Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (27): 4414-4419.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1395
Previous Articles Next Articles
Classification and research prospect of in vitro and in vivo models of psoriasis
Xu Yongyue1, Chen Haiming1, Deng Jingwen1, Wang Maojie1, 2, Yan Yuhong1, Huang Runyue1, 3, Lu Chuanjian1, 3
- (1the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 2Utrecht University Medical Center, Utrecht, Holland; 3Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Clinical Research, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China)
-
Received:2019-03-29Online:2019-09-28Published:2019-09-28 -
Contact:Lu Chuanjian, MD, Professor, Chief physician, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome Clinical Research, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510006, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Xu Yongyue, Master, Researcher, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No.81873302 (to LCJ); the Project of Guangdong Province Traditional Chinese Medical Hospital (Key Laboratory Project), No. YN2018ZD01 (to LCJ) and YN2019QJ09 (to XYY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Yongyue1, Chen Haiming1, Deng Jingwen1, Wang Maojie1, 2, Yan Yuhong1, Huang Runyue1, 3, Lu Chuanjian1, 3. Classification and research prospect of in vitro and in vivo models of psoriasis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(27): 4414-4419.
share this article

2.1 动物模型 由于自然界动物几乎不会自发出现类似银屑病皮损的临床表现,因此需要模拟其发病特点。目前,研究者或使用基因工程、或筛选基因突变鼠、或给予外源刺激等手段去构建银屑病小鼠,以期一定程度上符合其病理特征。 2.1.1 基因工程小鼠模型 基因工程小鼠是研究特定基因对疾病发病机制的重要模式生物,利用基因工程技术(如条件基因打靶、基因捕获、RNA干扰等),可实现目的基因的转入、敲除/沉默。以银屑病转基因鼠为例,通常选择在K5或K14启动子插入目的基因全片段cDNA,然后将其显微注射进小鼠胚胎原核中,待后代繁殖发育后,行聚合酶链式反应(PCR)检测去筛选、鉴定基因型。 (1)白细胞介素1α转基因小鼠模型:通过对模型鼠(TgIL1.1)的研究证实,高表达白细胞介素1α基因使小鼠皮肤出现银屑病样改变,其中红斑、鳞屑多集中在胸部,病理特征包括非皮损处真皮单核/巨噬细胞浸润,皮损处混合淋巴细胞浸润。但伴随消瘦体质,11个月大的小鼠逐渐秃顶、体质量损失、皮肤变皱[5]。另一种IL1rn-/-小鼠模型由于白细胞介素1α受体拮抗剂缺乏,有约60%的小鼠耳郭皮肤出现类银屑病炎症[6]。除了皮肤炎症,该模型还会出现动脉炎症和关节炎,肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素36α在白细胞介素1α转基因鼠模型中发挥关键作用[7-8]。 (2)PL/J/CD18缺陷小鼠模型:该模型CD18(即β2整合素)表达降低,其在多种炎症反应中起重要作用。PL/J/CD18缺陷小鼠通常在出生11周后,会出现类银屑病皮损。有趣的是,在PL/JxC57BL/6J基因背景上的纯合突变F1代小鼠没有发展出银屑病,而回交实验(即F1代与任何亲本的交配)表明除了CD18之外,还有少量基因决定了疾病的易感性[9]。β2整合素主要与角质形成细胞过度增殖和分化异常有关。另有研究报道使用JAK抑制剂通过影响T细胞功能而显著减轻该模型皮损[10]。 (3)K5-IL-17C转基因小鼠:白细胞介素17C是白细胞介素17家族的成员之一,研究显示白细胞介素17C或白细胞介素17A均可诱导皮肤炎症反应,而白细胞介素17C是银屑病皮损部位表达最高的白细胞介素17蛋白。白细胞介素17C小鼠出生后8周后出现背部皮肤增厚、红斑和表皮脱落,病理特征显示CD4和CD8 T细胞、巨噬细胞和髓样树突状细胞局部浸润,血管生成增多。皮损处表达多种促炎症因子,而应用肿瘤坏死因子抑制剂后皮损明显消退,机制与NF-κB通路调节或白细胞介素17A的协同作用有关[11]。另一种K14-IL-17Aind/+小鼠由白细胞介素17Aind和K14-Cre等位基因杂交后产生,该模型会出现严重的银屑病样皮损[12]。研究其发病机制与活性氧生成增加和血液中循环炎性白细胞、内皮功能障碍、收缩增加有关[13]。 (4)K5.TGFbeta1wt转基因小鼠:转换生长因子β参与角质细胞增殖、血管生成、T细胞分化,在银屑病的发生发展过程中起作用。从第17天开始,转基因角质细胞在皮肤扩增,K5.TGFbeta1wt转基因小鼠逐渐出现严重的银屑病样皮损,血管生成伴血管扩张,多种趋化因子上调;该模型至6个月大时已全身皮肤红斑鳞屑,和人类的红皮型银屑病表现相似[14-15]。 (5)K5.Stat3C转基因小鼠:证实了信号转导因子和转录激活因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription,STAT3)在角质形成细胞中的作用。转录激活因子3C缺陷小鼠会导致伤口愈合延迟,而K5.Stat3C小鼠则会出现红斑鳞屑,伴随伤口处的皮损肥厚。皮损处毛细血管数量增加,血管内皮生长因子、细胞间黏附分子1、IκB-α蛋白等表达上调,转录激活因子3C与活化的T细胞(特别是Th17细胞)一起,促进皮肤的炎症反应[16-18]。见表1。 2.1.2 自发银屑病样小鼠模型 (1)Scd1ab/Scd1ab纯合子小鼠:是首个出现角化过度的体内模型,其编码硬脂酰辅酶A去饱和酶的Scd1基因突变引起皮脂腺缺失,成年小鼠出现鳞屑、血管增加及巨噬细胞浸润等部分类似人类银屑病,缺点是该模型真皮也过度增长、成纤维密度增高;在皮损处缺乏T细胞和中性粒细胞的浸润,表皮增生可能由肥大细胞分泌的炎性递质引起,因而实际应用不广泛[24]。 (2)Ttcfsn/ Ttcfsn鼠:是常染色体隐性突变模型,该模型出生2周后会出现皮肤鳞屑、炎症、角化过度和Koebner阳性反应,并且皮损处中性粒细胞浸润。然而,该模型血中表皮生长因子受体和IgE抗体水平升高,且对环孢素治疗并无效果,加之相对寿命较短,因而其应用也受到限制[25]。 (3)Sharpincpdm/Sharpincpdm鼠:Hogen等[26]发现C57BL/Ka小鼠上的cpd突变,该模型会活化肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的NF-κB活性,出现多器官炎症包括腹背部慢性增生性皮炎的表现。该皮炎用皮质类固醇治疗有效,对环孢素A无效。但该鼠缺点是口腔、胃部也有类似上皮细胞增殖的病变,缺乏临床表型特异性[27]。 除此之外,还有研究者利用小鼠尾部鳞片中表皮颗粒层作为模型,观察药物给药对表皮颗粒层的治疗作用[28]。其余几种基因突变品种小鼠(ic/ic突变鼠、hr/hr突变鼠等),因其与银屑病病理相差较大,因而使用范围较少。 2.1.3 诱发银屑病样模型 (1)咪喹莫特(5%)诱导小鼠模型:咪喹莫特为Toll样受体(Toll-like receptor,TLR)7/8激动剂,激活固有免疫系统导致中性粒细胞、γδT细胞在皮损浸润,产生炎症因子、趋化因子等,促进或加重银屑病样皮损改变,同时伴随食欲减退、体质量损失、脾脏增大等全身表现。该模型小鼠通常诱导7 d后背部皮损改变最为严重,机制主要通过白细胞介素23/白细胞介素17通路介导[29-30]。该模型优点为操作简单、易于复制,成为国内研究的主要诱导银屑病小鼠模型;缺点为该模型具有自愈倾向,随着诱导时间延长,其背部皮损逐渐稳定或减轻,因此不太适于发病机制的长期研究。 (2)十二烷基硫酸钠(10%)诱导小鼠模型:背部皮肤涂抹十二烷基硫酸钠诱导7 d之后,小鼠出现皮肤增厚、局部红肿和皮下血管增生,病理改变包括角化过度、角质层增厚,真皮层和皮下毛细血管扩张和充血。通过检测血清蛋白显示蛋白激酶Cβ、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素23等细胞因子表达上调。该小鼠模型反映了银屑病的部分特征,但国外应用此模型研究较少,其刺激的信号通路亦不甚清楚[31-32]。 (3)普萘洛尔诱导豚鼠模型:20世纪90年代,科学 "
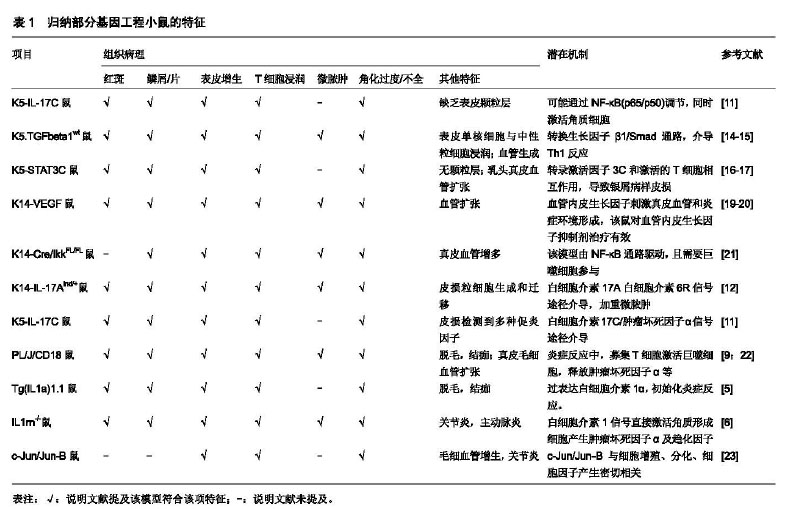

家最初给豚鼠单纯灌胃普萘洛尔0.1 mg/d并没有诱导出银屑病样改变,但每周皮下注射完全弗氏佐剂之后能诱导成功[33]。后来经过逐渐改进造模方法,现多采用在豚鼠耳部涂抹5%普萘洛尔乳剂,几天后可观察到包括皮损局部红肿、糜烂,角化不全,毛细血管扩张等病理改变,皮损部位多种促炎因子(如白细胞介素)表达增加[34-35]。 (4)皮内注射白细胞介素23诱导模型 通过向小鼠皮内注射1 μg量的白细胞介素23刺激产生白细胞介素19和白细胞介素24,它们通过肿瘤坏死因子信号途径影响角质形成细胞的分化和增殖。小鼠会出现皮损红斑、角化不全、表皮增生等表现,伴随CD4+淋巴细胞、树突状细胞、中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞浸润,与许多银屑病的显著症状相吻合[36]。 此外,尚有研究体内注射雌激素刺激小鼠阴道上皮组织增生来模拟银屑病皮损表现,该小鼠上皮细胞的增殖核抗原表达水平对照组升高,阴道上皮基底细胞的有丝分裂指数增高[37]。 2.1.4 异种移植银屑病模型 异种移植模型是目前最接近人类银屑病改变的模型,它对银屑病发病机制和新药研发方面有重要价值。异种移植模型主要使用严重免疫缺陷小鼠作为受体,亦有研究使用裸鼠或AGR129鼠为受体[38]。国外学者将银屑病受累皮肤移植至严重免疫缺陷鼠,10周之后再将自体皮损处T细胞(而非外周血T细胞)注射进移植的真皮内,可观察到银屑病病理改变的维 持[39]。该模型优点是代表性较好,缺点是需要大量银屑病患者供体皮肤,供体来源受到限制,同时还要考虑供体间的遗传异质性。此外,该模型价格昂贵且对饲养方面要求较高,限制了其推广应用。 2.1.5 中医病证结合动物模型(银屑病) 目前,经过研究报道的银屑病病证结合动物模型共有3种,涉及脾虚证、湿热证和血瘀证。银屑病中医病证结合动物模型均采用2种或多种因素复合造模,步骤较多,造模周期从1周到3周不等。经过造模后,研究报道这些方法均能够一定程度上模拟特定的银屑病病证结合的临床表现,如脾虚证豚鼠除了银屑病皮损,还会出现体质量增长变缓、纳呆少饮、嗜睡懒动、大便时干时溏,肛温升高、血脂水平升高,类似人的脾虚证表现[40-41]。但是,由于人的中医证候指标与豚鼠/小鼠的物种差异,国内学界对脾虚证、湿热证和血瘀证的指标选择尚无统一的认识,有待进一步的研究证实病证结合模型与临床指标之间的关联。具体病证结合模型分类见表2。 2.2 细胞模型 2.2.1 二维(2-Dimensional,2D)细胞模型 角质形成细胞是银屑病研究最为常见的2D细胞类型。银屑病皮损角质形成细胞呈过度增殖和异常分化,其诱发过程可能与接受皮损局部的易感因素(基因易感性、炎症微环境等)有关。从银屑病皮损处分离、体外培养角质形成细胞虽然代表性好,但这种方法可重复性、可获得性和稳定性都较差,并且其银屑病表型的维持需要添加细胞因子。因此,目前最常用的细胞有正常表皮角质形成细胞和 "

| [1]Hawkes JE, Yan BY. Discovery of the IL-23/IL-17 Signaling Pathway and the Treatment of Psoriasis. 2018; 201(6): 1605-1613.[2]Capon F. The Genetic Basis of Psoriasis.Int J Mol Sci.2017;18(12).[3]Langley RG,Elewski BE,Lebwohl M,et al.Secukinumab in plaque psoriasis--results of two phase 3 trials. N Engl J Med.2014;371(4): 326-338.[4]Zollner TM, Renz H,Igney FH, et al.Animal models of T-cell-mediated skin diseases. Bioessays.2004; 26(6): 693-696.[5]Groves RW, Mizutani H, Kieffer JD, et al.Inflammatory skin disease in transgenic mice that express high levels of interleukin 1 alpha in basal epidermis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1995; 92(25): 11874-11878.[6]Shepherd J,Little MC,Nicklin MJ.Psoriasis-like cutaneous inflammation in mice lacking interleukin-1 receptor antagonist.J Invest Dermatol.2004; 122(3): 665-669.[7]Nakajima A,Matsuki T,Komine M,et al.TNF, but not IL-6 and IL-17, is crucial for the development of T cell-independent psoriasis-like dermatitis in Il1rn-/- mice.J Immunol.2010;185(3): 1887-1893.[8]Milora KA,Fu H,Dubaz O,et al.Unprocessed Interleukin-36α Regulates Psoriasis-Like Skin Inflammation in Cooperation With Interleukin-1. J Invest Dermatol. 2015;135(12):2992-3000..[9]Bullard DC,Scharffetter-Kochanek K,Mcarthur MJ, et al.A polygenic mouse model of psoriasiform skin disease in CD18-deficient mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.1996;93(5): 2116-2121.[10]Chang BY,Zhao F,He X,et al.JAK3 inhibition significantly attenuates psoriasiform skin inflammation in CD18 mutant PL/J mice.J Immunol. 2009;183(3): 2183-2192.[11]Johnston A, Fritz Y, Dawes SM, et al. Keratinocyte overexpression of IL-17C promotes psoriasiform skin inflammation.J Immunol.2013; 190(5): 2252-2262.[12]Croxford AL,Karbach S,Kurschus FC,et al.IL-6 regulates neutrophil microabscess formation in IL-17A-driven psoriasiform lesions.J Invest Dermatol.2014;134(3): 728-735.[13]Karbach S, Croxford AL,Oelze M,et al.Interleukin 17 drives vascular inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and arterial hypertension in psoriasis-like skin disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(12): 2658-2668.[14]Li AG, Wang D, Feng XH, et al. Latent TGFbeta1 overexpression in keratinocytes results in a severe psoriasis-like skin disorder. Embo J.2004;23(8): 1770-1781.[15]Li F, Bian L,Iriyama S, et al.Smad7 Ameliorates TGF-β-Mediated Skin Inflammation and Associated Wound Healing Defects but Not Susceptibility to Experimental Skin Carcinogenesis.J Invest Dermatol. 2019;139(4):940-950.[16]Sano S,Chan KS,Carbajal S,et al.Stat3 links activated keratinocytes and immunocytes required for development of psoriasis in a novel transgenic mouse model.Nat Med.2005;11(1): 43-49.[17]Takaishi M,Ishizaki M,Suzuki K,et al.Oral administration of a novel RORgammat antagonist attenuates psoriasis-like skin lesion of two independent mouse models through neutralization of IL-17. J Dermatol Sci.2017;85(1): 12-19.[18]Nakajima K, Kataoka S, Sato K, et al. Stat3 activation in epidermal keratinocytes induces Langerhans cell activation to form an essential circuit for psoriasis via IL-23 production. J Dermatol Sci. 2019;93(2):82-91.[19]Xia YP, Li B,Hylton D,et al.Transgenic delivery of VEGF to mouse skin leads to an inflammatory condition resembling human psoriasis.Blood. 2003;102(1): 161-168.[20]Chen T,Zhang LW,Fu LX, et al. Systemic ALA-PDT effectively blocks the development of psoriasis-like lesions and alleviates leucocyte infiltration in the K14-VEGF transgenic mouse.Clin Exp Dermatol.2017; 42(8): 849-856.[21]Stratis A,Pasparakis M,Rupec RA, et al.Pathogenic role for skin macrophages in a mouse model of keratinocyte-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J Clin Invest.2006;116(8): 2094-2104.[22]Gatzka M, Hainzl A, Peters T, et al. Reduction of CD18 promotes expansion of inflammatory gammadelta T cells collaborating with CD4+ T cells in chronic murine psoriasiform dermatitis.J Immunol.2013; 191(11): 5477-5488.[23]Zenz R,Eferl R,Kenner L,et al.Psoriasis-like skin disease and arthritis caused by inducible epidermal deletion of Jun proteins. Nature.2005; 437(7057): 369-375.[24]Schon MP. Animal models of psoriasis: a critical appraisal.Exp Dermatol. 2008;17(8): 703-712.[25]Danilenko D M. Review paper: preclinical models of psoriasis.Vet Pathol. 2008;45(4): 563-575.[26]Peuhu E, alomaa SI,De Franceschi N,et al.Integrin beta 1 inhibition alleviates the chronic hyperproliferative dermatitis phenotype of SHARPIN-deficient mice.2017;12(10): e0186628.[27]Hogenesch H,Gijbels MJ,Offerman E,et al.A spontaneous mutation characterized by chronic proliferative dermatitis in C57BL mice.Am J Pathol.1993;143(3): 972-982.[28]郭政宏,周彪,唐冬梅,等.新型小分子化合物对银屑病模型小鼠尾部鳞片颗粒层细胞的影响[J].生命科学研究, 2016, 20(4): 340-344.[29]Van Der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JS, et al. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis.J Immunol.2009;182(9): 5836-5845.[30]Moos S, Mohebiany AN, Waisman A, et al.Imiquimod-induced psoriasis in mice depends on the IL-17 signaling of keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2019 ;23. pii: S0022-202X(19)30022-3. [31]张海婧,周琬琪,张翼,等. 十二烷基硫酸钠诱导银屑病动物模型的建立[J].武警医学,2013,24(5): 373-375.[32]Ji M,Xue N,Lai F,et al.Validating a Selective S1P1 Receptor Modulator Syl930 for Psoriasis Treatment. Biol Pharm Bull.2018;41(4): 592-596.[33]Wolf R,Shechter H, Brenner S. Induction of psoriasiform changes in guinea pig skin by propranolol. Int J Dermatol.1994; 33(11): 811-814.[34]Yao N, Xia JX, Liu XM, et al. Topical application of a new monoclonal antibody against fibroblast growth factor 10 (FGF 10) mitigates propranolol-induced psoriasis-like lesions in guinea pigs.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.2014;18(7): 1085-1091.[35]樊丹采. 基于血瘀证的银屑病机制初探[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学, 2016.[36]Chan JR,Blumenschein W,Murphy E,et al.IL-23 stimulates epidermal hyperplasia via TNF and IL-20R2-dependent mechanisms with implications for psoriasis pathogenesis.J Exp Med.2006;203(12): 2577-2587.[37]施惠娟,周茹,金少举,等. 氧化苦参碱对银屑病模型雌激素周期小鼠阴道上皮细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 临床皮肤科杂志, 2011,40(11): 669-672.[38]Di Domizio J, Conrad C, Gilliet M. Xenotransplantation Model of Psoriasis. Methods Mol Biol.2017; 1559: 83-90.[39]Gilhar A,David M,Ullmann Y,et al. T-lymphocyte dependence of psoriatic pathology in human psoriatic skin grafted to SCID mice.J Invest Dermatol.1997; 109(3): 283-288.[40]郭姗姗,郭菲,刘红霞.银屑病模型与脾虚证银屑病病证结合模型的实验研究[C].南京:2012全国中西医结合皮肤性病学术会议, 2012.[41]郭菲. 健脾解毒汤对脾虚证银屑病豚鼠模型的实验研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学, 2012.[42]周萌, 伍秋云, 陈会茹. 银屑病血瘀证动物模型的构建探讨[C].上海: 2010全国中西医结合皮肤性病学术会议, 2010.[43]王玉芝. 银屑病湿热证动物模型的构建[J]. 山东中医杂志, 2013, 32(7): 489-490.[44]郭菲,刘红霞. 银屑病脾虚证豚鼠模型构建初探[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2012,18(15): 242-245.[45]Boukamp P,Petrussevska RT,Breitkreutz D,et al.Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line.J Cell Biol.1988; 106(3): 761-771.[46]Martin G, Guerard S, Fortin M M, et al.Pathological crosstalk in vitro between T lymphocytes and lesional keratinocytes in psoriasis: necessity of direct cell-to-cell contact. Lab Invest.2012;92(7): 1058-1070.[47]Van Den Bogaard EH,Tjabringa GS,Joosten I,et al.Crosstalk between keratinocytes and T cells in a 3D microenvironment: a model to study inflammatory skin diseases. J Invest Dermatol.2014;134(3): 719-727.[48]Kim Y,Park N,Rim YA,et al.Establishment of a complex skin structure via layered co-culture of keratinocytes and fibroblasts derived from induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther.2018;9(1): 217.[49]Berg EL,Yang J,Melrose J,et al.Chemical target and pathway toxicity mechanisms defined in primary human cell systems. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods.2010;61(1): 3-15.[50]Greb JE,Goldminz AM,Elder JT,et al.Psoriasis.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2: 16082.[51]Wang X, Sun J, Hu J. IMQ Induced K14-VEGF Mouse: A Stable and Long-Term Mouse Model of Psoriasis-Like Inflammation. PLoS One. 2015;10(12): e0145498. |
| [1] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [2] | Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Expression of interleukin-24 in a mouse model of periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 679-684. |
| [3] | Yang Yang, Yao Yu, Shen Xiaotian, Liu Jiajia, Xue Jianhua. Expression and significance of interleukin-21 in intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 690-694. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Jiang Shengyuan, Li Dan, Jiang Jianhao, Shang-you Yang, Yang Shuye. Biological response of Co2+ to preosteoblasts during aseptic loosening of the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [6] | Chen Yutong, Li Chenchen, Liu Yang, Zheng Yaqin, Yang Xihua, An Meiwen. Establishment of an acute radioactive skin injury model in Wistar rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 237-241. |
| [7] | Wang Yan, Dong Benchao, Wang Ying, Sun Lei, Lu Bin, Bai Haohao, Tian Aixian, Ma Jianxiong, Ma Xinlong. Animal models of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: modeling methods and characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 292-297. |
| [8] | Ma Dujun, Peng Liping, Chen Feng, Jiang Shunwan, Jiang Jinting, Gao Kun, Lin Zhanpeng. Research strategy of gene editing technology in the gene treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 298-303. |
| [9] | Wang Kang, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Effect of stem cell derived exosomes on repairing peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3083-3089. |
| [10] | Yang Youwei, Feng Wei . Quadrilateral plate fractures: research progress of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2416-2422. |
| [11] | Wang Guoxiang, Zhang Xiaoyun. Mechanisms of inflammatory cytokines and related signaling pathways in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2266-2273. |
| [12] | Liu Hong, Wan Zhe, Zhang Zhen, Zhang Qin. Relationship between root resorption and intrusive force during maxillary molar intrusion in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2172-2176. |
| [13] | Mo Caifeng, Cheng Xiaoyang, Liao Ming, He Dongling, Huang Zhi. A Guangxi Bama minipig model of Trimeresurus stejnegeri snakebite: modeling and evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1688-1692. |
| [14] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Pan Xinghua. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating systemic lupus erythematosus in a tree shrew model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 90-95. |
| [15] | Zhu Bingbing, He Haibin, Deng Jianghua, Wang Wenqiang, Mu Xiaoling. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin 8 receptor inhibit inflammation and promote vascular repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 61-66. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||