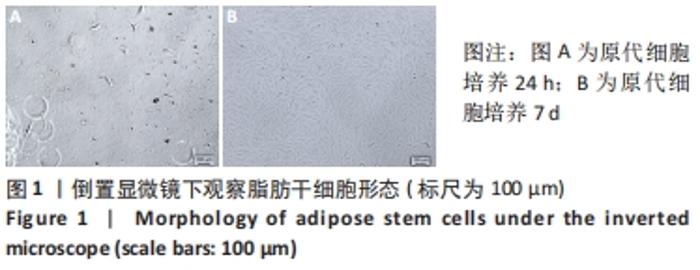
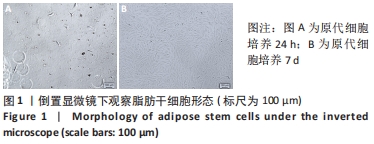
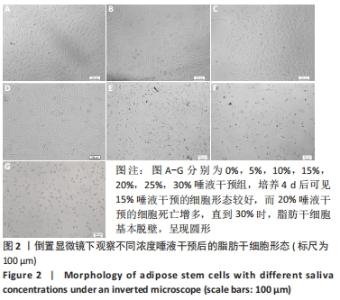
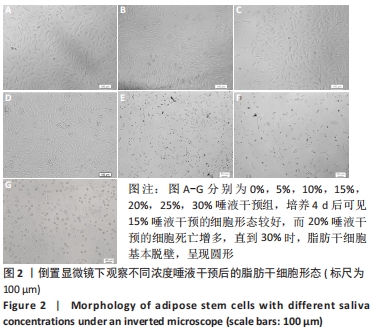
[1] KIM YH, KIM GH, KIM SW. Reconstruction of a Complex Scalp Defect after the Failure of Free Flaps: Changing Plans and Strategy. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2017;18(2):112-116.
[2] BORDIANU A, BOBIRCĂ F, PĂTRAŞCU T. Skin Grafting in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Soft Tissue Defects. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2018;113(5):644-650.
[3] EGYEDI P. Utilization of the buccal fat pad for closure of oro-antral and/or oro-nasal communications. J Maxillofac Surg. 1977;5(4):241-244.
[4] KABLAN F. The use of buccal fat pad free graft in closure of soft-tissue defects and dehiscence in the hard palate. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2016;6(2):241-245.
[5] 张圣敏,陈刚,王晨星,等.人颊脂垫脂肪干细胞与皮下脂肪干细胞生物学特性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(32):5941-5945.
[6] ZUK PA, ZHU M, ASHJIAN P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12):4279-4295.
[7] HATA Y. Do not forget the fundamental merits of microtia repair using a tissue expander. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(2):819-822.
[8] BAER PC, BEREITER-HAHN J, MISSLER C, et al. Conditioned medium from renal tubular epithelial cells initiates differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2009;42(1):29-37.
[9] CHEN S, WANG M, CHEN X, et al. In Vitro Expression of Cytokeratin 19 in Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Is Induced by Epidermal Growth Factor. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:4254-4261.
[10] 尹小朋,许慧芬,刘慧,等.带蒂颊脂垫瓣与碘仿纱条在腭裂松弛切口处理中的对比分析[J].中国美容医学,2018,27(7):108-111.
[11] CHAUDHARY B, GONG Z, LIN Z, et al. Reconstruction of intraoral maxillary defect with buccal fat pad. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(6):2174-2177.
[12] KANZOW P, WEGEHAUPT FJ, ATTIN T, et al. Etiology and pathogenesis of dental erosion. Quintessence Int. 2016;47(4):275-278.
[13] ZHANG L, HAO L, ZUO W, et al. Preparation and application of polyclonal antibody against Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;31(8):1120-1123.
[14] 李小英,李倩,崔博淼,等.慢性牙周炎患者唾液诱导巨噬细胞分化和活化的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(5):50-55.
[15] FUJISAWA K, MIYAMOTO Y, NAGAYAMA M. Basic fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor reverse impaired ulcer healing of the rabbit oral mucosa. J Oral Pathol Med. 2003;32(6):358-366.
[16] AZUMA N, KATADA Y, SANO H. Deterioration in saliva quality in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome: impact of decrease in salivary epidermal growth factor on the severity of intraoral manifestations. Inflamm Regen. 2018;38:6.
[17] INO M, USHIRO K, INO C, et al. Kinetics of epidermal growth factor in saliva. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1993;500:126-130.
[18] THESLEFF I, VIINIKKA L, SAXÉN L, et al. The parotid gland is the main source of human salivary epidermal growth factor. Life Sci. 1988;43(1): 13-18.
[19] INO M, USHIRO K, INO C, et al. Epidermal Growth Factor in Salivary Glands-epidermal Growth Factor and its Receptor in Human Salivary Glands. Jibirinsho.1992;85(5):805-814.
[20] 王程,徐潇,陈冲,等.体外诱导脂肪来源干细胞向黏膜上皮细胞分化的研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2015,40(10):798-802.
[21] 郭凯,罗燕,李涛,等.人脂肪间充质干细胞向视网膜色素上皮样细胞的诱导分化及其在体应用研究[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2015, 33(9):794-797.
[22] MAO Y, MA J, XIA Y, et al. The Overexpression of Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) in HaCaT Cells Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Transdifferentiation to Epidermal Stem Cell Immunophenotyping of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs). Int J Stem Cells. 2020;13(1):93-103.
[23] 胡亚暖,姚永明,张泽敏,等.不同浓度EGF对兔ADSCs体外诱导分化为表皮细胞的实验研究[J].中国美容医学,2016,25(7):47-50.
|