼠佐剂性关节炎中TH1/TH2的变化[J].中华中医药学刊,2012,30(1):131-133.[24] 孙国杰,盛灿若,严洁,等.针灸学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社, 1997.[25] 林玉敏.艾灸对慢性疲劳模型大鼠的免疫干预及临床研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2014.[26] 赵丽.艾灸对慢性疲劳模型大鼠神经内分泌免疫系统的影响[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2012.[27] 郁洁,易受乡,常小荣,等.艾灸足三里、梁门穴对大鼠不同组织器官HSP70表达的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2009,29(4):67-69.[28] 向导,袁林,苏林冲.金边祛风饮对类风湿关节炎滑膜细胞IL-1β、TNF-α及MMP-3 表达的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2013,29(9): 952-959. |