Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (23): 3734-3739.doi: 10.12307/2021.047
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ferroptosis and stroke
Zhu Rui1, Zeng Qing1, Huang Guozhi1, 2
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China; 2School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-09-24Revised:2020-09-28Accepted:2020-11-11Online:2021-08-18Published:2021-02-24 -
Contact:Huang Guozhi, MD, Professor, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China; School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhu Rui, MD candidate, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510280, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81874032 (to HGZ); Guangdong Provincial Medical Science and Technology Research Project, No. A2017610 (to ZQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhu Rui, Zeng Qing, Huang Guozhi. Ferroptosis and stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3734-3739.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
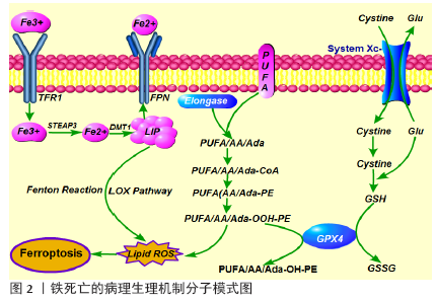
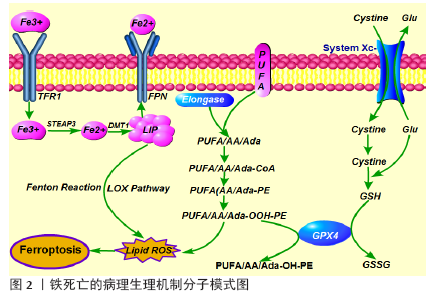
2.1 铁死亡的定义与特征 铁死亡是一种铁依赖性的,且与细胞凋亡、细胞坏死、细胞自噬有所区别的新型细胞程序性死亡方式,其主要机制是在二价铁或脂氧合酶的作用下,催化细胞膜上高表达的不饱和脂肪酸发生脂质体过氧化,从而诱导细胞死亡;其主要特征还包括抗氧化体系(谷胱甘肽和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶)表达量的降低[7]。铁死亡的发现过程中,有两个化合物至关重要。2003年DOLMA等[8]筛选出一种化合物Eaststin,显示出抑制抗氧化剂谷胱甘肽合成的作用,它对表达RAS的癌细胞具有选择性致死作用,且与已知的细胞死亡形式不同:没有核形态变化、DNA片段化和caspase活化,并且其他细胞死亡抑制剂无法逆转这一过程。随后,2008年YAGODA等[7]和YANG等[9]发现了另一种化合物RSL3,能够触发类似非凋亡形式且具有铁依赖性的细胞死亡方式。2012年,铁死亡首次被DIXON等[10]明确定义为一种铁依赖性、以细胞内脂质过氧化物及相关代谢产物累积为特征、非凋亡形式的细胞死亡方式。铁死亡是一种新的细胞死亡方式,其在形态、生化和遗传上与其他形式的细胞死亡都不同,并且还涉及多种疾病[11-12]。形态学上,铁死亡主要表现为细胞的线粒体萎缩、双层膜密度增加和线粒体内膜嵴消失,但细胞膜保持完整,细胞核大小正常,且没有染色质不浓缩[9-10];生化方面,细胞发生铁死亡往往伴随着谷胱甘肽耗竭,谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶4(glutathione peroxidase 4,GPX4)活性降低,脂质过氧化物不能被GPX4催化的还原反应代谢,脂质被二价铁以芬顿(Fenton)反应被氧化,产生大量活性氧,从而进一步促进铁死亡的发 生[9,13];从基因上讲,铁死亡是由多个基因调控的生物过程,大致包括:铁代谢紊乱、脂质过氧化物及其代谢产物累积、GPX4产生受阻、氨基酸和谷胱甘肽代谢紊乱等表观遗传学改变,具体的调控机制有待进一步研究[10]。 目前研究发现能够诱发铁死亡的物质可分为四类。一类包括Erastin,它是通过直接抑制Xc系统减少谷胱甘肽的铁死亡诱导剂[8],其还具有另一个靶标,即电压依赖性阴离子通道(voltage-dependent anion channels, VDAC),能够引起线粒体功能障碍。最近还发现,由Erastin引起的铁死亡激活增加了溶酶体相关膜蛋白2A(lysossomal associated protein 2a, Lamp2a)的表达水平,从而促进伴侣蛋白介导的自噬,进而促进GPX4 的降解[14]。第二类包括RSL3和DPI7,它们直接抑制GPX4活性从而诱导铁死亡[7,9]。第三类包括FIN56,能促进GPX4降解,另外它还与角鲨烯合酶结合,导致内源性抗氧化剂辅酶Q10消耗,这个过程增强了细胞对FIN56引起的铁死亡的敏感性[15]。最后一类包括FINO2及其类似物如青蒿素,通过影响直接铁氧化,脂质的过氧化和GPX4的失活等诱导铁死亡[16-17]。 随着对铁死亡发生机制的不断深入研究,诸多铁死亡的特异性抑制剂逐渐被发现,如Ferrostatin-1(Fer-1), Liproxstatin-1(Lip-1)和维生素E,这些物质通过抑制脂质过氧化物的形成来抑制铁死亡[7,9]。2014年,SKOUTA等[18]发现Fer-1在亨廷顿氏病、脑白质病和肾功能不全的3种体外模型中抑制了细胞铁死亡,该研究丰富了在疾病模型中使用铁他汀类药物的基础,并且它是第一个在体内实验逆转铁死亡的重要性研究。其产生的治疗作用基于铁死亡病理生理机制:不具有活性的三价铁通过转铁蛋白受体(transferrin receptor1, TFR1)传递到细胞中,并在体内还原为二价铁,二价金属离子转运体(divalent metal transporter 1,DMT1)将二价铁输送至不稳定的铁矿池(labile iron pool,LIP),核受体共激活子4(nuclear receptor coactivators 4,NCOA4)介导铁蛋白自噬降解从而将二价铁从铁蛋白中释放,二价铁通过Fenton反应和脂氧合酶途径产生脂质活性氧,此外,作为关键调节剂,酰基辅酶A合成酶长链家族成员4(Cyl-CoA synthetase long-chain familymember4,ACSL4)催化花生四烯酸(arachidonic acid,AA)或肾上腺酸(adrenic acid,AA)酯化为磷脂酰乙醇胺(phosphatidyl ethanolamine,PE);其次,溶血磷脂酰胆碱酰基转移酶3(lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase,LPCAT)对基于磷脂酰乙醇胺的底物具有特异性,并生成质膜多不饱和脂肪酸-磷脂酰乙醇胺(PUFA-PE)。最后,脂氧合酶15(15-lipoxygenase,15-LOX)将花生四烯酸-磷脂酰乙醇胺(AA-PE)和肾上腺酸-磷脂酰乙醇胺(AdA-PE)氧化成花生四烯酸-氢过氧化物-磷脂酰乙醇胺(PE-AdA-OOH)和肾上腺素-氢过氧化物-磷脂酰乙醇胺(PE-AA-OH)[19-20]。这些脂质过氧化累积在线粒体膜上是诱发铁死亡的关键因素(图2)。通过特异性抑制剂修饰或使得某些脂质氧化相关的关键蛋白失活,可抑制细胞铁死亡的发展。简而言之,铁死亡作为一种新的细胞死亡方式被发现,为治疗多种疾病提供了新的方向。 2.2 铁死亡与缺血性脑卒中 缺血性脑卒中发生一段时间后再重新恢复正常血液循环,低灌注缺血缺氧脑组织再次获得血液供给时,缺血性损伤不但没有逆转反而进一步加重,甚至出现更严重的脑损伤现象包括神经细胞死亡、致死性脑水肿等,即脑缺血再灌注损伤[21]。脑缺血再灌注导致多种细胞死亡途径的激活,其中坏死、凋亡和自噬相关的细胞死亡被认为是导致脑缺血再灌注损伤的关键因素[22-23]。然而,越来越多的研究发现,脑缺血再灌注损伤中出现脂质过氧化增多和细胞内铁水平升高的现象[24-28],这些细胞事件与铁依赖性非凋亡形式的铁死亡表现相一致,且可以通过铁螯合剂或抗氧化剂来预防[29]。有研究证实在缺血性脑卒中发生后,脑缺血再灌注阻碍了ATP的产生,而大脑需要持续产生高水平的ATP才能维持代谢活性和神经元稳态以对抗氧化应激[30]。因此,与其他器官相比,在缺血条件下大脑更容易累积更多有害的线粒体代谢副产物[31]。此外,神经元膜富含多不饱和脂肪酸,很容易被氧化,因此大脑中抗氧化剂的平衡十分重要[32]。有研究发现在严重的缺血缺氧性损伤后,4例患者的T2加权磁共振图像上证实了由于铁沉积而导致基底节、丘脑和白质区域出现低强度信号[26]。同样,在脑缺血再灌注损伤的实验动物模型中均观察到了患病大脑区域中铁的蓄积[24-25,27]。目前,铁死亡已经越来越被重视,并有望作为逆转缺血性脑卒中神经元损伤的关键角色。 近年来,铁螯合疗法已被证明可以减轻啮齿动物脑缺血再灌注损伤模型中的铁死亡,例如在大脑中动脉闭塞(middle cerebral artery occlusion,MCAO)模型动物中,铁的摄入量与梗死体积成正相关[33]。另外,Deferoxamine(DFO)作为一种高亲和力的铁螯合剂,已获得美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)批准用于治疗铁超负荷[34]。如上所述,Lip-1和Fer-1都是具有特定抗铁蛋白体活性的化合物,临床前研究表明,脑缺血再灌注后立即或6 h内通过鼻内给药Fer-1或Lip-1可以显著减少MCAO小鼠的神经元损伤和功能缺陷,这表明特殊的外源性铁死亡抑制剂可能具有逆转脑缺血再灌注损伤的能力[34-35]。 越来越多的证据表明,铁死亡是体内急性病理性脑细胞死亡的真正机制[36]。TUO等[37]在3月龄的MCAO大鼠模型中进行了一项研究,观察到敲除微管蛋白基因Tau可以显著减少铁死亡,并抑制脑缺血再灌注损伤,这表明抑制Tau蛋白可以抵抗铁死亡;然而,在12月龄的MCAO老年小鼠模型中进行Tau基因敲除后,出现了年龄依赖性加速累积的脑铁死亡,否定了抑制Tau蛋白对缺血性脑卒中诱导的局灶性脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用,最后,通过联合铁螯合剂及Tau基因敲除的共同作用逆转了老年小鼠的脑缺血再灌注损伤。有趣的是,另一项研究发现,局部缺血还会导致Tau蛋白减少,从而抑制淀粉样蛋白前体蛋白(amyloid precursor protein, App),进一步减少亚铁出口铁转运蛋白(Ferroportin,FPN)影响铁输出,导致细胞内铁积聚,增加神经元对铁死亡的敏感性,通过增加血液中载脂蛋白的水平可减少脑损伤并改善神经功能,这可能与减少神经元脂质过氧化有关[38]。这些发现印证了铁螯合剂和抗氧化剂的相互作用,可作为铁死亡和缺血性卒中预后的多效调节剂,暗示着临床转化中可能需要结合多种干预手段来取得更有效的治疗成果。同样,Tau蛋白的作用还在其他疾病模型中也被验证:LEI等[39-40]发现Tau蛋白的高表达可能会导致阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病中神经元铁蓄积,通过敲除Tau可阻碍铁蓄积及其神经毒性。 此外,辅酶Q10作为一种内源性脂溶性抗氧化剂能够有效抑制脂质过氧化,有望成为抑制铁死亡的药物[41-42]。研究发现:口服辅酶Q10可显著改善大鼠MCAO模型和急性缺血性脑卒中患者的神经功能损伤预后[43-44]。最近,GUAN等[45]发现一种植物来源的单萜酚——香芹酚,可抑制缺血再灌注损伤后海马神经元的损害并逆转神经功能缺陷,深入探索后发现再灌注后腹膜内注射香芹酚可有效降低活性氧表达,减少铁沉积和升高GPX4水平,表明香芹酚可能通过抑制铁死亡而发挥神经保护作用。该研究证明了再灌注后2 h腹膜内给予香芹酚的好处,YU等[46]证实脑室内给药可延长治疗窗口至6 h。以上研究提示香芹酚可能是治疗缺血性脑卒中潜在的治疗选择。 目前,已有研究证明补充硒(Se)可通过促进GPX4的表达来有效抑制GPX4依赖性的铁死亡以及内质网应激引起的细胞死亡[47]。当缺血性脑卒中发生后,全身使用脑渗透性硒肽可激活体内稳态转录,从而抑制细胞铁死亡并改善神经功能[47]。此外,磷脂酰乙醇胺结合蛋白1(phosphatidyl ethanolamine binding protein 1,PEBP1)作为一种蛋白激酶级联反应的细胞骨架蛋白抑制剂,可以与脂氧合酶15结合,通过产生脂质死亡信号来促进铁死亡,因此WENZEL等[48]证实通过下调PEBP1 /15-LOX复合物水平,可以抑制铁死亡来保护海马组织免受脑缺血再灌注损伤。综上所述,铁死亡已被证实参与脑缺血再灌注损伤的发生发展中,且通过抑制铁死亡可逆转神经功能损伤,甚至改善预后。 尽管越来越多的研究证实缺血性脑卒中后铁死亡发挥着重要的作用,但更深层的分子机制尚不清楚,具有临床转化性的研究也仍在探索中。同时,铁死亡的发现也让科学家们更加深入地认识到多种细胞死亡对脑缺血再灌注损伤的影响作用有所交叉,因此在未来,科学家们还需要探究不同细胞死亡方式之间的联系,进而有效且全面的多靶点抑制达到更好的保护作用。 2.3 铁死亡与出血性脑卒中 脑出血发生后,早期由于血肿的形成引起颅内压升高,出现脑疝,从而导致原发性脑损伤。随后,血液进入大脑间隙,从而出现神经元损伤和组织炎症,导致继发性脑损伤。临床前研究表明,血红蛋白作为血液中最丰富的蛋白质,可在脑出血后从溶解的红细胞中大量释放,血红蛋白被血红素加氧酶降解为一氧化碳、胆绿素和游离铁,诱导铁死亡,成为继发性脑损伤和神经元死亡的主要原因[49-50]。有研究证实,血红蛋白可以被小胶质细胞和血肿周围区域浸润的巨噬细胞吞噬,并将其含有的二价铁代谢为三价铁,从而诱导活性氧产生和脂质过氧化,随后,过量的亚铁从小胶质细胞运出并通过FPN系统将铁积聚在神经元中,并通过Fenton反应与过氧化氢反应形成高毒性羟基,这些羟基自由基攻击DNA、蛋白质和脂质膜,从而破坏细胞功能,诱导铁死亡发生[51]。最近的研究提示,通过限制铁沉积和活性氧的产生,可以降低早期脑损伤并预防继发性脑损伤从而改善脑出血患者的预后[52-53]。此外,GPX4作为铁死亡的主要上游调节剂之一,其功能失活与脑出血不良预后相关[54]。ZHANG等[55]进一步在自体血液注射诱发的脑出血大鼠模型中证实,脑出血发生后,脑组织中GPX4的表达水平降低,而高表达GPX4赋予了部分神经元抵抗铁死亡的能力,减轻继发性脑损伤并改善神经功能。 从理论上讲,应用Fer-1或Lip-1可以直接抑制血红蛋白中释放的游离铁,LI等[51]通过体内外实验证实了该结论,应用Fer-1可以有效减少出血性脑卒中后脂质过氧化及活性氧的产生,并降低前列腺素内过氧化物合酶2(prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2,PTGS2)及其产物环氧合酶2的表达水平,进一步的实验发现脑出血后环氧合酶2在神经元中高度表达,抑制环氧合酶2可以减少脑出血引起的继发性脑损伤,这也提示环氧合酶2可能是铁死亡潜在的生物标记物。最近的许多研究提出了减轻脑出血后脑损伤的潜在治疗方法。曾劲松等[56-58]在血红蛋白诱导的大鼠脑出血模型中证实脑泰方通过调节神经元细胞铁代谢,减轻神经元铁负荷及脂质活性氧累积,从而提高神经元细胞活力,其作用与铁死亡抑制剂去铁胺一致,提示脑泰方可能通过抑制脑出血后神经元铁死亡而发挥神经保护作用。ALIM等[59]证实应用硒可有效地驱动大脑中GPX4表达,从而抑制铁死亡保护神经元并改善神经功能。KARUPPAGOUNDER等[52]发现N-乙酰半胱氨酸作为一种含硫醇的氧化还原调节化合物,可与前列腺素E协同作用共同抑制脑出血后引起的铁死亡并改善小鼠出血性中风的预后。这些发现填补了脑出血后铁死亡的重要知识空白,并为将来靶向铁死亡改善脑出血预后提供了重要的研究基础。与缺血性卒中相关研究比较发现,铁死亡在脑出血中的发生机制与其不完全相同,更多的是由于血红蛋白的释放及氧化,进而诱导铁死亡。而治疗方式二者类似,都是以应用GPX4抑制剂或Fer-1来减轻铁死亡。不过,在缺血性脑卒中研究中提出的问题在脑出血模型中得到了初步的答案:环氧合酶2可作为铁死亡的生物标记物,同时研究者也发现在脑出血后自噬与铁死亡并存,且应用双抑制剂效果更佳。这提示探索不同细胞死亡方式的联系尤为重要,且多靶点抑制是可行的治疗手段。"
| [1] BENJAMIN EJ, MUNTNER P, ALONSO A, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139:e56-e528. [2] BENJAMIN EJ, BLAHA MJ, CHIUVE SE, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2017 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e146-e603. [3] SEKERDAG E, SOLAROGLU I, GURSOY-OZDEMIR Y. Cell Death Mechanisms in Stroke and Novel Molecular and Cellular Treatment Options. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018;16(9):1396-1415. [4] KOH SH, PARK HH. Neurogenesis in stroke recovery. Transl Stroke Res. 2017;8:3-13. [5] FEIGIN VL, NORRVING B, MENSAH GA. Global Burden of Stroke. Circ Res. 2017;120:439-448. [6] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171(2):273-285. [7] YAGODA N, VON RECHENBERG M, ZAGANJOR E, et al. RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature. 2007;447(7146):864−868. [8] DOLMA S, LESSNICK SL, HAHN WC, et al. Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell. 2003;3:285-296. [9] YANG WS, STOCKWELL BR. Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem Biol. 2008;15:234-245. [10] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072. [11] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171(2):273-285. [12] WU JR, TUO QZ, LEI P. Ferroptosis, a recent defined form of critical cell death in neurological disorders. J Mol Neurosci. 2018;66(2):197-206. [13] 姚鹏, 陈勇, 李依玲, 等. 海马神经细胞铁死亡通过Nrf2/GPX4信号通路导致脓毒症相关性脑病大鼠认知功能障碍[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2019,31(11):1389-1394. [14] WU Z, GENG Y, LU XJ, et al. Chaperone-mediated autophagy is involved in the execution of ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:2996-3005. [15] LIANG C, ZHANG X, YANG M, et al. Recent progress in ferroptosis inducers for cancer therapy. Adv Mater Weinh. 2019;31:1904197. [16] GASCHLER MM, ANDIA AA, LIU HR, et al. FINO2 initiates ferroptosis through GPX4 inactivation and iron oxidation. Nat Chem Biol. 2018; 14(5):507-515. [17] 易仁鑫, 王歆悦, 王汉东. 青蒿素及其衍生物通过铁死亡途径发挥抗肿瘤作用的研究进展[J]. 科学技术创新,2020(8):31-32. [18] SKOUTA R, DIXON ST, WANG JL, et al. Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:4551-4556. [19] D’HERDE K, KRYSKO DV. Ferroptosis: oxidized PEs trigger death. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13:4-5. [20] DOLL S, PRONETH B, TYURINA YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13:91–98. [21] FANN DY, LEE SY, MANZANERO S, et al. Pathogenesis of acute stroke and the role of inflammasomes. Ageing Res Rev. 2013;12(4):941-966. [22] 张玮,马静萍.丁苯酞通过NLRP3炎性小体信号通路对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤后细胞焦亡的影响[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2020,18(6):898-902. [23] ZENG Q, ZHOU Y, LIANG D, et al. Exosomes Secreted From Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Pyroptosis in PC12 Cells by Promoting AMPK-Dependent Autophagic Flux. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020;14:182. [24] DING H,YAN CZ,SHI HL,et al. Hepcidin is involved in iron regulation in the ischemic brain.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25324. [25] PARK UJ, LEE YA, WON SM, et al. Gwag BJ Blood-derived iron mediates free radical production and neuronal death in the hippocampal ca1 area following transient forebrain ischemia in rat. Acta Neuropathologica. 2011;121(4):459-473. [26] DIETRICH RB, BRADLEY WG JR. Iron accumulation in the basal ganglia following severe ischemic-anoxic insults in children. Radiology. 1988; 168(1):203-206. [27] FANG KM, CHENG FC, HUANG YL, et al. Trace element, antioxidant activity, and lipid peroxidation levels in brain cortex of gerbils after cerebral ischemic injury. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013;152(1):66-74. [28] CASTELLANOS M, PUIG N, CARBONELL T, et al. Iron intake increases infarct volume after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res. 2002;952(1):1-6. [29] HANSON LR, ROEYTENBERG A, MARTINEZ PM, et al. Intranasal deferoxamine provides increased brain exposure and significant protection in rat ischemic stroke. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;330(3): 679-686. [30] BÉLANGER M, ALLAMAN I, MAGISTRETTI PJ. Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metabolism. 2011;14(6):724-738. [31] CARDOSO BR, HARE DJ, BUSH AI, et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4: a new player in neurodegeneration? Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(3):328-335. [32] CONRAD M, PRATT DA. The chemical basis of ferroptosis. Nature Chemical Biology. 2019;15(12):1137-1147. [33] GARCÍA-YÉBENES I, SOBRADO M, MORAGA A, et al. Iron overload, measured as serum ferritin, increases brain damage induced by focal ischemia and early reperfusion. Neurochem Int. 2012;61:1364-1369. [34] FRERET T, VALABLE S, CHAZALVIEL L, et al. Delayed administration of deferoxamine reduces brain damage and promotes functional recovery after transient focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Eur J Neurosci. 2006; 23:1757-1765. [35] 何晓敏, 莫绪明, 陈风. 去铁胺预处理对幼龄大鼠深低温脑缺血/再灌注损伤的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2008,25(12):1673. [36] ZHU Q, GONG Y, GUO T, et al. Thermo-sensitive keratin hydrogel against iron-induced brain injury after experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. Int J Pharm. 2019;566:342-351. [37] TUO QZ, LEI P, JACKMAN KA, et al. Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(11): 1520-1530. [38] DEGREGORIO-ROCASOLANO N, MARTÍ-SISTAC O, PONCE J, et al. Iron-loaded transferrin (Tf) is detrimental whereas iron-free Tf confers protection against brain ischemia by modifying blood Tf saturation and subsequent neuronal damage. Redox Biol. 2018;15:1. [39] LEI P, AYTON S, FINKELSTEIN DI, et al. Tau deficiency induces parkinsonism with dementia by impairing APP-mediated iron export. Nature Med. 2012;18(2):291-295. [40] LEI P, AYTON S, APPUKUTTAN AT, et al. Lithium suppression of tau induces brain iron accumulation and neurodegeneration. Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(3):396-406. [41] MORRIS G, ANDERSON G, BERK M, et al. Coenzyme Q10 depletion in medical and neuropsychiatric disorders: potential repercussions and therapeutic implications. Mol Neurobiol. 2013;48:883-903. [42] VISWANATHAN VS, RYAN MJ, DHRUV HD, et al. Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 2017;547:453-445 [43] RAMEZANI M, SAHRAEI Z, SIMANI L, et al. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation in acute ischemic stroke: is it beneficial in short-term administration? Nutr Neurosci. 2020;23(8):640-645. [44] NASOOHI S, SIMANI L, KHODAGHOLI F, et al. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation improves acute outcomes of stroke in rats pretreated with atorvastatin. Nutr Neurosci. 2019;22:264-272. [45] GUAN X, LI X, YANG X, et al. The neuroprotective effects of carvacrol on ischemia/reperfusion-induced hippocampal neuronal impairment by ferroptosis mitigation. Life Sci. 2019;235:116795. [46] YU H, ZHANG ZL, CHEN J, et al. Carvacrol, a food-additive, provides neuroprotection on focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. PLoS One. 2012;7:e33584. [47] ALIM I, CAULFIELD JT, CHEN YX, et al. Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell. 2019; 177(5):1262-1279. [48] WENZEL SE, TYURINA YY, ZHAO J, et al. Pebp1 wardens ferroptosis by enabling lipoxygenase generation of lipid death signals. Cell. 2017; 171(3):628-641. [49] KEEP RF, HUA Y, XI G. Intracerebral haemorrhage: mechanisms of injury and therapeutic targets. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11:720-731. [50] WU Y, SONG J, WANG Y, et al. The potential role of ferroptosis in neonatal brain injury. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:115. [51] LI Q, HAN X, LAN X, et al. Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis protects hemorrhagic brain. JCI Insight. 2017;2:e90777. [52] KARUPPAGOUNDER SS, ALIN L, CHEN Y, et al. N-acetylcysteine targets 5 lipoxygenase-derived, toxic lipids and can synergize with prostaglandin E-2 to inhibit ferroptosis and improve outcomes following hemorrhagic stroke in mice. Ann Neurol. 2018;84:854-872. [53] SELIM M, FOSTER LD, MOY CS, et al. Deferoxamine mesylate in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage (i-DEF): a multicentre, randomised, placebo- controlled, double-blind phase 2 trial. Lancet Neurol. 2019;18:428-438. [54] FORCINA GC, DIXON SJ. GPX4 at the crossroads of lipid homeostasis and ferroptosis. Proteomics. 2019;19:e180031. [55] ZHANG Z, WU Y, YUAN S, et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4 participates in secondary brain injury through mediating ferroptosis in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res 2018;1701:112-125. [56] 曾劲松,喻坚柏,廖君,等.脑泰方对脑出血大鼠脑组织铁沉积致神经细胞过氧化损伤的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2020,27(4):46-51. [57] 曾劲松,喻坚柏,刘检,等.脑泰方对血红蛋白诱导的大鼠皮质神经元铁超载及过氧化损伤的多靶点干预作用[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2020,30(6):708-714. [58] 曾劲松,喻坚柏,刘检,等.脑泰方对血红蛋白诱导的大鼠皮质神经元损伤的保护作用及机制[J]. 北京中医药大学学报,2019,42(10): 825-832. [59] ALIM I, CAULFIELD JT, CHEN Y, et al. Selenium drives a transcriptional adaptive program to block ferroptosis and treat stroke. Cell. 2019;177: 1262-1279. |
| [1] | Xie Jingshu, Zhang Xianglin, Liu Jinlei, Wen Jing. Application of High Resolution reconstruction algorithm in precision CT scans of the middle and inner ears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3614-3618. |
| [2] | Liang Meifu, Qu Shuhua. Optimal power load forecasting of the skeletal muscle based on back propagation neural network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3641-3647. |
| [3] | Huang Maomao, Hu Yue, Wang Binchuan, Zhang Chi, Xie Yujie, Wang Jianxiong, Wang Li, Xu Fangyuan. Bibliometric and visual analysis of international literature addressing ischemic stroke rehabilitation in recent 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3725-3733. |
| [4] | Li Shanshan, You Ran, Guo Xiaoxiao, Zhao Lu, Wang Yanling, Chen Xi. Advances in the mechanisms of optic nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3740-3745. |
| [5] | Liu Zhiwei, Xie Rui, Sun Kai, Li Kaiming, Wang Xiongwei, Zhan Jiawen, Zhu Liguo. Interpretation of diagnostic criteria for cervicogenic headache: challenges and understandings in diagnosis and differential diagnosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3746-3751. |
| [6] | Lin Haishan, Mieralimu Muertizha, Li Peng, Ma Chao, Wang Li. Correlation between skeletal muscle fiber characteristics and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with hip fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3144-3149. |
| [7] | Zuo Xiuqin, Yin Sasa, Xie Huimin, Jia Zishan, Zhang Lining. Applicability and specifications of platelet-rich plasma in musculoskeletal repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3239-3245. |
| [8] | Bai Xiaotian, Huo Hongfeng. Biomechanical evaluation of foot and ankle function: constructing static and dynamic indexes of the foot [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2747-2754. |
| [9] | He Shaobo, Liu Jichao, Yang Lifeng, Ding Yongfeng, Li Wujian. Finite element analysis of transposition of posterior tibial tendon for foot drop [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2334-2340. |
| [10] | Xu Xiaopei, Lü Xin. Classification of intertrochanteric fractures with medial wall destruction in elderly patients and recovery of bony support and continuity of the cortical bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2259-2265. |
| [11] | Liu Lu, Zhang Nini, Dai Min, Huang Guilin. Pathological changes and functional reconstruction of radiation-induced salivary glands repaired by stem cells and biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2103-2107. |
| [12] | Zhang Yicen, Wang Peixin, Liu Zhicheng. Ultrasound-guided injection of hyaluronic acid and corticosteroid for treating plantar fasciitis: evaluation of pain, fascia thickness and ankle-foot function [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1670-1674. |
| [13] | Tian Yanping, Li Juan, Liu Xiaobo, Zhang Huiling, Shi Lihong, Jin Rongjiang. Knowledge network mapping of literature regarding platelet-rich plasma in recent 5 years: a visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1745-1752. |
| [14] | Xu Baoyun, Fu Weili. Posterior cruciate ligament injury: diagnosis, treatments and rehabilitation strategies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1766-1772. |
| [15] | Long Qian, Guan Xiaoyan, Wang Qian, Hu Huan, Liu Jianguo. Transcriptome sequencing technology and its application in oral diseases, dental implants and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1791-1798. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||