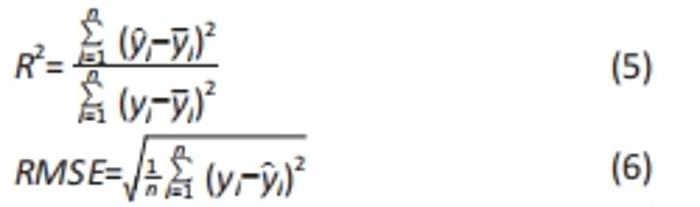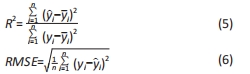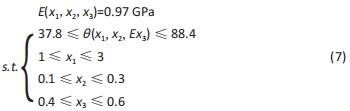Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (28): 4429-4434.doi: 10.12307/2022.293
Design and optimization of artificial femoral unit cell structure based on response surface methodology
Lian Tingting1, Chen Xuewen1, Zhang Bo1, Wang Guangxin1, Akiyoshi Osaka1, 2
- 1College of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan Province, China; 2Institute of Engineering, Okayama University, Tsushima 700-8530, Okayama, Japan
-
Received:2021-01-22Accepted:2021-03-18Online:2022-10-08Published:2022-03-17 -
Contact:Chen Xuewen, MD, Distinguished professor, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan Province, China Akiyoshi Osaka,MD,Professor, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan Province, China; Institute of Engineering, Okayama University, Tsushima 700-8530, Okayama, Japan -
About author:Lian Tingting, Master, College of Materials Science and Engineering, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang 471023, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Chinese 03 Special Fund, Grand No. 2017ZX02408003 (to WGX); Innovative Science and Technology Team Project of High Purity Material Preparation and Application Technology in Henan Province (to CXW)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lian Tingting, Chen Xuewen, Zhang Bo, Wang Guangxin, Akiyoshi Osaka. Design and optimization of artificial femoral unit cell structure based on response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4429-4434.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
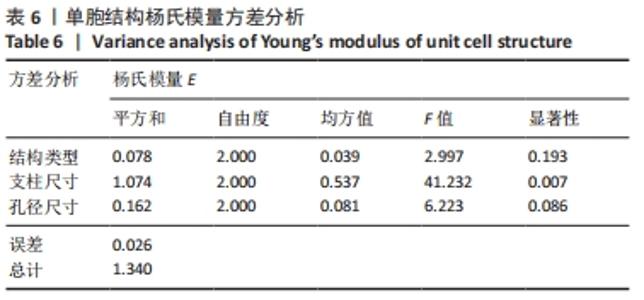
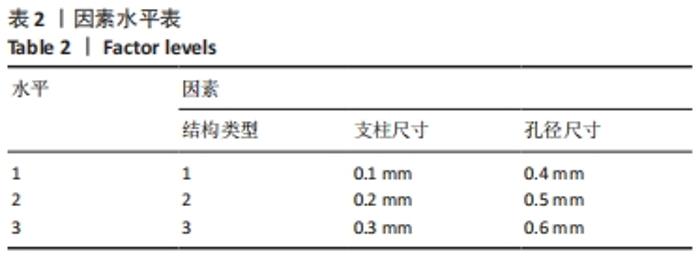
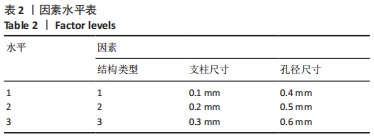
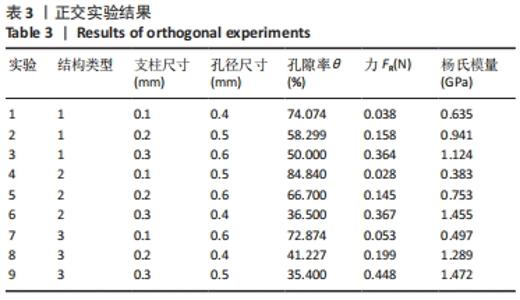
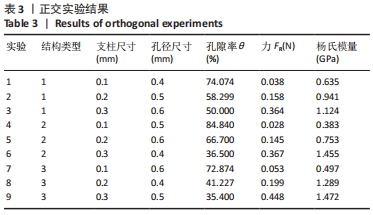
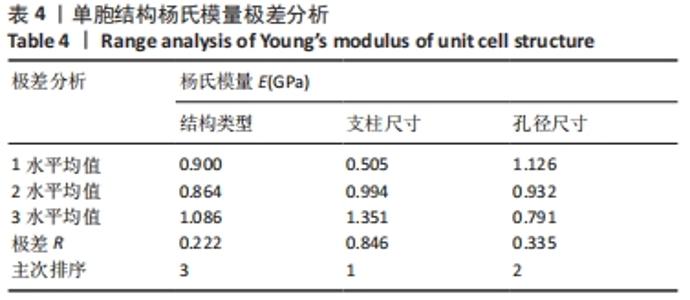
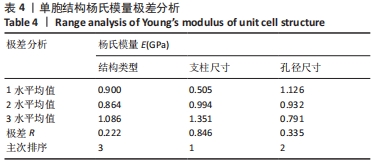
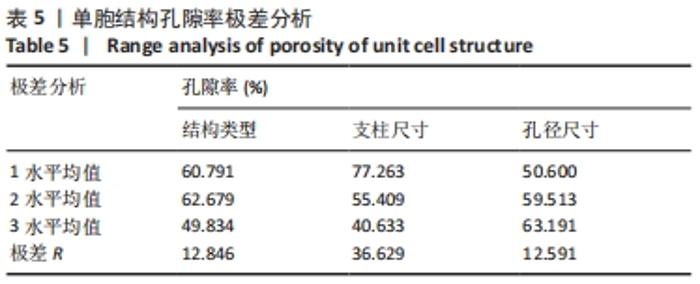
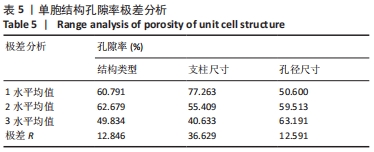
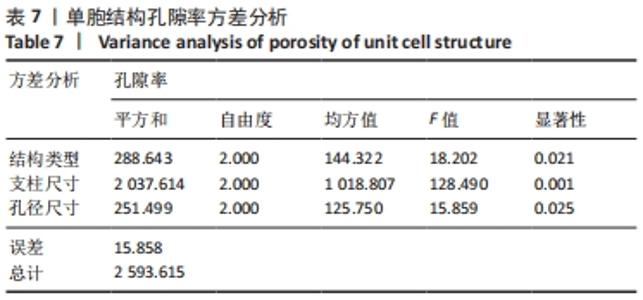
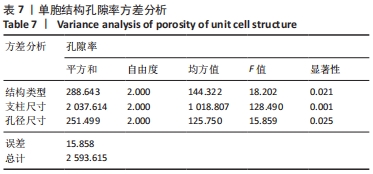
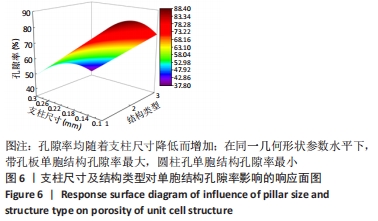
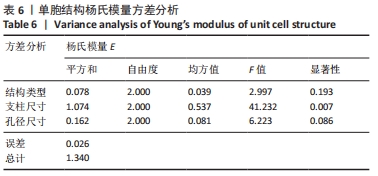
由表4可以得出,影响单胞结构杨氏模量的主次顺序为:支柱尺寸>孔径尺寸>结构类型。3个因素中支柱尺寸的极差较大,而孔径尺寸和结构类型的极差相差不大,这说明对单胞结构杨氏模量影响较大的是支柱尺寸。 由表5可知,在3个因素中影响单胞结构孔隙率的主次顺序为:支柱尺寸>结构类型>孔径尺寸。其中支柱尺寸的极差较大,采用极差分析能够较为直观地比看而其余两因素的极差相差不大,这说明对单胞结构杨氏模量影响较大的是支柱尺寸。 对正交实验进行方差分析,其结果如表6,7所示。由方差分析可知支柱尺寸对单胞结构杨氏模量的影响显著(P < 0.05),孔径尺寸及结构类型对其的显著性不够明显;而3个因素均对单胞结构孔隙率有显著影响(P < 0.05),且支柱尺寸对其的影响最为显著。"
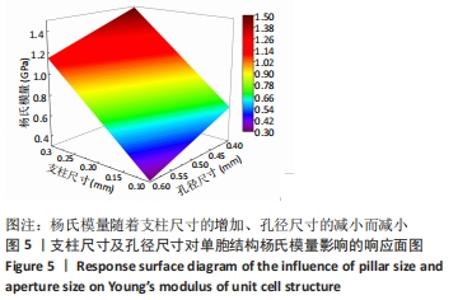
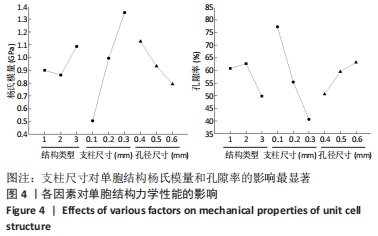
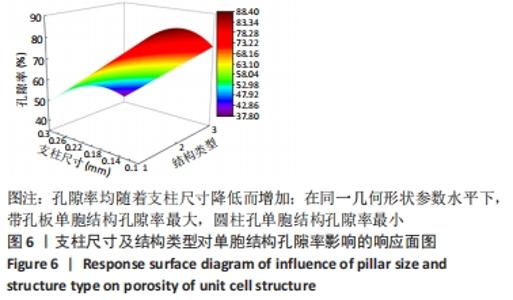
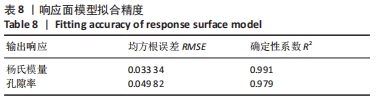
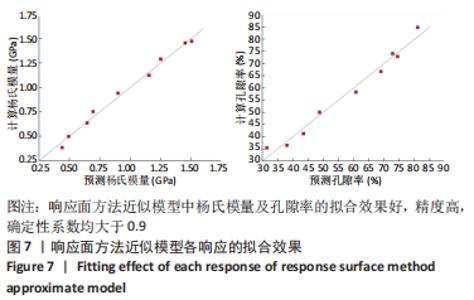
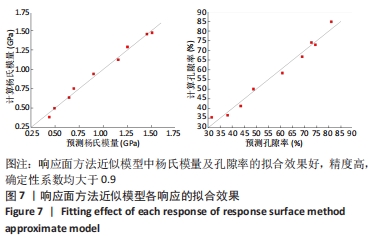
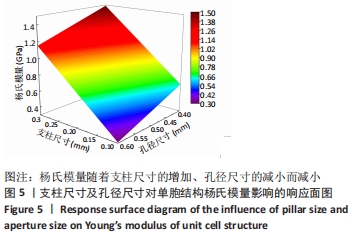
2.2 近似模型的建立与分析 近似模型是通过数学模型来逼近一组输入变量与输出变量的方法,20世纪70年代,SCHMIT等在结构优化中首次引入近似模型的概念,收到了良好的效果[17]。响应面方法采用多项式函数拟合设计空间,它实用性强、适用范围广,具有良好的鲁棒性[18]。为了精确地拟合三因素激励参数与杨氏模量、孔隙率响应参数之间的关系,建立近似模型。该文以杨氏模量(E)和孔隙率(θ)作为响应输出,以结构类型(x1)、支柱尺寸(x2)和孔径尺寸(x3)作为输入变量,选择二阶响应面法建立近似模型,拟合结果如下: 杨氏模量响应面模型可以表示为: E=1.186-0.424×x1+4.228×x2-1.674×x3+0.129×x12 (3) 孔隙率响应面模型可以表示为: θ=49.319-23.991×x1-183.147×x2+62.955×x3-7.367×x12 (4) 杨氏模量响应面图如图5所示。"

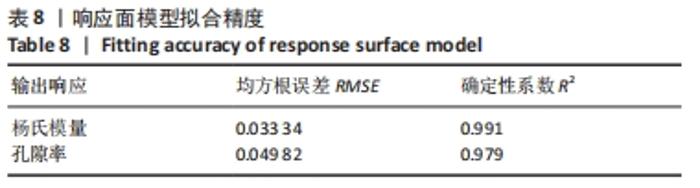
式中,E(x1,x2,x3)为微孔结构杨氏模量,θ(x1,Ex2,x3)为孔隙率,x1,x2,x3分别为结构类型、支柱尺寸及孔径尺寸。 采用序列二次规划算法梯度优化在优化空间寻求最优解,结合响应面方法近似模型,得到优化后参数,即最优参数为:单胞类型x1=1(支杆单胞),支柱尺寸x2=0.220 863 mm,孔径尺寸x3=0.510 721 mm,孔隙率θ=57.644 97%,杨氏模量E=0.970 286 GPa。 为了验证优化后结果的可信度,对得到的设计参数采用有限元模拟,并通过计算出杨氏模量与孔隙率分别为1.05 GPa和55.42%,二者结果相差7.6%和4.01%。因此,采用响应面方法近似模型结合序列二次规划算法对微孔结构的优化结果是可信的。"

| [1] SYLVIA S, DANIELA H, MATTHIAS G, et al. Fatal falls in the elderly and the presence of proximal femur fractures. Int J Legal Med. 2018;132(6):1699-1712. [2] LI F, LI J, XU G, et al. Fabrication, pore structure and compressive behavior of anisotropic porous titanium for human trabecular bone implant applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2015;46:104-114. [3] YUNOKI S, IKOMA T, MONKAWA A, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Porous Material from Self-Organized Hydroxyapatite/Collagen Nanocomposite. Mat Res Soc Symp Proc. 2005;873:97. [4] JANG DW, NGUYEN TH, SARKAR SK, et al. Microwave sintering and in vitro study of defect-free stable porous multilayered HAp–ZrO2 artificial bone scaffold. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2012;(3):035009. [5] PATE R, LU MY, DIERMANN SH, et al. Deformation behavior of porous PHBV scaffold in compression: A finite element analysis study. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;96:1-8. [6] SARA RODRIGO-VÁZQUEZ C, KAMBOJ N, AGHAYAN M, et al. Manufacturing of silicon – Bioactive glass scaffolds by selective laser melting for bone tissue engineering. Ceram Int. 2020;46(17):26936-26944. [7] KUMARESAN T, GANDHINATHAN R, RAMU M, et al. Design, analysis and fabrication of polyamide/ hydroxyapatite porous structured scaffold using selective laser sintering method for bio-medical applications. J Mech Sci Technol. 2016; 30(11):5305-5312. [8] CHE GHANI SA, WAN HARUN WS, MAT TAIB ZA, et al. Finite Element Analysis of Porous Medical Grade Cobalt Chromium Alloy Structures Produced by Selective Laser Melting. Adv Mat Res. 2016;1133:113-118. [9] PARTHASARATHY J, STARLY B, RAMAN S, et al. Mechanical evaluation of porous titanium (Ti6Al4V) structures with electron beam melting (EBM). J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010;3(3):249-259. [10] 李军超,赵泽,鄢然,等.SLS成形PA12/HA多孔支架的工艺参数优化及力学性能[J].中国激光,2019,46(11):97-104. [11] 杨立军,张佳,王哲,等.承力骨支架微孔结构设计及力学特性有限元分析[J].机械设计与制造,2017(7):157-160. [12] XIE YM, STEVEN GP. Evolutionary Structural Optimization with FEA. Comput Struct. 1996;58(6):1067-1073. [13] CHEN Y, LIN LV L. The multi-objective optimization of combustion chamber of DI diesel engine by NLPQL algorithm. Appl Therm Eng. 2014;73(1):1332-1339. [14] XIE YM. On Applying Kriging Approximate Optimization to Sheet Metal Forming. Appl Mech Mater. 2011;63-64:3-7. [15] 肖惠萍,孙书琴,刘洋,等.电动修复红壤镉污染的正交试验研究[J].工业安全与环保,2020,46(9):79-84. [16] 唐佳丽,徐章韬.正交试验中的极差分析与方差分析[J].中学数学,2017(9): 31-34. [17] 董桂西,王藏柱.结构优化设计的现状及展望[J].电力情报,2000,1(1):5-5. [18] 王永菲,王成国.响应面法的理论与应用[J].中央民族大学学报(自然科学版),2005,14(3):236-240. [19] SUN W, STARLY B, DARLING A, et al. Computer-aided tissue engineering: application to biomimetic modelling and design of tissue scaffolds. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2004;39(Pt 1):49-58. [20] 刘博,张智超,卢晓晖,等.基于AVL-Cruise的AMT自动变速器速比优化研究[J].中国科技成果,2020,21(15):21-25. [21] 韩邦成,袁倩.大型磁悬浮CMG转子的组合优化策略[J].宇航学报,2012, 33(2):275-280. |
| [1] | Xu Xinzhong, Wu Zhonghan, Yu Shuisheng, Zhao Yao, Xu Chungui, Zhang Xin, Zheng Meige, Jing Juehua. Biomechanical analysis of different ways of inserting Steinmann Pins into the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Wei Guoqiang, Li Yunfeng, Wang Yi, Niu Xiaofen, Che Lifang, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Shi Guopeng, Bai Ling, Mo Kai, Zhang Chenchen, Xu Yangyang, Li Xiaohe. Biomechanical analysis of non-uniform material femur under different loads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1318-1322. |
| [3] | Zhang Yufang, Lü Meng, Mei Zhao. Construction and verification of a full spine biomechanical model of adolescent scoliosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1351-1356. |
| [4] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [5] | Li Guijun, Fang Xiaohui, Kong Weifeng, Yuan Xiaoqing, Jin Rongzhong, Yang Jun. Finite element analysis of the treatment of hallux valgus deformity by microplate combined with super strong suture elastic fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 938-942. |
| [6] | Wen Mingtao, Liang Xuezhen, Li Jiacheng, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Mechanical stability of Sanders II type calcaneal fractures fixed by two internal fixation methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 838-842. |
| [7] | Wang Hailong, Li Long, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Chen Hongtao, Liu Xu, Yilihamu·Tuoheti. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of acetabular prosthesis in the Lewinnek safety zone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 843-847. |
| [8] | Li Shuo, Su Peng, Zhang Li, Wu Qiulong, Hu Xiangyu, Lai Yuliang. Positive effect of supracondylar femoral osteotomy on the correction of knee varus based on three-dimensional reconstruction and finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 858-863. |
| [9] | Wei Bing, Chang Shan. Finite element analysis of different angles of nail placement in sagittal plane of spinal fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 864-869. |
| [10] | Zhang Jianguo, Chen Chen, Hu Fengling, Huang Daoyu, Song Liang. Design and biomechanical properties of dental implant pore structure based on three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 585-590. |
| [11] | Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Renaguli·Maihemuti, Aizimaitijiang·Saiyiti, Wang Junxiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun. Stress analysis of maxillary central incisor crown implant restoration in different occlusal modes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 567-572. |
| [12] | Wang Can, Gu Weiping, Jiang Yubin, Zhu Lin, Chen Gang. Finite element analysis of the influence of different implant designs on the stress of mandibular edentulous jaw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 573-578. |
| [13] | Lin Boying, Shen Mao. Biomechanical stability of endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw combined with contralateral translaminar facet screw fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 329-333. |
| [14] | Ye Linqiang, Lu Guoliang, Jiang Xiaobing, Li Zhen, Weng Rui, Liang De, Huang Xuecheng, Feng Yonghong. Biomechanical effects of cement filling location on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(28): 4435-4440. |
| [15] | Wang Yuan, Zhang Yang. Finite element biomechanical analysis of various bone mineral densities on edentulous mandibular four-implant-supported overdentures fixed using Locator attachments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(22): 3492-3497. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||