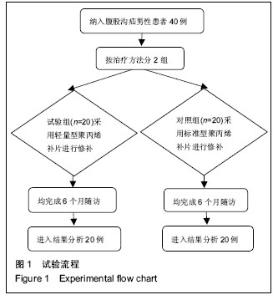
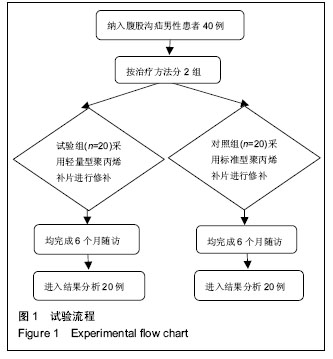
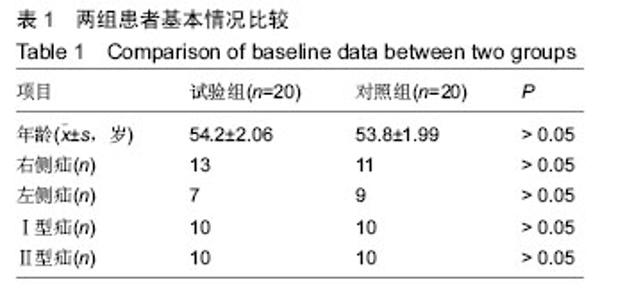
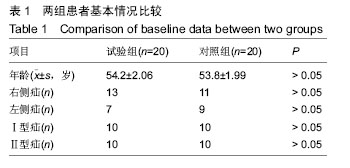
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (21): 3156-3162.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.21.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of lightweight polypropylene mesh versus standard polypropylene mesh on tension-free repair of inguinal hernia
Zhou Xian-feng1, Ma Cong1, Wang Qi1, Hu Hao2
- 1Department of General Surgery, First People’s Hospital of Huainan, Huainan 232007, Anhui Province, China; 2Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2016-03-19Online:2016-05-20Published:2016-05-20 -
About author:Zhou Xian-feng, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of General Surgery, First People’s Hospital of Huainan, Huainan 232007, Anhui Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Xian-feng, Ma Cong, Wang Qi, Hu Hao. Effect of lightweight polypropylene mesh versus standard polypropylene mesh on tension-free repair of inguinal hernia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(21): 3156-3162.
share this article
| [1] 中华医学会外科学分会疝和腹壁外科学组, 中国医师协会外科医师分会疝和腹壁外科医师委员会.成人腹股沟疝诊疗指南[J].中华外科杂志, 2012,52(7): 481-484. [2] Inan I,Myers PO,Hagen ME.Amyand'S hernia: 10 years experience.Surgeon.2009;7(4): 198-202.[3] Hureibi KA,MeLatehie GR,Kidambi AV.Is herniorrhaphy useful and safe? Eur J Radiol. 201l;80(2):e86-90.[4] 陈智平.腹腔镜疝修补术与开放式无张力疝修补术的对比研究[J].临床医学工程,2011,18 (6):105-106.[5] 狄挺松.Bassini法、Mcvay法与补片修补法在腹股沟斜疝治疗中的效果对比[J].中国医药指南, 2013,11(36):78-79.[6] 郜国均,张萍.聚丙烯平片修补腹股沟疝85例应用体会[J].中国药物经济学,2013,8(S3): 23-25. [7] 刘小胜.手术修补术结合中药治疗中老年疝气60例临床体会[J].实用中西医结合临床,2013,13(8):83-84. [8] 徐颖璐,李建海.腹股沟疝无张力修补术切口感染的影响因素分析及干预对策[J].中国现代医生, 2013,51(32): 59-60. [9] 付敬伟.Millikan改良法疝修补术治疗马鞍疝121例[J].中国现代普通外科进展,2013,16(10):45-46. [10] 沙广春.疝环充填式无张力修补术在成人腹股沟疝中的应用研究[J].吉林医学,2011,32(2):101-102. [11] 鲍荣学.充填式无张力疝修补术治疗腹股沟疝72例的临床分析[J].中国医药指南,2011,9(24):743-744. [12] 何川,陈磊,蔡波,等.充填式无张力疝修补术治疗腹股沟疝155例疗效分析[J].中国医药科学, 2011,1(14):105-106. [13] 曹佩银.充填式无张力疝修补术临床应用研究[J].中国实用医药,2010,5(10):984-995. [14] 顾彬.无张力疝修补手术治疗腹股沟疝效果分析[J].医学信息:上旬刊, 2011,24(8): 833-834. [15] 韩重鑫,梁锦积.68例腹股沟疝无张力修补术临床分析[J].中国医药科学,2011,1 (5):213-215. [16] 张程鹏.指拨分离法在完全腹膜外疝修补入路及操作空间建立中的应用[J].中华疝和腹壁外科杂志:电子版, 2013, 7(12):175-177.[17] Negro P,Gossetti F,Dassatti MR,et al. Bioabsorbable Gore BIO-A plug and patch hernia repair in young adults.Hernia.2012;16(1):121-122.[18] Ratto C,Litta F,Parello A,et al.Gore Bio-A Fistula Plug: a new sphincter-sparing procedure for complex anal fistula.Colorectal Dis. 2012;14(5):e264-e269.[19] Campanelli G,Pascual MH,Hoeferlin A,et al. Randomized, controlled, blinded trial of Tisseel/ Tissucol for mesh fixation in patients undergoing Lichtenstein technique for primary inguinal hernia repair: results of the TIMELI trial.Ann Surg. 2012; 255(4): 650-657.[20] Chastan P.Tension-free open hernia repair using an innovative self-gripping semi-resorbable mesh Hernia. 2009;13(2):137-142.[21] Kingsnorth A,Gingell-Littlejohn M,Nienhuijs S,et al.Randomized controlled multicenter international clinical trial of self-gripping ParietexTM ProGripTM polyester mesh versus lightweight polypropylene mesh in open inguinal hernia repair: interim results at 3 months.Hernia.2012;16(3):287-294.[22] Amid PK,Shulman AG,Lichtenstein IL,et al. Biomaterials for abdominal wall hernia surgery and principles of their applications.Langenbecks Arch Chir.1994;379(3): 168-171.[23] Beets GL,van Geldere D,Baeten CG,et al.Long-term results of giant prosthetic reinforcement of the visceral sac for complex recurrent inguinal hernia.Br J Surg. 1996; 83(2):203-206.[24] Schumpelick V,Conze J,Klinge U.Preperitoneal mesh-plasty in incisional hernia repair: a comparative retrospective study of 272 operated incisional hernias.Chirurg.1996;67(10):1028-1035.[25] Klosterhalfen B,Klinge U,Schumpelick V.Functional and morphological evaluation of different polypropylene-mesh modifications for abdominal wall repair.Biomaterials.1998;19(24):2235-2246.[26] Klinge U,unge K,Stumpf M,et al.Functional and morphological evaluation of a low-weight,monofilament polypropylene mesh for hernia repair.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;63(2):129-136.[27] Rosch R,Junge K,Quester R,et al.Vypro Ⅱ mesh in hernia repair: impact of polyglactin on long-term incorporation in rats.Eur Surg Res. 2003;35(5):445-450. [28] Junge K,Rosch R,Krones CJ,et al.Influence of polyglecaprone 25(Monocryl) supplementation on the biocompatibility of a polypropylene mesh for hernia repair.Hernia.2005;9(3):212-217.[29] Tanaka K,Mutter D,Inoue H,et al.In vivo evaluation of a new composite mesh( 10% polypropylene /90% poly-L-lactic acid) for hernia repair.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2007;18(6):991-999.[30] Di Vita G,Patti R,Barrera T,et al.Impact of heavy polypropylene mesh and composite light polypropylene and polyglactin 910 on the inflammatory response.Surg Innov.2010;17(3):229-235.[31] Orenstein SB,Saberski ER,Kreutzer DL,et al. Comparative analysis of histopathologic effects of synthetic meshes based on material,weight, and pore size in mice.J Surg Res.2012;176(2):423-429.[32] d'Acampora AJ,Kestering Dde M,Soldi Mda S,et al. Experimental study comparing the tensile strength of different surgical meshes following aponeurotic-muscle deformity synthesis on Wistar rats.Acta Cir Bras. 2007; 22(1):47-52.[33] Post S,Weiss B,Willer M,et al.Randomized clinical trial of lightweight composite mesh for Lichtenstein inguinal hernia repair.Br J Surg.2004;91(1):44-48.[34] Bringman S,Wollert S,Osterberg J,t al.Three-year results of a randomized clinical trial of lightweight or standard polypropylene mesh in Lichtenstein repair of primary inguinal hernia.Br J Surg. 2006;93(9): 1056-1059.[35] Polish Hernia Study Group,?mietański M.Randomized clinical trial comparing a polypropylene with a poliglecaprone and polypro-pylene composite mesh for inguinal hernioplasty.Br J Surg. 2008;95(12): 1462-1468.[36] Koch A,Bringman S,Myrelid P,et al.Randomized clinical trial of groin hernia repair with titanium-coated lightweight mesh compared with standard polypropylene mesh. Br J Surg. 2008;95(10): 1226-1231.[37] Nikkolo C,Lepner U,Murruste M,et al.Randomised clinical trial comparing lightweight mesh with heavyweight mesh for inguinal hernioplasty. Hernia. 2010;14(3): 253-258.[38] Sadowski B,Rodriguez J,Symmonds R,et al. Comparison of polypropylene versus polyester mesh in the Lichtenstein hernia repair with respect to chronic pain and discomfort.Hernia.2011;15(6):643-654.[39] Khan LR,Liong S,de Beaux AC,et al.Lightweight mesh improves functional outcome in laparoscopic totally extra-peritoneal inguinal hernia repair.Hernia. 2010; 14(1): 39-45.[40] O'Dwyer PJ,Kingsnorth AN,Molloy RG,et al. Randomized clinical trial assessing impact of a lightweight or heavyweight mesh on chronic pain after inguinal hernia repair.Br J Surg.2005;92(2):166-170.[41] Agarwal BB,Agarwal KA,Mahajan KC. Prospective double-blind randomized controlled study comparing heavy-and lightweight polypropylene mesh in totally extraperitoneal repair of inguinal hernia:early results. Surg Endosc.2009;23(2):242-247.[42] Chowbey PK,Garg N,Sharma A,et al.Prospective randomized clinical trial comparing lightweight mesh and heavyweight polypropylene mesh in endoscopic totally extraperitoneal groin hernia repair.Surg Endosc. 2010;24(12):3073-3079.[43] Chui LB,Ng WT,Sze YS,et al. Prospective, randomized, controlled trial comparing lightweight versus heavyweight mesh in chronic pain incidence after TEP repair of bilateral inguinal hernia.Surg Endosc. 2010; 24(11):2735-2738.[44] Bittner R,Leibl BJ,Kraft B,et al.One-year results of a prospective,randomised clinical trial comparing four meshes in laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair (TAPP). Hernia.2011;15(5):503-510. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Liu Jun, Yang Long, Wang Weiyu, Zhou Yuhu, Wu Ying, Lu Tao, Shu Liping, Ma Minxian, Ye Chuan. Preparation and properties of poly3-hydroxybutyrate 4-hydroxybutyrate/polyethylene glycol/graphene oxide tissue-engineered scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3466-3472. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||