Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (17): 2755-2760.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3110
Previous Articles Next Articles
MicroRNAs for assessing the motion control of human skeletal muscles
Zhang Shuang1, Tan Rui2, Wang Chunxiao3, Wu Fengyu3, Guo Hongyu4
- 1Institute of Sports Science, 2Winter Olympic College, 3College of Sports and Human Sciences, 4College of Sports Training, Harbin Sport University, Harbin 150008, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2020-04-11Revised:2020-04-17Accepted:2020-06-05Online:2021-06-18Published:2021-01-08 -
About author:Zhang Shuang, PhD candidate, assistant experimentalist, Institute of Sports Science, Harbin Sport University, Harbin 150008, Heilongjiang Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Shuang, Tan Rui, Wang Chunxiao, Wu Fengyu, Guo Hongyu. MicroRNAs for assessing the motion control of human skeletal muscles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2755-2760.
share this article
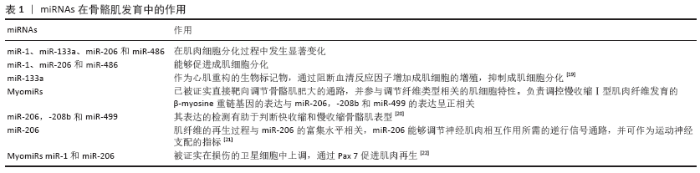
2.1 miRNAs与骨骼肌运动调控 骨骼肌发育是一个复杂的过程,由多个因素调控。miRNAs参与了迄今为止所研究的骨骼肌的大部分生物学过程,在调节肌肉生成、肌肉质量、肌肉类型、再生和组织代谢中具有重要作用。 2.1.1 肌肉特异miRNAs MyomiRs为一类肌肉特异性miRNAs, 是骨骼肌发育的重要组成部分,对于骨骼肌增殖、分化和再生具有重要作用,并在横纹肌中高水平表达。2007年首次证实miR-1为横纹肌组织特异表达miRNA[15],2年后,SEMPERE等描述了30种在特定组织中富集的miRNAs并命名为肌肉特异性miRNAs。骨骼肌miRNAs以9种不同的肌团组成,即miR-1、miR-133a、miR-133b、miR-206、miR-208a、miR-208b、miR-378、miR-486和miR-499[16]。MyomiR-378参与骨骼肌发育,在成肌细胞分化过程中靶向肌源性抑制因子MyoR[17]。MyomiR-486通过抑制肌萎缩叉头盒子(forkhead box O1,FOXO1)的转录因子中间产物来促进肌生成。肌肉特异性miR-1、miR-133和miR-206是迄今为止研究最多和最具特征的肌团[18],在骨骼肌的正确发育和功能维持中发挥重要作用,并对多种病理状态下的分子机制有着深远的影响[17]。 2.1.2 MyomiRs与肌肉再生 人胚胎骨骼肌生成包含以下主要过程:肌前体细胞的增殖及分化;成肌细胞向肌管的分化及融合;肌管向肌纤维分化,多种基因参与骨骼肌发育的调控。一项动物实验发现,胚胎小鼠骨骼肌DICER敲除能够导致骨骼肌发育不全、肌纤维数量减少及生肌细胞凋亡和成肌细胞死亡等有害表型,进而证实miRNAs在骨骼肌发育中的作用(表1)。 2.1.3 MyomiRs与肌肉退化 研究发现,肌肉功能紊乱常伴随MyomiRs降解现象。一项临床研究指出,miR-1、miR-133和miR-206能够作为Duchenne和Becker’s肌营养不良症患者生物学判定标志物[23]。miR-206表达水平的上调与肌萎缩性脊髓侧索硬化症的进展一致,呈正相关性[24]。与健康患者相比,横纹肌肉瘤肿瘤患者组织中miR-1、miR-133a、 miR-133b和miR-206的表达下调[25]。miR -1水平下调与慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者的肌肉功能恶化相关[26]。在一项健康年轻男性的研究中发现,卧床休息7 d导致miR-1和miR-133a 下调[27]。 2.2 miRNAs与心脏功能调控 miRNAs在生理及病理条件下对心脏功能维持具有重要作用。研究发现基因敲除DICER能够导致自发性心脏重构且多种miRNAs参与该生物过程,该研究证实miRNAs在心脏器官生成及功能中具有重要的调控作用[28]。 2.2.1 心脏特异miRNAs 研究发现miR-1、miR133a、miR-208a/b及miR-499在心脏中高度富集,为心脏特异miRNAs。这些miRNAs参与成年成纤维细胞、肌成纤维细胞基质前体的分化、向成熟心肌细胞的转分化、重编程,以及心肌细胞的功能和存活[28]。心脏特异miRNAs活性和功能的严格调控对于维持心脏正常收缩和传导具有重要意义。病理条件下,心脏特异性miRNAs的降解能够导致心房纤颤、缺氧、缺血、纤维化等。 2.2.2 miRNAs与心肌肥厚 心肌肥厚是一种心脏重构的形式,具有心肌细胞增大,心脏体积增大,心室增大的特征[29]。生理性心肌肥厚若得不到及时治疗会诱发病理性心肌肥厚,进而形成高血压、肥胖、糖尿病等疾病。研究发现,miRNAs能够通过靶向前肥大信号通路,如钙信号通路和细胞周期相关通路,进而正向或负向调控心肌肥厚。 miR-1是肌肉特异性miRNA,在心脏中大量表达,通过靶向钙信号通路、细胞周期蛋白D激酶6-视网膜母细胞瘤通路及甲状腺激素水平促肥厚通路保护心肌肥厚[30-32]。 miR-133a也是一种肌肉特异miRNA,通过靶向钙通路、细胞生长及发育通路发挥抗肥厚作用。miR-133a还可以通过抑制血清响应因子和细胞周期素D2的表达来缓解心肌肥厚[33-34]。miR-10a通过下调心肌发育相关转录因子T-box5抑制心肌肥厚[35]。 miR-155、miR-22、miR-217、miR-29及miR-200c是一种促进心肌肥厚的调控因子。miR-155通过靶向促肥厚通路如炎症和钙信号促进心肌肥厚[36]。miR-22在心肌肥厚及肌细胞分化中表达上调,通过靶向钙调磷酸酶通路促进心肌肥厚[37]。miR-217通过调节蛋白甲基化促进心肌肥厚,研究发现过表达miR-217促进心肌肥厚,抑制miR-217水平能够逆转心肌肥厚[38-39]。miR-29通过抑制核受体过氧化物酶体增殖活化受体δ发挥促心肌肥厚作用,且与心肌纤维化正相关[40-41]。miR-200c通过MAPK、过氧化/凋亡通路及直接靶向肌球蛋白轻链激酶(myosin light chain kinase,MLCK)发挥促心肌肥厚作用[42]。 2.2.3 miRNAs与心肌细胞损伤 心肌细胞损伤或丢失发生于多种心血管疾病中。大量研究指出miRNAs通过调控凋亡、自噬和炎症反应而成为心肌细胞损伤的主要调控因子。 miR-145通过阻断线粒体凋亡起始因子Bnip3的表达诱导线粒体凋亡通路,抑制氧化应激导致的心肌细胞死亡[43]。miR-494通过激活AKT-线粒体信号通路和抗凋亡蛋白表达保护心肌细胞死亡[44]。miR-499通过抑制钙调神经磷酸酶介导的动力相关蛋白1去磷酸化和减少线粒体分裂来抑制细胞死亡[45]。miR-30家族通过β-肾上腺素通路调控心肌细胞凋亡[46]。 自噬是一个进化保守和高度可调的细胞循环,能够清除受损的细胞器及受损的细胞。多种miRNAs能够通过调控自噬过程而影响自噬反应。miR-17家族成员如miR-106b和miR-20a能够抑制自噬反应[47],miR-375、miR-20a、 miR-137、miR-96、miR-188-3p及 miR-199a-5p能够通过直接靶向自噬蛋白Atg7抑制自噬反应[48-52]。 miRNAs在调控炎症反应中具有重要作用。miR-155通过控制SOCS1和Akt1轴调节巨噬细胞的极化[53],通过上调SHIP1-Akt信号级联来促进巨噬细胞的存活[54],通过直接靶向促炎核因子κB信号转录因子抑制巨噬细胞活性[55]。 miR-125a及miR-125b通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白3表达抑制炎症反应[56]。miR-145-5p可抑制CD40介导的炎症反应和急性缺氧引起的心肌细胞死亡。 2.3 miRNAs与身体活动调控 运动训练对大多数器官系统都有积极的影响,包括心血管系统、呼吸系统、神经内分泌系统,特别是肌肉骨骼系统。身体活动是产生细胞内外信号的有力刺激,这些压力信号来自于生理过程,作用于积极的代谢和结构适应,如最佳肌纤维效率和神经肌肉补充,维持内环境平衡,线粒体生物发生,肌肉生长和再生[57]。研究指出,运动能够调节骨骼肌、心血管和免疫系统的miRNAs表达;同时,miRNAs的表达情况与运动类型相关。 2.3.1 耐力训练 耐力运动通过大肌肉群及心血管系统,促进对氧气的利用及改善身体状态。最大强度的重复长时间运动可引起骨骼肌的表型改变,如快速-慢纤维型转换、线粒体生物生成增强和血管生成增加。过氧化物酶体增殖激活受体γ家族在骨骼肌对耐力运动的适应中占据重要作用,涉及脂肪酸氧化、糖酵解和糖异生等代谢过程。miR-696和miR-23水平下调,可增加phosphatidylglycerol phospholipase α (PGC1 -α)蛋白表达[58]。研究发现急性运动可导致miR-1、miR-181和miR-107的过表达[59]。小鼠研究中,急性游泳训练下调miR-494及miR-16的表达水平,miR-494能够参与调控线粒体生物发生表达水平,而miR-16是血管内皮生长因子的有效靶点,可增加毛细血管密度。 HECKSTEDEN等[60]对信号级联的研究发现,长期进行力量和耐力运动人体表达异常的miRNAs对几个基因具有高度的调节作用,其中最重要的是miRNAs对血管内皮生长因子的调节。运动训练能够增加骨骼肌毛细血管密度,并通过增加扩散面积和缩短扩散距离来促进运动时的供氧。耐力和力量训练中均存在血管生成现象,血管内皮生长因子是一种关键的运动训练刺激下促血管生成的毛细血管生长调控子。由于训练状态的改变,miRNAs水平表达发生了变化,从而为训练适应提供了内源性调控。 有氧能力是耐力训练状态的标志。力量和力量表现型是耐力训练的个体的特征标志。最大摄氧量(VO2max)是心血管健康的指标,是健康和病理受试者心血管死亡的预测因子[61]。实际上,有氧适能水平较低的受试者的miR-210、miR-21和miR-222的循环水平明显较高[61],研究表明miRNAs在调节与氧传递相关的生物过程中起主要作用。 ELIA等[62]研究发现miR-29a-3p和miR193a-5p这2种miRNAs标志了2种不同类型的运动,即力竭运动和非力竭耐力运动,根据其表达情况可用于区分运动类型;同时也可用作损伤肌肉修复和恢复生物标志物,可进一步检测严重肢体缺血患者损伤肌肉恢复情况。上述生物标记可以帮助教练员改善训练和恢复计划,从而优化运动竞争力。 2.3.2 阻力运动 与耐力运动相比,阻力运动会改变肌肉质量,而对新陈代谢没有显著影响。事实上,阻力运动可以调节多种miRNAs的表达,如与肌肉肥大刺激相关的miR-1、miR-133和miR-206[11]。胰岛素生长因子1是miR-1的有效靶点之一,急性阻力运动降低骨骼肌的miR-1,增加IGF-1/AKT信号通路与蛋白合成[62]。miR-206相对于足底肌在比目鱼肌中高度表达,与Ⅰ型纤维密切相关[11];miR-206参与骨骼肌肥大的调节;miR-206抑制肌肉生长抑素mRNA的翻译,导致高肌肉生长抑素血清丢失,增加骨骼肌质量。虽然已开展若干耐力运动训练的研究,但阻力运动的相关研究却较少。因而,有必要对阻力运动进行深入研究,以探索体育锻炼与miRNAs调控的相关性。 2.4 循环miRNAs与运动调控 2.4.1 循环miRNAs 大部分miRNAs存在于细胞内,但也有研究证实miRNAs能够通过血液及其他体液进入循环系统。目前尚不明确miRNAs通过主动分泌进入循环进而发挥内分泌功能还是细胞损伤后的被动排泄。已有研究发现循环miRNAs(circulating miRNAs,c-miRNAs)与激素及细胞因子类似,通过调控靶细胞基因表达而发挥作用[63]。大部分循环miRNAs通过脂囊泡如外泌体[64]、微粒和凋亡小体或与RNA结合的蛋白如Argonaute -2或高密度脂蛋白的结合而稳定存在与血液中[65-67]。 当前体液miRNAs主要通过miRNA微阵列、荧光定量PCR及下一代测序等手段进行检测。血浆和血清具有取材简便、易获取等特点而成为最具前景和广泛研究的循环miRNAs来源。由于提取、定量、检测技术的相对简便性,循环miRNAs已成为可靠的非侵入性候选生物标志物[68]。 2.4.2 循环miRNAs与运动关系 循环miRNAs作为人类病例诊断及预后的标志物,被证明能够对运动刺激产生反应而成为运动潜能及训练适应的潜在生物标志物。身体活动及运动训练能够引起心血管系统、细胞代谢、炎症反应、肌肉重塑等多种生理变化,循环miRNAs能够反映生理应激,进而为理解身体活动的分子机制提供临床信息[69],了解身体活动及运动相关的生理过程对于运动能力判定及运动训练计划制定至关重要。 BAGGISH等[12]在2011年首次开展了有氧运动与循环miRNAs表达谱相关性的研究,研究发现有氧运动主要影响血管生成(miR-222,-20a)、炎症和缺氧(miR-21,-146a)、骨骼肌及心肌收缩相关循环miRNAs,进一步分析发现miR-146与有氧运动能力参数VO2max呈正相关。一项纵向队列有氧健身的研究对踏车运动前后血清中720 miRNAs进行了分析后发现[61],miR-210,miR-21及miR-222能够用于判断低及高VO2max反应者,且miR-210能够作为有氧能力的生物学标志物。AOI等[70]发现循环miR-486在急性及慢性有氧运动后表达水平下调,循环miR-486与VO2max呈负相关,由于miR-486可调节骨骼肌对葡萄糖的摄取,作者认为miR-486可能在运动诱导的代谢适应中发挥作用。 一项针对老年人的为期5个月阻力训练实验发现[71],血浆和肌肉的miR-499被认为是阻力训练后膝关节伸肌力量增加的最敏感的标志物。Wardle等[72]对从事精英运动的男性分别进行力量及阻力训练后发现,循环miR-21、循环miR-221、循环miR-222及循环miR-146a与训练的性能参数相关,且相较于力量训练,上述循环miRNAs对于阻力训练更敏感。 有学者对马拉松训练与循环miRNAs表达谱的相关性进行了研究。BYE等[61]的研究表明,马拉松跑后,循环 miR-1、 -133a、-206、-208b和-499的水平升高。Baggish等[73]报道了马拉松比赛之后心肌组织中循环miRNAs的增加(miRNAs-1,-133a,-499,-208a)、炎症(miR-146a)和内皮细胞(miR-126)的增加。由于全程马拉松和半程马拉松比赛是剧烈运动,而循环中的miR-133a可能是肌肉损伤的一个指标,因此有人提出,肌粒水平升高可能部分反映了运动对肌肉细胞的影响。 运动可以引起循环miRNAs的变化,循环miRNAs作为运动训练的潜在生物标志物,为运动适应的分子调控提供重要的信息,了解它们在控制生理运动适应中的机制作用对于运动方案的调整及优秀运动员选材具有重要意义。 "
| [1] NGUYEN HM, NGUYEN TD, NGUYEN TL, et al. Orientation of Human Microprocessor on Primary MicroRNAs. Biochemistry. 2018;58(4):189-198. [2] REINHART BJ, SLACK FJ, BASSON M, et al. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2000;403(6772):901-906. [3] GILLES ME, SLACK FJ. Let-7 microRNA as a potential therapeutic target with implications for immunotherapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018; 22(11):929-939. [4] YAO J, CHENG Y, ZHANG D, et al. Identification of key genes, MicroRNAs and potentially regulated pathways in alcoholic hepatitis by integrative analysis. Gene. 2019;720:144035. [5] POLAKOVICOVA M, MUSIL P, LACZO E, et al. Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Exercise Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;7(10): 1553. [6] CAMERA DM, SMILES WJ, HAWLEY JA. Exercise-induced skeletal muscle signaling pathways and human athletic performance. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;98:131-143. [7] GARAVELLI S, DE ROSA V, DE CANDIA P. The multifaceted interface between cytokines and microRNAs: An ancient mechanism to regulate the good and the bad of inflammation. Front Immunol. 2018;9:3012. [8] GEIGER J, DALGAARD LT. Interplay of mitochondrial metabolism and microRNAs.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017;74(4):631-646. [9] RODRIGUES J A, PRíMOLA-GOMES T N, SOARES L L, et al. Physical exercise and regulation of intracellular calcium in cardiomyocytes of hypertensive rats. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018;111(2):172-179. [10] YANG F, YOU X, XU T, et al.Screening and function analysis of MicroRNAs involved in exercise preconditioning-attenuating pathological cardiac hypertrophy . Int Heart J. 2018;59(5):1069-1076. [11] MCCARTHY JJ, ESSER KA. MicroRNA-1 and microRNA-133a expression are decreased during skeletal muscle hypertrophy.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;102(1):306-313. [12] BAGGISH AL, HALE A, WEINER RB, et al.Dynamic regulation of circulating microRNA during acute exhaustive exercise and sustained aerobic exercise training. J Physiol. 2011;589(16):3983-3994. [13] HORAK M,NOVAK J, BIENERTOVA-VASKU J. Muscle-specific microRNAs in skeletal muscle development. Dev Biol. 2016;410(1):1-13. [14] BEI Y, TAO L, CRETOIU D, et al. MicroRNAs Mediate Beneficial Effects of Exercise in Heart. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1000:261-280. [15] FAULKNER JA, LARKIN LM, CLAFLIN DR, et al. Age‐related changes in the structure and function of skeletal muscles. Biogerontology. 2018;19(6):519-536. [16] AOI W. Frontier impact of microRNAs in skeletal muscle research: a future perspective. Front Physiol. 2015;5:495. [17] HOU X, TANG Z, LIU H, et al. Discovery of MicroRNAs associated with myogenesis by deep sequencing of serial developmental skeletal muscles in pigs. PloS one. 2012;7(12):e52123. [18] 马翔,唐成林,吴梦佳,等. microRNA调节肌肉萎缩作用机制的研究进展[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,25(4):68-72. [19] RUBIŚ P, TOTOŃ‐ŻURAŃSKA J, WIŚNIOWSKA‐ŚMIAŁEK S, et al. The relationship between myocardial fibrosis and myocardial micro RNA s in dilated cardiomyopathy: A link between mir‐133a and cardiovascular events. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(4):2514-2517. [20] ENDO K, WENG H, NAITO Y, et al. Classification of various muscular tissues using miRNA profiling. Biomed Res. 2013;34(6):289-299. [21] YUASA K, HAGIWARA Y, ANDO M, et al. MicroRNA-206 is highly expressed in newly formed muscle fibers: implications regarding potential for muscle regeneration and maturation in muscular dystrophy. Cell Struct Funct. 2008;33(2):163-169. [22] CHEN J F, TAO Y, LI J, et al. microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 regulate skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by repressing Pax7. J Cell Biol. 2010;190(5):867-879. [23] CACCHIARELLI D, LEGNINI I, MARTONE J, et al. miRNAs as serum biomarkers for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. EMBO Mol Med. 2011; 3(5):258-265. [24] RUSSELL AP, WADA S, VERGANI L, et al. Disruption of skeletal muscle mitochondrial network genes and miRNAs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;49:107-117. [25] MISSIAGLIA E, SHEPHERD CJ, PATEL S, et al. MicroRNA-206 expression levels correlate with clinical behaviour of rhabdomyosarcomas. Br J Cancer. 2010;102(12):1769-1777. [26] DONALDSON A, NATANEK SA, LEWIS A, et al. Increased skeletal muscle-specific microRNA in the blood of patients with COPD. Thorax. 2013; 68(12):1140-1149. [27] RINGHOLM S, BIENSO RS, KIILERICH K, et al. Bed rest reduces metabolic protein content and abolishes exercise-induced mRNA responses in human skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;301(4): E649-658. [28] CHISTIAKOV DA, OREKHOV AN, BOBRYSHEV YV. Cardiac-specific miRNA in cardiogenesis, heart function, and cardiac pathology (with focus on myocardial infarction) . J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;94:107-121. [29] NAKAMURA M, SADOSHIMA J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(7):387-407. [30] DEWENTER M, VON DER LIETH A, KATUS HA, et al. Calcium Signaling and Transcriptional Regulation in Cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 2017; 121(8):1000-1020. [31] ZAGLIA T, CERIOTTI P, CAMPO A, et al. Content of mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) in cardiomyocytes is regulated by microRNA-1 in physiologic and pathologic hypertrophy . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(43):E9006-E9015. [32] DINIZ GP, LINO CA, MORENO CR, et al. MicroRNA-1 overexpression blunts cardiomyocyte hypertrophy elicited by thyroid hormone. J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(12):3360-3368. [33] LEE S Y, LEE C Y, HAM O, et al. microRNA-133a attenuates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy by targeting PKCdelta and Gq. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018; 439(1-2):105-115. [34] DINIZ GP, LINO CA, GUEDES EC, et al. Cardiac microRNA-133 is down-regulated in thyroid hormone-mediated cardiac hypertrophy partially via Type 1 Angiotensin II receptor. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015;110(5):49. [35] WANG D, ZHAI G, JI Y, et al. microRNA-10a Targets T-box 5 to Inhibit the Development of Cardiac Hypertrophy. Int Heart J. 2017;58(1):100-106. [36] YANG Y, ZHOU Y, CAO Z, et al. miR-155 functions downstream of angiotensin II receptor subtype 1 and calcineurin to regulate cardiac hypertrophy. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(3):1556-1562. [37] MATSUSHIMA S, SADOSHIMA J. The role of sirtuins in cardiac disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015;309(9):H1375-1389. [38] NIE X, FAN J, LI H, et al. miR-217 Promotes Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dysfunction by Targeting PTEN. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018;12:254-266. [39] THIENPONT B, ARONSEN JM, ROBINSON EL, et al. The H3K9 dimethyltransferases EHMT1/2 protect against pathological cardiac hypertrophy. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(1):335-348. [40] SASSI Y, AVRAMOPOULOS P, RAMANUJAM D, et al. Cardiac myocyte miR-29 promotes pathological remodeling of the heart by activating Wnt signaling. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1614. [41] ZHANG S, YIN Z, DAI F F, et al. miR-29a attenuates cardiac hypertrophy through inhibition of PPARdelta expression. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8): 13252-13262. [42] BUENO OF, DE WINDT LJ, LIM HW, et al. The dual-specificity phosphatase MKP-1 limits the cardiac hypertrophic response in vitro and in vivo. Circ Res. 2001;88(1):88-96. [43] LI R, YAN G, LI Q, et al. MicroRNA-145 protects cardiomyocytes against hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2))-induced apoptosis through targeting the mitochondria apoptotic pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44907. [44] WANG X, ZHANG X, REN X P, et al. MicroRNA-494 targeting both proapoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury . Circulation. 2010;122(13):1308-1318. [45] ZHAO YC. Effects of exercise training on myocardial mitochondrial miR-499-CaN-Drp-1 apoptotic pathway in mice. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015;31(3):259-263. [46] ROCA-ALONSO L, CASTELLANO L, MILLS A, et al. Myocardial MiR-30 downregulation triggered by doxorubicin drives alterations in beta-adrenergic signaling and enhances apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6: e1754. [47] WU H, WANG F, HU S, et al. MiR-20a and miR-106b negatively regulate autophagy induced by leucine deprivation via suppression of ULK1 expression in C2C12 myoblasts. Cell Signal. 2012;24(11):2179-2186. [48] CHANG Y, YAN W, HE X, et al. miR-375 inhibits autophagy and reduces viability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells under hypoxic conditions. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(1):177-87e8. [49] ZHAO S, YAO D, CHEN J, et al. MiR-20a promotes cervical cancer proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2015;10(3): e0120905. [50] ZENG Y, HUO G, MO Y, et al. MIR137 Regulates Starvation-Induced Autophagy by Targeting ATG7. J Mol Neurosci. 2015;56(4): 815-821. [51] WANG K, LIU CY, ZHOU LY, et al. APF lncRNA regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting miR-188-3p. Nat Commun. 2015;6: 6779. [52] XU N, ZHANG J, SHEN C, et al. Cisplatin-induced downregulation of miR-199a-5p increases drug resistance by activating autophagy in HCC cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;423(4):826-831. [53] XU F, KANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Akt1-mediated regulation of macrophage polarization in a murine model of Staphylococcus aureus pulmonary infection. J Infect Dis. 2013;208(3):528-538. [54] ROTHCHILD AC, SISSONS JR, SHAFIANI S, et al. MiR-155-regulated molecular network orchestrates cell fate in the innate and adaptive immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(41):E6172-E6181. [55] WU XQ, DAI Y, YANG Y, et al. Emerging role of microRNAs in regulating macrophage activation and polarization in immune response and inflammation. Immunology. 2016;148(3):237-248. [56] KIM SW, RAMASAMY K, BOUAMAR H, et al. MicroRNAs miR-125a and miR-125b constitutively activate the NF-kappaB pathway by targeting the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20) . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(20):7865-7870. [57] LIU X, XIAO J, ZHU H, et al. miR-222 is necessary for exercise-induced cardiac growth and protects against pathological cardiac remodeling. Cell metabolism. 2015;21(4):584-595. [58] AOI W, NAITO Y, MIZUSHIMA K, et al.The microRNA miR-696 regulates PGC-1α in mouse skeletal muscle in response to physical activity.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;298(4):E799-806. [59] SHARMA M, JUVVUNA P K, KUKRETI H, et al. Mega roles of microRNAs in regulation of skeletal muscle health and disease. Front Physiol. 2014;5:239. [60] HECKSTEDEN A, LEIDINGER P, BACKES C, et al. miRNAs and sports: tracking training status and potentially confounding diagnoses. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):219. [61] BYE A, ROSJO H, ASPENES S T, et al. Circulating microRNAs and aerobic fitness--the HUNT-Study. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57496. [62] ELIA L, CONTU R, QUINTAVALLE M, et al. Reciprocal regulation of microRNA-1 and insulin-like growth factor-1 signal transduction cascade in cardiac and skeletal muscle in physiological and pathological conditions. Circulation. 2009;120(23):2377-2385. [63] IGAZ I, IGAZ P. Possible role for microRNAs as inter-species mediators of epigenetic information in disease pathogenesis: is the non-coding dark matter of the genome responsible for epigenetic interindividual or interspecies communication?. Med Hypotheses. 2015;84(2):150-154. [64] VALADI H, EKSTROM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [65] RAYNER KJ, HENNESSY EJ. Extracellular communication via microRNA: lipid particles have a new message. J Lipid Res. 2013;54(5):1174-1181. [66] LI L, ZHU D, HUANG L, et al. Argonaute 2 complexes selectively protect the circulating microRNAs in cell-secreted microvesicles. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46957. [67] VICKERS KC, PALMISANO BT, SHOUCRI BM, et al. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13(4):423-433. [68] KELLER A, MEESE E. Can circulating miRNAs live up to the promise of being minimal invasive biomarkers in clinical settings?. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2016;7(2):148-156. [69] DE GONZALO-CALVO D, DáVALOS A, FERNáNDEZ-SANJURJO M, et al. Circulating microRNAs as emerging cardiac biomarkers responsive to acute exercise. Int J Cardiol. 2018;264:130-136. [70] AOI W, ICHIKAWA H, MUNE K, et al. Muscle-enriched microRNA miR-486 decreases in circulation in response to exercise in young men. Front Physiol. 2013;4:80. [71] ZHANG T, BIRBRAIR A, WANG ZM, et al. Improved knee extensor strength with resistance training associates with muscle specific miRNAs in older adults. Exp Gerontol. 2015;62:7-13. [72] WARDLE SL, BAILEY ME, KILIKEVICIUS A, et al. Plasma microRNA levels differ between endurance and strength athletes. PLoS One. 2015; 10(4):e0122107. [73] BAGGISH AL, PARK J, MIN PK, et al. Rapid upregulation and clearance of distinct circulating microRNAs after prolonged aerobic exercise. Appl Physiol (1985). 2014;116(5):522-531. |
| [1] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [2] | Luo Lin, Song Naiqing, Huang Jin, Zou Xiaodong. Review and prospect of international research on preschool children’s movement development assessment: a CiteSpace-based visual analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1270-1276. |
| [3] | Shu Wenbo, Chen Mengchi, Li Hua, Huang Liqian, Huang Binbin, Zhang Wenhai, Wu Yachen, Wang Zefeng, Li Qiaoli, Liu Peng. Correlation between body fat distribution and characteristics of daily physical activity in college students [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1277-1283. |
| [4] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [5] | Song Liming, Su Hailong. Muscle force response characteristics of the slipping leg after an unexpected slip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1184-1189. |
| [6] | Wang Mengting, Gu Yanping, Ren Wenbo, Qin Qian, Bai Bingyi, Liao Yuanpeng. Research hotspots of blood flow restriction training for dyskinesia based on visualization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1264-1269. |
| [7] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [8] | Yu Langbo, Qing Mingsong, Zhao Chuntao, Peng Jiachen. Hot issues in clinical application of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in orthopedics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 449-455. |
| [9] | Jiang Xiaoyan, Zhu Haifei, Lin Haiqi, Lin Wentao. Cold therapy promotes self-limited recovery of delayed-onset muscle soreness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3609-3613. |
| [10] | Bai Shengchao, Gao Yang, Wang Bo, Li Junping, Wang Ruiyuan. Dynamic changes of mitochondrial function of the skeletal muscle after acupuncture intervention in rats with heavy load exercise-induced injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3648-3653. |
| [11] | Wang Zhen, Lin Haiqi, He Fei, Lin Wentao. Exercise activates skeletal muscle satellite cells: exercise prevention and treatment for age-related sarcopenia and muscle injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3752-3759. |
| [12] | Xiong Xiaolong, Wang Guangji, Fang Yehan, Du Xiufan, Hang Hui, Ye Zhifang. Meta-analysis of comparison of the effect of tibial fixation using absorbable screws and metal screws in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autologous hamstrings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3438-3444. |
| [13] | Yang Xinhua, Yan Yindi, Luo Xuguang, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei. Bmal1 and Clock regulate the development and differentiation of skeletal muscle [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3130-3137. |
| [14] | Bao Sairong, Lin Lihua, Shan Sharui, Yang Xingping, Liu Chunlong. Effect of electrical deep muscle stimulate on muscle tone, elasticity, and stiffness of biceps brachii in stroke patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3138-3143. |
| [15] | Lin Haishan, Mieralimu Muertizha, Li Peng, Ma Chao, Wang Li. Correlation between skeletal muscle fiber characteristics and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with hip fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3144-3149. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||