Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (14): 2259-2265.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3112
Previous Articles Next Articles
Classification of intertrochanteric fractures with medial wall destruction in elderly patients and recovery of bony support and continuity of the cortical bone
Xu Xiaopei, Lü Xin
- Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-11Revised:2020-05-14Accepted:2020-06-03Online:2021-05-18Published:2020-12-31 -
Contact:Lü Xin, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Xu Xiaopei, Master candidate, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, the Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Xiaopei, Lü Xin. Classification of intertrochanteric fractures with medial wall destruction in elderly patients and recovery of bony support and continuity of the cortical bone[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2259-2265.
share this article
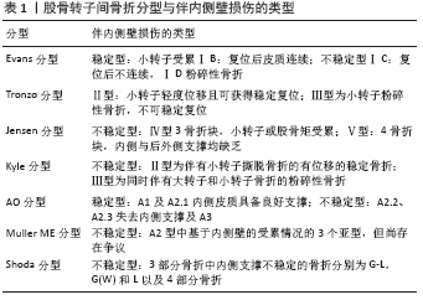
2.1 内侧壁的概念及提出 股骨转子间内侧壁是由股骨颈下端、小转子和位于其深部的股骨矩组成,是决定骨折稳定性和预后的重要因素。股骨转子间后内侧壁包括小转子及其深部的股骨矩等部位[7]。股骨矩位于股骨颈干连接处的后内侧,为致密的纵行骨板,是股骨近端压力侧重要的应力传导部分,其完整性决定了股骨转子间骨折的稳定性。股骨转子间骨折最早的分型是由Evans于1949年提出,这一分型是基于股骨转子间内侧壁完整性及稳定性来定,他提出了内侧壁的重要性。1975 年,Jensen 进一步将Evans分型进行细分,认为大转子、小转子 (即股骨转子间内侧壁) 的支撑作用决定了股骨转子间骨折的稳定性。股骨转子间骨折内侧壁缺损严重影响其力学稳定性,许多学者认为骨折块都必须得到复位固定,否则容易导致旋转、内翻移位及髋部力量下降[8- 9]。 当出现股骨内侧壁损伤严重时,应力则传导至前方皮质。所以在股骨转子间骨折复位时,后内侧皮质的复位,尤其是股骨矩的复位极为重要,股骨矩的复位可使老年患者提前下床活动。 2.2 分型 股骨转子间骨折的分型众多,同时有着较长的发展历程,一般来说,转子间骨折是基于骨折形态学及生物力学进行分型,并无不同年龄间的显著差异及分型[10],从早期通过X射线影像学数据到现在进一步根据CT数据作出分型,ISIDA等[11]认为X射线片不能准确评估股骨转子间骨折,在敏感性方面,普通X射线片为44%,而CT可达95%。 基于普通X射线片数据的分型大多是在20世纪左右提出,包括Evans分型、Boyd Griffin分型、Ramadier分型、Dxcoulx Lavarde分型,这些分型是基于解剖学描述的;而另一类则是基于内固定术后预后的分型,包括Ender分型、Tronzo分型、Jensen分型、Deburge分型、Kyle分型、Briot分型、AO分型等分型,这些分型对内固定治疗的指导及术后评估方面均具有较大的贡献。在这两类分型中,其中基于解剖学描述的分型临床应用较为广泛,但不断有研究显示之前的这类分型尚存在局限性。而近几年基于CT数据的分型被逐渐提出,其中包括Nakano分型、Shoda分型以及 Kijima分型等[12],但应用并不广泛。 1949年Evans首先提出了内侧壁的概念,认为股骨转子间内侧的皮质是股骨近端的主要支撑结构,内侧皮质的完整性决定了股骨转子间骨折的稳定性。Evans分型中Ⅰ型为顺行骨折,骨折线从小转子向外上延伸,Ⅰ型又包含了4个亚型,其中小转子受累,复位后皮质连续为ⅠB,为稳定型;而复位后不连续为ⅠC,与粉碎性骨折ⅠD均为不稳定型。Ⅱ型为逆转子间骨折,骨折线为从小转子向外下延伸,骨折线为反斜型。1973年Tronzo将股骨转子间分为5型,其中Ⅱ型为小转子骨折轻度位移或者股骨矩完整,小转子轻度位移且可获得稳定复位;Ⅲ型为小转子粉碎性骨折(累及股骨矩骨折),往往伴有后外侧的粉碎骨折而不能获得稳定的复位。1980年Jensen分型是对Evans分型进一步改进[13],在评估骨折稳定性与内固定术后稳定性及预后方面优于Evans分型、Tronzo 分型等。Jensen分型将大小转子的受累情况及复位后稳定情况均考虑进去,认为小转子(股骨转子间后内侧)或股骨矩受累可导致股骨近端缺乏内侧支撑,Jensen分型分为5型,Ⅰ型:2骨折块,无位移;Ⅱ型:2骨折块,有位移;Ⅲ型:3骨折块,大转子骨折并移位;Ⅳ型:3骨折块,小转子或股骨矩受累导致内侧支持缺失;Ⅴ型:4骨折块,内侧与后外侧支撑均缺乏。从Ⅲ型开始认为是不稳定性骨折。1979年Kyle等[14]同样对Evans分型进行了改良,将股骨转子间骨折分为4型,其中Ⅱ型为伴有小转子撕脱骨折的有位移的稳定骨折,Ⅲ型为同时伴有大转子和小转子骨折的粉碎性骨折,为不稳定性骨折。1981年在AO分型中,主要分为3型,A1型为两部分骨折,外侧皮质完整,内侧皮质具备良好支撑,A2型为粉碎性骨折,外侧壁完整,内侧皮质及后方皮质在数个平面破裂而失去内侧支撑,又根据中间骨块的不同数量分为3个亚型,A3型为股骨转子间外侧皮质破裂,逆向骨折。1990年MULLER等将股骨转子间骨折纳入长骨的研究,发现在A2型中有3个亚型的分型是基于股骨近端内侧壁的受累情况[15],有学者认为是不稳定型,但尚存在争议[16]。2017年SHODA等[17]利用3D-CT技术分析239例股骨转子间骨折患者,认为单纯利用X射线片很难评估大转子的骨折形态,尤其是小转子在内的大斜型碎块,且根据骨折断裂的骨折块数将股骨转子间骨折分为2,3,4部分骨折分型,其中3部分骨折根据大小转子受累情况分为5个亚型,且将合并小转子损伤或合并股骨矩损伤而导致的内侧支撑不稳定的骨折归入3部分骨折,分别为 G-L,G(W)和L,以上3个亚型和4部分骨折均为不稳定性骨折。王郑浩等[18]通过3D-CT分析了136例合并后内侧壁损伤的患者,绘制骨折地图、骨折线形态,进一步完善了AO分型后内侧壁的骨折线分布,认为A2型骨折后内侧壁骨折线破坏股骨矩下段,常集中于小转子及其下方,A3型则破坏股骨矩上段,常集中于小转子及其上方。见表1。 近年来,外侧壁损伤的重要性在不断提及,AO/OTA-2018按照外侧壁的状况进行第二步分类[19],将含有小转子骨块原A2.1型重新划分为简单骨折中的A1.3型,该划分并非否定内侧壁的重要性,而是将原归为稳定骨折类型与不稳定的小转子骨折类型A2.2、A2.3相区别。综合上述分型可见,稳定性成为目前股骨转子间骨折分型的核心。转子间骨折的分型仍然在不断完善,从不同的分型来看,不管是基于X射线片还是目前更加精确的CT分型,股骨转子间骨折是否稳定的主要因素还是包括了股骨矩的完整性、内侧弓的完整性及小转子(后内侧壁)的完整性[12]。 2.3 内侧壁损伤机制 股骨转子间骨折损伤主要分为两种原因,一种是直接暴力损伤,多为老年患者因骨质疏松、髋部着地受力导致的低暴力损伤,而出现单纯的股骨转子间内侧壁骨折多为年轻患者,是由高处坠落、交通事故等高暴力损伤导致的,但这一类型损伤较少见;另一种是间接暴力损伤导致的,髋关节内翻或向前成角的应力所导致的骨折,或是髂肌及腰大肌强烈收缩导致小转子的撕脱骨折,这是由于股骨转子间内侧壁为髂腰肌附着点。 2.4 生物力学分析 国内外学者通过生物力学实验研究发现,前内侧皮质的对位关系为术中重要的参考标准,尤其是内侧皮质的前侧缘和前侧皮质的内侧缘,内侧皮质支撑为著,因此影像学上出现3种皮质对位关系,正性支撑、中性支撑及负性支撑。在正性对位中,内侧皮质的支撑力较前侧皮质的支撑力大,且认为要避免内侧皮质成为负性对位[20- 21]。 NIE等[22]将12对离体股骨标本进行生物力学测定,认为内侧壁较外侧壁更加重要,内侧壁是否存在与其完整程度决定了股骨破坏的载荷及维持股骨轴向的刚度,当内侧皮质缺损时,股骨近端所受应力应变主要集中在外侧、前侧以及后侧皮质,其中后侧皮质最为显著。闵重函等[23]通过对64根老年国人尸体股骨标本进行生物力学测试,认为内侧皮质应力应变于纵向压应力下明显,这说明内侧皮质是主要的应力传道区域,结合解剖形态,其坚实程度较其他位置强。 在不同载荷下,股骨近端应力主要由压力骨小梁和股骨矩向下传导,股骨近端最大等效应力从高到低依次为股骨内侧皮质、股骨颈下方、股骨颈上方和外侧皮质[24],股骨近端内侧区域所承受的压缩应力集中在小转子及其下方1-3 cm的内侧皮质处[25]。ZHANG等[26]通过生物实验发现,破坏的股骨矩导致股骨转子间后内侧压应力明显增大,从而易造成轴向应力下塌陷,形成髋内翻畸形。若术中未对内侧壁进行处理,最后出现髋关节内翻畸形发生率达10%-16%[27- 28]。 2.5 内侧壁损伤的内固定治疗 Harrington等[29]早在1973年就提出,不管通过何种内固定方式治疗,内侧骨皮质缺损就会导致近端骨折块的旋转及内翻,直到坎嵌在断端为止。老年股骨转子间骨折患者累及内侧壁损伤的特点是股骨近端内侧皮质不稳定,小转子处骨皮质破裂受损,这使得股骨近端压力侧皮质完全失去支撑功能,加之股骨转子间周围外展肌、外旋肌和髂腰肌等肌群的作用,导致骨折复位困难,复位后难以维持[7]。KIM等[30]报道了动力髋螺钉(DHS)、锁定加压接骨板(LCP)及股骨近端防旋髓内钉(proximal femoral nail anti-rotation,PFNA)治疗老年股骨转子间骨折,术后2年内固定失败的发生率为4.54%-19.23% ,所以股骨转子间骨折合并内侧壁选用何种内固定具有十分重要的意义。 治疗股骨转子间骨折的内固定方法主要分为髓外固定及髓内固定两大类,髓外内固定材料常见为动力髋螺钉、股骨近端解剖锁定钢板(proximal femur anatomic locking plate,PF-LCP)、股骨近端经皮加压钢板(percutaneous compression plating,PCCP),髓内固定常见股骨近端防旋髓内钉、Gamma钉及联合加压交锁髓内钉系统(InterTan)。对于不稳定型转子间骨折而言,由于髓内固定较髓外固定力臂更短,有更明显的力学优势[31]。但有研究发现髓内系统尚不完善,对于伴有骨质疏松的亚洲老年女性而言,内侧壁受累的不稳定型骨折可致髓内固定手术时间长、难度大、失血量增加等的手术风险,适合采用PCCP或动力髋螺钉等髓外固定[32]。同时近年来同样有不少国内外学者支持行人工关节置换术治疗不稳定性股骨转子间骨折[33]。下面将股骨转子间骨折合并内侧壁损伤分型不同手术方式治疗进行简单阐述。 2.5.1 髓外固定 (1)动力髋螺钉:髓外固定中动力髋螺钉固定系统(DHS)作为钉板系统的代表之一,发明于20世纪50年代,是临床应用最广泛的系统之一,曾被作为治疗转子间骨折的“金标准”[34]。动力髋螺钉由1枚头颈内拉力螺钉及贴于股骨干外侧壁带套筒的钢板构成,具备静态和动态双重加压作用,加强了断端之间的接触,使得骨折具有良好的固定和愈合过程[35]。当未累及内侧壁时,内侧壁皮质与外侧动力髋螺钉所受应力大小无显著改变;当内侧骨皮质一半受累时,内侧壁应力增加约 28%,而位于外侧的动力髋螺钉钢板应力增加约 9%;当完全累及内侧壁时,内侧壁皮质交界处所承受应力则增高约125%[36]。该装置具有使用方便、成本低、失血少、再手术率低、功能效果好等优点。 随着手术量的增加,动力髋螺钉也逐渐显现出它的不足,SIWACH等[37]报道了其失败率为24%-56%。患者年龄、复位质量及骨质疏松是动力髋螺钉失败的考虑因素,以骨质疏松为著,故老年患者所占失败比例最高[38]。陆勇[39]认为加压钉切割股骨头以及髋内翻畸形的主要原因为内固定后小转子仍处于分离或骨折内侧皮质对位不良等情况。股骨矩是承载纵向负荷的力学基础,同样是股骨颈向股骨干移行的解剖结构,如果内侧壁损伤明显,内侧应力则明显增大,例如小转子缺损破坏股骨矩,影响内固定的固定强度,可导致钢板螺钉交界处螺钉断裂及螺钉切割股骨头等内固定的失败[30, 40]。对于骨质疏松的高龄患者而言,由于股骨颈后内侧皮质缺损,股骨近端骨质并不坚硬,导致压应力无法经股骨矩传导,使螺钉对骨的把持力减弱,从而不能达到坚强的内固定。 因此不少国内外学者通过动力髋螺钉固定并植骨、利用动力髋螺钉复位小转子、动力髋螺钉联合小转子拉力螺钉固定并植骨及联合钢丝固定内侧壁,通过动力髋螺钉附加抗旋螺钉等方法复位并固定后内侧壁骨块,尽量恢复解剖复位,同时可以起到诱导生长的作用[41-44]。CEYNOWA等[45]通过生物力学研究显示2孔动力髋螺钉的断裂力最小,4孔动力髋螺钉比2孔动力髋螺钉强约20%(P<0.05)。有学者通过骨水泥来加强动力髋螺钉,这可减少术后并发症且有利于髋关节活动度[46]。MüLLER等[47]通过分析375例年龄≥65岁的AO/OTA 31-A2型骨折患者,认为是否伴有转子稳定板(TSP)与动力髋螺钉的植入相关并发症的发生率显著相关,并推荐这一类型骨折使用股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗。 (2)PF-LCP:PF-LCP与动力髋螺钉最大的不同是,动力髋螺钉存在后期滑动加压效果,而锁定加压接骨板当即获得坚固的固定,因此术中复位要求更加严格。WIRTZ等[48]利用PF-LCP治疗不稳定型转子间骨折时结果并不理想,特别是对于治疗内侧骨皮质缺损的骨折,近端锁定螺钉断裂率为29%,认为是由于缺乏骨块间的加压作用,使压力集中在钢板和近端锁定螺钉之间,导致螺钉断裂。有学者通过植入同种异体骨,植骨联合锁定钢板等方式来填补内侧骨皮质的缺损,恢复连续性[49]。房冰等[50]通过临床对比研究认为股骨近端防旋髓内钉与PF-LCP两种内固定对于治疗老年患者转子间骨折的效果相当,但在术中出血、手术时长及术后并发症方面PF-LCP更具有优势。 (3)PCCP:PCCP属于髓外固定,在设计方面,PCCP相比动力髋螺钉更具有优势,当远、近端螺钉固定后,可以滑动股骨颈部分,内侧支撑作用则是由钢板锁定和套筒来提供,所以PCCP具备抗剪切、抗旋转及抗滑脱的作用[51]。一项荟萃分析认为与动力髋螺钉相比,PCCP组的失血量、输血量和相关并发症的发生率均显著降低,但在手术时间、住院时间、死亡率等方面无明显统计学差异[52],因此,PCCP可作为一种微创手术治疗方法,同时其无需扩髓,术式简单,在手术时间及出血量上,均较PFNA-Ⅱ有优势[53];但稳定型及无移位骨折或易复位的骨折是其主要适应证,相对于有骨质疏松症同时伴有大小转子受损的骨折及逆转子粉碎性骨折是不适用的,故伴有内侧壁损伤的不稳定型的老年患者不是其主要适应证。 2.5.2 髓内固定 髓内固定装置主要为Gamma钉和股骨近端防旋髓内钉,以及近年来出现InterTan、适合亚洲人的PFNA-Ⅱ及具有前弓的金属髓内钉(zimmer natural nail, ZNN)。大多数学者认为,髓内装置的主钉置于股骨髓腔中,较髓外固定更接近内侧,合并内侧壁损伤的股骨转子间骨折因受力学影响,使用髓内钉治疗不稳定型骨折时,对患者活动性、功能性有更好的疗效[54]。 (1)股骨近端防旋髓内钉:股骨近端防旋髓内钉的结构更加符合转子间的生物力学,同时也具备较强的抗剪切力等优势,所以对于伴有内侧壁缺损的不稳定性中老年患者均可采用股骨近端防旋髓内钉[55],在临床上也取得了满意的疗效。NIE等[22]通过生物力学研究发现股骨近端防旋髓内钉是治疗不稳定股骨转子间骨折的一种有效的髓内固定系统。WANG等[56]认为相比动力髋螺钉而言,股骨近端防旋髓内钉具有固定牢固、组织创伤小、适应证广和并发症少的优点,更利于老年患者的治疗。 对于伴有骨质疏松的老年骨折患者而言,骨质对于螺钉及刀片的把持能力有限,尤其是合并有内侧壁缺损时,螺旋刀片及螺钉更易切出,进入髋关节内造成髋内翻畸形及内固定失败,因此不少学者提出了先将小转子及内侧壁进行良好复位及固定。KIM等[57]通过“糖果钢丝环扎技术”将小转子复位并环扎固定,然后再利用股骨近端防旋髓内钉、Gamma钉等髓内钉进行固定。彭硕和周铁军[58]应用空心钉联合股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗合并有后内侧壁骨皮质缺损的转子间骨折,先将转子进行整复。石少辉等[59]应用U-Blade钉建立通道,并于后内侧壁进行植骨,再通过髓内钉固定。上述方法均是为了恢复内侧壁骨质缺损,恢复内侧支撑及连续性。徐锴等[60]利用有限元分析认为,对于包括内侧壁损伤在内的不稳定型转子间骨折而言,内侧钢板联合股骨近端防旋髓内钉的应用可显著降低内侧的压应力,有效减少骨块位移程度。此外,卫禛等[61]越来越重视前内侧皮质正性支撑复位的作用,正性支撑复位可作为一种功能复位形式,起到一定的支撑作用,从而降低内固定载荷、提高稳定性,为不能实现解剖复位的备选方案。 (2)PFNA-Ⅱ:目前适合亚洲人的PFNA-Ⅱ逐步进入临床,更加适用于合并有小转子移位的不稳定性骨折,同时有效防止对外侧骨皮质的撞击[62]。采用PFNA-Ⅱ行内固定时,内侧壁受累缺损较内侧壁完整的股骨转子间骨折患者术中出血量更多,且手术时长有明显增加,但住院时间、骨折愈合时间及髋关节Harris评分比较无显著性差异[53,63]。王炜等[64]通过有限元分析认为合并有内侧壁缺损的股骨转子间骨折后,采用动力髋螺钉是不安全的,对于PFNA-Ⅱ是理想的。DURMAZ等[65]认为在综合评价股骨转子间骨折的一些手术参数、功能及影像学表现上,PFNA-Ⅱ优于InterTan。 新一代股骨近端防旋髓内钉系列对防止切出、穿透等进行改进,通过将骨水泥注入螺旋刀内进行增强,平均注入骨水泥4.2 mL,这显著提高了螺旋刀片在股骨头颈内的把持度,明显降低术后并发症,因而可显著降低伴有骨质疏松的老年患者的切出率,提高活动水平[66]。 (3)InterTan:InterTan是另一种髓内固定系统,外翻角较PFNA-Ⅱ小,12°的前倾角设计使其更加符合股骨近端解剖结构。InterTan采用带2个头颈部螺钉的大转子顺行髓内钉,可使头颈部骨折块在术中保持线性压缩和旋转稳定,防止复位丢失,在股骨头中有广泛的应用前景,其固有的连续稳定性允许早期负重和活动[67]。与股骨近端防旋髓内钉相比,ZHANG等[68]通过对伴有内侧壁损伤的老年骨质疏松患者进行平均38.8个月的随访,认为应用InterTan有助于减少螺钉切断、主钉远端或近端股骨干骨折、股骨头内翻塌陷等影像学方面并发症,但在预后方面组间功能无显著差异。于晨等[69]通过Meta分析认为InterTan具有更好的轴向加压作用及抗旋转稳定性,有利于早期下地活动,减少因老年患者长期卧床的相关并发症,恢复髋关节功能,且术后并发症及内固定失败数较少,但应综合考虑作出合理选择。ZHANG等[70]认为InterTan在AO/OTA 31-A2型骨折术后假体周围骨折和再手术方面的治疗效果具有优势;GAVASKAR等[71]通过临床比较认为InterTan组在不稳定型骨折的术后功能及术后并发症发生率方面更具优势。对于不稳定型骨折患者而言,于晨等[69]认为与PFNA-Ⅱ组相比,InterTan组股骨干骨折、旋转复位丢失、头颈内翻塌陷、髋和大腿疼痛、切出和股骨颈缩短的发生率降低。由于其并发症发生率较低,InterTan可能更有优势。林荣侯等[72]通过对120例不稳定型中老年患者进行综合分析认为髓内固定治疗的疗效显著优于动力髋螺钉,其中InterTan最具优势。 WU等[73]对不稳定型股骨转子间骨折患者进行临床对比分析,认为Gamma3钉组在切出和股骨干骨折的发生率明显高于InterTan钉组(P值分别为0.024和0.044),但InterTan钉组手术时间长且术中透视多。朱贵伟等[74]通过有限元分析发现InterTan与ZNNCM(zimmer natural nail cephalomedullary) 对于治疗Evans-Jensen Ⅳ型骨折均可提供可靠固定,对于预期活动量较高者推荐使用InterTan,而对于明显骨质疏松的老年患者ZNNCM具有明显生物力学优势。 然而髓内钉系统并非适用于任何转子间骨折,当髓内钉主钉入钉点被破坏,比如大转子的粉碎骨折、梨状窝粉碎骨折及冠状面骨折,均不建议采用髓内固定[75]。股骨近端防旋髓内钉具备有效抗旋转优势的同时起到了良好的复位作用,但由于长期应力作用可致术后股骨干骨折。白浪等[53]认为股骨转子间骨折合并有内侧壁缺损的不稳定型骨折在术后远期的功能恢复情况方面,仍不能明确髓内固定较髓外固定更具优势。李坛珠等[76]通过对极高龄不稳定型骨折患者行临床研究发现,髓外固定可获得较好疗效;髓内组总出血量、隐性出血量和总输血量均明显高于髓外组。对于骨质疏松情况较轻且活动能力较好的极高龄骨折患者而言,髓内固定在生物力学方面存在明显优势。不同于欧美患者,在国内对于内侧壁损伤的不稳定型老年患者而言,术后常规早期不负重锻炼,这规避了髓外固定在生物力学方面的相对不足之处。 "
| [1] 张世民, 胡孙君, 张立智,等.老年髋部转子间骨折[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.2019. [2] LEUNG F, BLAUTH M, BAVONRATANAVECH S. Surgery for fragility hip fracture-streamlining the process. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(Suppl 4): S519-521. [3] 曹军, 胡攀勇, 蔡保塔, 等. 三种植入物内固定治疗老年股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11):1683-1688. [4] NING GZ, LI YL, WU Q, et al. Cemented versus uncemented hemiarthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fractures: an updated meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(1):7-14. [5] HIRAGAMI K, ISHII J. Embedding the lateral end of the lag screw within the lateral wall in the repair of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric femur fracture. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(3): 1103-1108. [6] 蔡振存,朴成哲,陈拥,等. PFNA固定治疗老年人内侧壁不完整的股骨粗隆间骨折[J]. 沈阳医学院学报,2016,18(4):253-255. [7] HAMMER A.The calcar femorale: A new perspective. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2019;27(2):2309499019848778. [8] ARIRACHAKARAN A, AMPHANSAP T, THANINDRATARN P, et al. Comparative outcome of PFNA, Gamma nails, PCCP, Medoff plate, LISS and dynamic hip screws for fixation in elderly trochanteric fractures: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017;27(7):937-952. [9] AGRAWAL P, GABA S, DAS S, et al. Dynamic hip screw versus proximal femur locking compression plate in intertrochanteric femur fractures (AO 31A1 and 31A2): A prospective randomized study. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2017;8(1):87-93. [10] 徐高翔,李建涛,张浩,等.中老年股骨转子间骨折患者股骨近端解剖参数的性别和年龄差异研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020, 22(3):224-231. [11] ISIDA R, BARIATINSKY V, KERN G, et al. Prospective study of the reproducibility of X-rays and CT scans for assessing trochanteric fracture comminution in the elderly: a series of 110 cases. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(7):1165-1170. [12] 王人楷,章浩,李迪,等. 股骨粗隆间骨折临床分型研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(20):1882-1887. [13] JENSEN JS. Classification of trochanteric fractures. Acta Orthop Scand.1980;51(5):803-810. [14] Kyle RF, Gustilo RB, Premer RF. Analysis of six hundred and twenty-two intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979; 61(2):216-221. [15] NEWMAN RJ. The comprehensive classification of fractures of long bone. Current Orthopaeclics. 1991;5(4):287. [16] MATRE K, VINJE T, HAVELIN LI, et al. TRIGEN INTERTAN intramedullary nail versus sliding hip screw: a prospective, randomized multicenter study on pain, function, and complications in 684 patients with an intertrochanteric or subtrochanteric fracture and one year of follow-up.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(3):200-208. [17] SHODA E, KITADA S, SASAKI Y, et al. Proposal of new classification of femoral trochanteric fracture by three-dimensional computed tomography and relationship to usual plain X-ray classification. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(1):2309499017692700. [18] 王郑浩,李开南,兰海.基于三维CT的股骨转子间骨折后内侧壁骨折地图的研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(9):745-751. [19] KELLAM JAMES F, MEINBERG ERIC G, JULIE A, et al. Introduction: Fracture and Dislocation Classification Compendium-2018: International Comprehensive Classification of Fractures and Dislocations Committee. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32( Suppl 1):S1–S10. [20] 李双, 张世民,张立智,等.不同组合前内侧皮质支撑复位对股骨转子间骨折髓内钉术后稳定性影响的生物力学研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2019;21(1):57-64. [21] Chang SM, Zhang YQ, Du SC, et al. Anteromedial cortical support reduction in unstable pertrochanteric fractures: a comparison of intra-operative fluoroscopy and post-operative three dimensional computerised tomography reconstruction. Int Orthop. 2018;42(1):183-189. [22] Nie B, Chen X, Li J, et al. The medial femoral wall can play a more important role in unstable intertrochanteric fractures compared with lateral femoral wall: a biomechanical study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):197. [23] 闵重函, 周瑛, 张洪美, 等. 老年国人股骨近端生物力学特点与股骨粗隆间骨折内固定选择的试验研究[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(8):789-793. [24] SEKER A, BAYSAL G, BILSEL N, et al. Should early weightbearing be allowed after intramedullary fixation of trochanteric femur fractures? A finite element study. J Orthop Sci. 2020;25(1):132-138. [25] TAN BY, LAU AC, KWEK EB. Morphology and fixation pitfalls of a highly unstable intertrochanteric fracture variant. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2015;23(2):142-145. [26] ZHANG Q, CHEN W, LIU HJ, et al. The role of the calcar femorale in stress distribution in the proximal femur. Orthop Surg. 2009;1(4):311-316. [27] DOMINGO LJ, CECILIA D, HERRERA A, et al. Trochanteric fractures treated with a proximal femoral nail. Int Orthop. 2001;25(5): 298-301. [28] 曹培锋,洪勇平,王以近,等.股骨小转子缺损及复位固定的生物力学比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(22):1722-1724. [29] HARRINGTON KD, JOHNSTON JO. The management of comminuted unstable intertrochanteric fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(7): 1367-1376. [30] KIM JW, LEE JI, PARK KC. Pseudoaneurysm of the deep femoral artery caused by a guide wire following femur intertrochanteric fracture with a hip nail: A case report. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(3):266-269. [31] EHRNTHALLER C, OLIVIER AC, GEBHARD F, et al. The role of lesser trochanter fragment in unstable pertrochanteric A2 proximal femur fractures - is refixation of the lesser trochanter worth the effort. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2017;42:31-37. [32] 熊蠡茗, 胡益强, 邵增务, 等. 股骨近端锁定板固定治疗老年不稳定型股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(2):115-120. [33] 左进步,余磊, 梁宏伟,等.钉板固定、髓内固定及人工股骨头置换修复高龄股骨转子间骨折:选择与比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(17):2711-2718. [34] JACOB J, DESAI A, TROMPETER A. Decision Making in the Management of Extracapsular Fractures of the Proximal Femur - is the Dynamic Hip Screw the Prevailing Gold Standard. Open Orthop J. 2017;11:1213-1217. [35] MATAR HE, CHANDRAN P. Outcomes of internal fixation of intracapsular hip fractures using dynamic locking plate system (Targon® FN). J Orthop. 2018;15(3):829-831. [36] 郭晓泽,章莹, 肖进. 动力髋螺钉固定股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2012,15(4):458-461. [37] SIWACH RC, ROHILLA R, SINGH R, et al. Radiological and functional outcome in unstable, osteoporotic trochanteric fractures stabilized with dynamic helical hip system. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2013;8(2):117-122. [38] 张一鹏, 刘伟新, 梁献会. DHS治疗股骨转子间骨折失败原因分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2014,20(2):165-168. [39] 陆勇. 动力髋螺钉治疗股骨粗隆间骨折失败原因分析[J]. 骨与关节损伤杂志,2003,18(11):730-732. [40] YOO JI, HA YC, LIM JY, et al. Early Rehabilitation in Elderly after Arthroplasty versus Internal Fixation for Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures of Femur: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Korean Med Sci. 2017;32(5):858-867. [41] 徐锋,吕建元,洪嵘,等.植骨在DHS固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折中的作用[J]. 实用骨科杂志, 2008,14(12):722-725. [42] 罗小荣, 梁路石. 应用动力髋螺钉系统结合小粗隆复位固定治疗股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(8):659-660. [43] 张松,王晓,尹桂荣,等.小粗隆拉力螺钉固定、植骨结合DHS治疗不稳定型股骨粗隆间骨折[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2004,19(9):618-619. [44] 陈燕才. 动力髋螺钉联合钢丝对股骨粗隆间骨折合并内侧壁骨折疗效分析[J].现代诊断与治疗,2017,28(4):607-609. [45] Ceynowa M, Zerdzicki K, Klosowski P, et al. The early failure of the gamma nail and the dynamic hip screw in femurs with a wide medullary canal. A biomechanical study of intertrochanteric fractures. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;71:201-207. [46] 葛旻, 程飚, 陈富强, 等. 骨水泥强化动力髋螺钉内固定治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017, 32(10):1066-1067. [47] MÜLLER F, DOBLINGER M, KOTTMANN T, et al. PFNA and DHS for AO/OTA 31-A2 fractures: radiographic measurements, morbidity and mortality. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2019 Oct 31. doi: 10.1007/s00068-019-01251-w. [48] WIRTZ C, ABBASSI F, EVANGELOPOULOS DS, et al. High failure rate of trochanteric fracture osteosynthesis with proximal femoral locking compression plate. Injury. 2013;44(6):751-756. [49] 张施展, 张卫国, 徐钧, 等. 结构性植骨联合锁定钢板治疗股骨距粉碎性股骨转子间骨折的临床研究[J]. 重庆医学,2017,46(14):1919-1921. [50] 房冰,李晓波,王硕磊.不同固定方式修复老年股骨转子间骨折的临床对比研究[J].实用老年医学 2017,31(6):551-554. [51] 张斌,常军,杨志刚,等. 内侧壁缺损面积对股骨转子间骨折经皮加压钢板固定术后断端稳定性影响的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(1):61-65. [52] LONG H, LIN Z, LU B, et al. Percutaneous compression plate versus dynamic hip screw for treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures: A overview of systematic reviews and update meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 2016;33 Pt A:1-7. [53] 白浪, 侯毅龙, 张晟, 等. 三种内固定方式治疗内侧壁缺损的不稳定型股骨转子间骨折的疗效比较[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018, 20(5):412-418. [54] SANDERS D, BRYANT D, TIESZER C, et al. A Multicenter Randomized Control Trial Comparing a Novel Intramedullary Device (InterTAN) Versus Conventional Treatment (Sliding Hip Screw) of Geriatric Hip Fractures. J Orthop Trauma.2017;31(1):1-8. [55] 史彦海. 伴内侧壁和外侧壁缺损老年股骨粗隆间骨折PFNA治疗的临床疗效对比分析[J]. 苏州:苏州大学, 2018. [56] WANG W, ZHAI S, HAN XP, et al. [Comparative study of proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and dynamic hip screw in the unstable intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;98(5):357-361. [57] KIM GM, NAM KW, SEO KB, et al. Wiring technique for lesser trochanter fixation in proximal IM nailing of unstable intertrochanteric fractures: A modified candy-package wiring technique. Injury. 2017; 48(2):406-413. [58] 彭硕, 周铁军. 一种治疗股骨转子间骨折合并后内侧壁骨折的新方法[J].实用骨科杂志, 2018,24(12):1132-1135. [59] 石少辉, 李茂廷, 李海啸, 等. U-Blade钉通道下植骨在股骨转子间内侧壁骨折Gamma 3型髓内钉内固定中的应用效果[J]. 广西医学,2018,40(9):1021-1024. [60] 徐锴, 李开南. 股骨近端内侧支撑固定的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(1):72-78. [61] 卫禛, 陈时益, 张世民. 股骨转子间骨折治疗中前内侧皮质正性支撑复位的研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(10): 1216-1222. [62] MACHERAS GA, KOUTSOSTATHIS SD, GALANAKOS S, et al. Does PFNA II avoid lateral cortex impingement for unstable peritrochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(11):3067-3076. [63] LIU X, LIU Y, PAN S,et al.Does integrity of the lesser trochanter influence the surgical outcome of intertrochanteric fracture in elderly patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2015;16:47. [64] 王炜,周鹏鹤,郦志文,等.股骨小转子在转子间骨折内固定术中作用的有限元研究[J].现代实用医学, 2013,25(1):14-17+121. [65] DURAMAZ A, İLTER MH. The impact of proximal femoral nail type on clinical and radiological outcomes in the treatment of intertrochanteric femur fractures: a comparative study.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(7):1441-1449. [66] KULACHOTE N, SA-NGASOONGSONG P, SIRISREETREERUX N, et al. Predicting Factors for Return to Prefracture Ambulatory Level in High Surgical Risk Elderly Patients Sustained Intertrochanteric Fracture and Treated With Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) With and Without Cement Augmentation. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2020;11:2151459320912121. [67] KAYNAK G, ÜNLÜ MC, GÜVEN MF, et al. Intramedullary nail with integrated cephalocervical screws in the intertrochanteric fractures treatment: Position of screws in fracture stability. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2018;24(3):268-273. [68] ZHANG H, ZHU X, PEI G, et al. A retrospective analysis of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients with osteoporosis: a minimum follow-up of 3 years. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):147. [69] 于晨, 江龙海, 蔡大卫, 等. PFNA与InterTAN髓内钉治疗老年股骨转子间骨折疗效的Meta分析[J]. 中国骨伤,2019,32(2):120-129. [70] ZHANG C, XU B, LIANG G, et al. Optimizing stability in AO/OTA 31-A2 intertrochanteric fracture fixation in older patients with osteoporosis. J Int Med Res. 2018;46(5):1767-1778. [71] GAVASKAR AS, TUMMALA NC, SRINIVASAN P, et al. Helical Blade or the Integrated Lag Screws: A Matched Pair Analysis of 100 Patients With Unstable Trochanteric Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(6): 274-277. [72] 林荣侯, 刘勇, 隋丽娟, 等. InterTAN、PFNA、DHS治疗不稳定性股骨粗隆间骨折的比较[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(6):507-511. [73] WU D, REN G, PENG C, et al. InterTan nail versus Gamma3 nail for intramedullary nailing of unstable trochanteric fractures. Diagn Pathol 2014;9:191. [74] 朱贵伟,吕欣,刘晋元,等.两种髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2017,34(8):1425. [75] 陶正刚, 韦盛旺, 赵友明, 等. 三种不同内固定方式治疗股骨转子间不稳定型骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(2): 108-112. [76] 李坛珠, 张保焜, 莫小联, 等. 极高龄不稳定股骨粗隆间骨折的髓内和髓外固定疗效比较[J].中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2017, 3(1):17-21. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [4] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [5] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [6] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [7] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [9] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [10] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [11] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [12] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [13] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [14] | Yang Weiqiang, Ding Tong, Yang Weike, Jiang Zhengang. Combined variable stress plate internal fixation affects changes of bone histiocyte function and bone mineral density at the fractured end of goat femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 890-894. |
| [15] | Zhang Lei, Ma Li, Fu Shijie, Zhou Xin, Yu Lin, Guo Xiaoguang. Arthroscopic treatment of greater tuberosity avulsion fractures with anterior shoulder dislocation using the double-row suture anchor technique [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 895-900. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||