Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (24): 3870-3874.doi: 10.12307/2022.568
Previous Articles Next Articles
In vitro differentiation of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes
Liang Tingting1, Chen Li2, Fan Mingsong2, Zhang Guoying2, Zhang Shichang1
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2Department of Obstetrics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2021-05-22Accepted:2021-06-17Online:2022-08-28Published:2022-01-24 -
Contact:Zhang Shichang, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Laboratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Liang Tingting, Master, Department of Laboratory Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81671836 (to ZSC)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Tingting, Chen Li, Fan Mingsong, Zhang Guoying, Zhang Shichang. In vitro differentiation of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3870-3874.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

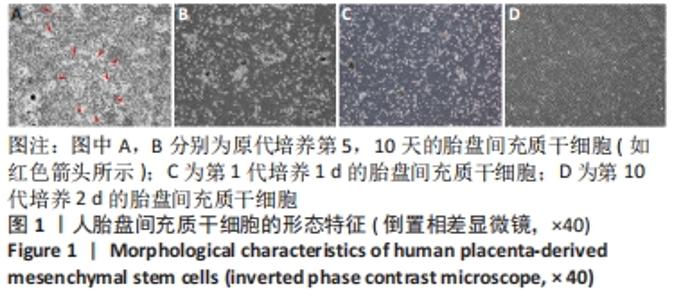
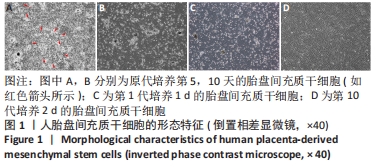
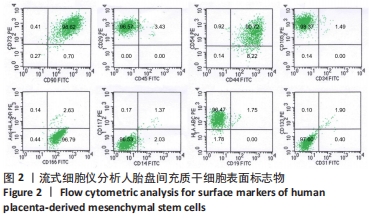
2.2 人胎盘间充质干细胞的表型鉴定结果 流式细胞分析结果显示,传至第4代的人胎盘间充质干细胞的干细胞或间质细胞标志CD90、CD73、CD105、CD29、CD44、CD166、CD54均为阳性,特别是CD73、CD90、CD105、CD29、CD44、CD166均在98%以上;而造血细胞相关标志CD34、CD45、CD14、CD117、CD19、CD133以及组织相容性抗原Ⅱ分子HLA-DR均为阴性,而组织相容性抗原Ⅰ分子HLA-ABC为阳性;CD31为阴性排除了血管内皮细胞;CD105+CD34-的细胞达98.37%,CD73+CD90+的细胞达98.62%,CD133-CD31-和CD117-CD14-的细胞超过96.00%,见图2。结果表明分离获得的细胞是来源于间质的干细胞,并排除造血细胞的污染。"

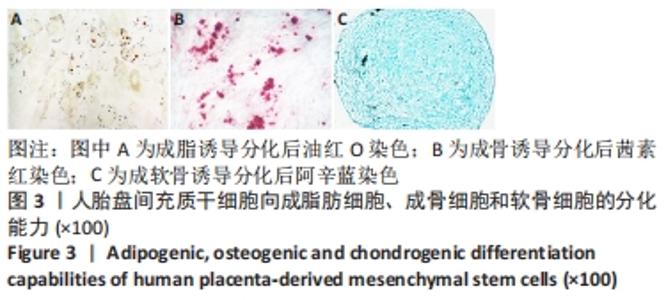
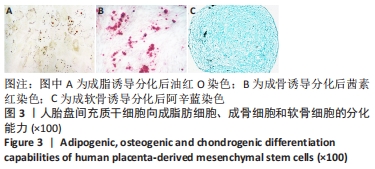
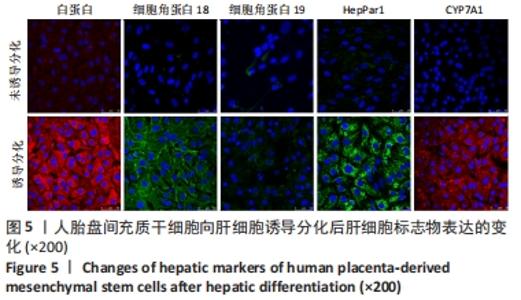
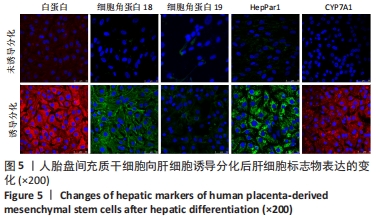
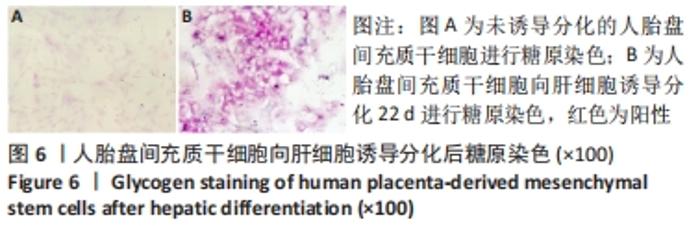
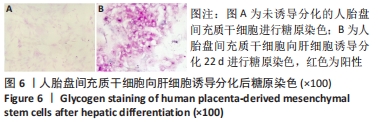
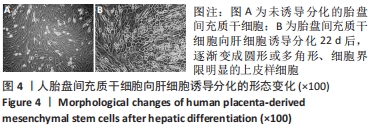
2.4 人胎盘间充质干细胞诱导分化为肝细胞 向肝细胞诱导22 d后,在倒置相差显微镜下可见胎盘间充质干细胞由诱导分化前的成纤维细胞样、梭形细胞,逐渐变成圆形或多角形、细胞界限明显的上皮样细胞,见图4,与体外培养的人肝细胞形态相似。免疫荧光染色结果显示:向肝细胞诱导分化后,成熟肝细胞标志物白蛋白、细胞角蛋白18、HepPar1等阳性表达;生物转化的关键酶类CYP7A1由原来的阴性转为阳性表达,而未诱导分化的胎盘间充质干细胞为阴性,胆管上皮细胞的标志物细胞角蛋白19的表达未见明显变化,提示人胎盘间充质干细胞可以分化为肝细胞,见图5。人胎盘间充质干细胞向肝细胞诱导分化后糖原染色阳性,而未诱导的胎盘间充质干细胞糖原染色阴性,见图6。"
| [1] ZERN MA. Cell transplantation to replace whole liver transplantation. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):767-769. [2] TERATANI T, YAMAMOTO H, AOYAGI K, et al. Direct hepatic fate specification from mouse embryonic stem cells. Hepatology. 2005;41(4):836-846. [3] DWYER BJ, MACMILLAN MT, BRENNAN PN, et al. Cell therapy for advanced liver diseases: Repair or rebuild. J Hepatol. 2021;74(1):185-199. [4] 孙婷,李凡,杜联芳.间充质干细胞治疗急性肝损伤:肝脏归巢率及定向分化能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1):125-131. [5] QIAO Y, XU Z, YU Y, et al. Single cell derived spheres of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance cell stemness properties, survival ability and therapeutic potential on liver failure. Biomaterials. 2020;227:119573. [6] CHEN L, ZHANG J, YANG L, et al. The Effects of Conditioned Medium Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Cocultured with Hepatocytes on Damaged Hepatocytes and Acute Liver Failure in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:9156560. [7] ZHANG S, LIU P, CHEN L, et al. The effects of spheroid formation of adipose-derived stem cells in a microgravity bioreactor on stemness properties and therapeutic potential. Biomaterials. 2015;41:15-25. [8] ZHANG S, CHEN L, LIU T, et al. Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells efficiently rescue acute liver failure through paracrine effects rather than hepatic differentiation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(13-14):1352-1364. [9] WEI T, LV Y. Immediate intraportal transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells prevents death from fulminant hepatic failure in pigs. Hepatology. 2013;58(1):451-452. [10] WANG YH, WU DB, CHEN B, et al. Progress in mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for acute liver failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):227. [11] FU Y, DENG J, JIANG Q, et al. Rapid generation of functional hepatocyte-like cells from human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):105. [12] CUI L, SHI Y, ZHOU X, et al. A set of microRNAs mediate direct conversion of human umbilical cord lining-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(11):e918. [13] JI R, ZHANG N, YOU N, et al. The differentiation of MSCs into functional hepatocyte-like cells in a liver biomatrix scaffold and their transplantation into liver-fibrotic mice. Biomaterials. 2012;33(35):8995-9008. [14] STOCK P, BRÜCKNER S, EBENSING S, et al. The generation of hepatocytes from mesenchymal stem cells and engraftment into murine liver. Nat Protoc. 2010; 5(4):617-627. [15] AURICH H, SGODDA M, KALTWASSER P, et al. Hepatocyte differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue in vitro promotes hepatic integration in vivo. Gut. 2009;58(4):570-581. [16] YEN MH, WU YY, LIU YS, et al. Efficient generation of hepatic cells from mesenchymal stromal cells by an innovative bio-microfluidic cell culture device. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):120. [17] BHARTI D, SHIVAKUMAR SB, PARK JK, et al. Comparative analysis of human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells derived from different parts of the same umbilical cord. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;372(1):51-65. [18] STANKO P, KAISEROVA K, ALTANEROVA V, et al. Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp, bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue by gene expression. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014;158(3):373-377. [19] 赵姝灿,郑桂纯,林连蓬,等.人羊水、脐带、胎盘来源间充质干细胞体外增殖、分化、运输和免疫学特性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(25): 4028-4034. [20] CHIEN CC, YEN BL, LEE FK, et al. In vitro differentiation of human placenta-derived multipotent cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(7):1759-1768. [21] LEE CW, CHEN YF, WU HH, et al. Historical Perspectives and Advances in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Research for the Treatment of Liver Diseases. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(1):46-56. [22] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317. [23] LEE KD, KUO TK, WHANG-PENG J, et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275-1284. [24] DI CAMPLI C, PISCAGLIA AC, PIERELLI L, et al. A human umbilical cord stem cell rescue therapy in a murine model of toxic liver injury. Dig Liver Dis. 2004;36(9): 603-613. [25] 马晨,李晓国,徐明均,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞的扩增与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(33):5293-5299. [26] ULLAH I, SEO K, WI H, et al. Induction of the differentiation of porcine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into premature hepatocyte-like cells in an indirect coculture system with primary hepatocytes. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2020;24(5):289-298. [27] REBELO SP, COSTA R, SILVA MM, et al. Three-dimensional co-culture of human hepatocytes and mesenchymal stem cells: improved functionality in long-term bioreactor cultures. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(7):2034-2045. [28] OUYANG JF, LOU J, YAN C, et al. In-vitro promoted differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells towards hepatocytes induced by salidroside. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010; 62(4):530-538. [29] VOLAREVIC V, NURKOVIC J, ARSENIJEVIC N, et al. Concise review: Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of acute liver failure and cirrhosis. Stem Cells. 2014;32(11):2818-2823. [30] CAMPARD D, LYSY PA, NAJIMI M, et al. Native umbilical cord matrix stem cells express hepatic markers and differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells. Gastroenterology. 2008;134(3):833-848. [31] AFSHARI A, SHAMDANI S, UZAN G, et al. Different approaches for transformation of mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):54. [32] YU J, SU X, ZHU C, et al. GFP Labeling and Hepatic Differentiation Potential of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35(6):2299-2308. [33] PASSARETTA F, BOSCO D, CENTURIONE L, et al. Differential response to hepatic differentiation stimuli of amniotic epithelial cells isolated from four regions of the amniotic membrane. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(7):4350-4355. [34] FORTE G, MINIERI M, COSSA P, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor effects on mesenchymal stem cells: proliferation, migration, and differentiation. Stem Cells. 2006;24(1):23-33. [35] ZHANG S, ZHANG Y, CHEN L, et al. Efficient large-scale generation of functional hepatocytes from mouse embryonic stem cells grown in a rotating bioreactor with exogenous growth factors and hormones. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(6):145. [36] SAHABIAN A, DAHLMANN J, MARTIN U, et al. Production and cryopreservation of definitive endoderm from human pluripotent stem cells under defined and scalable culture conditions. Nat Protoc. 2021;16(3):1581-1599. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [4] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [5] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [6] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [7] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [8] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [9] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [10] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [11] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [12] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [13] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [15] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||