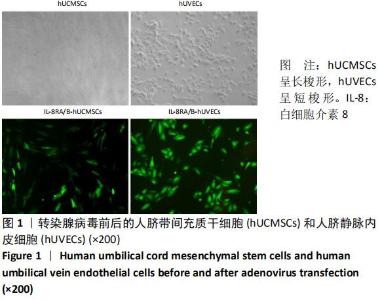
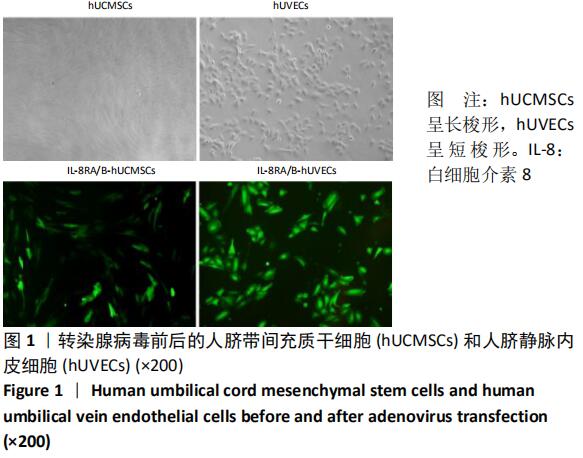
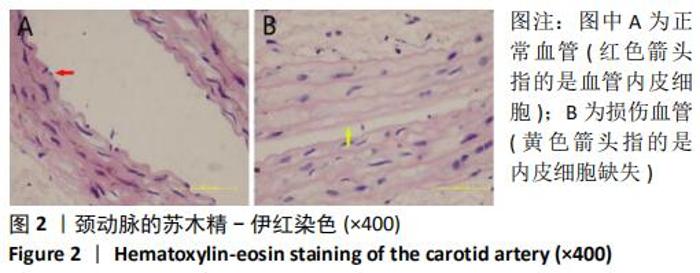
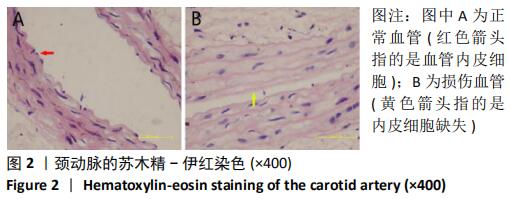
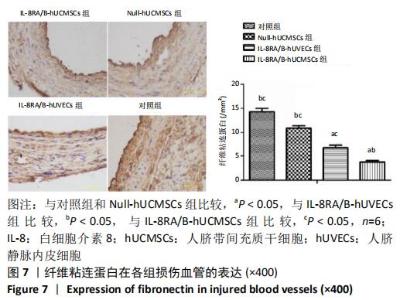
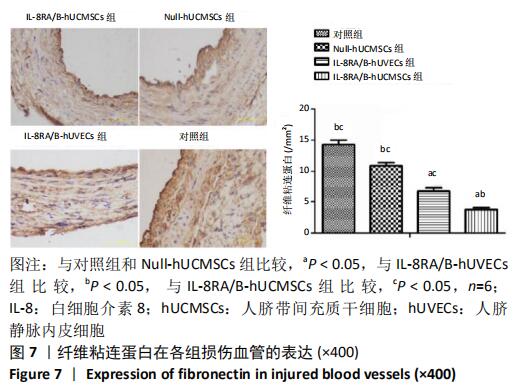
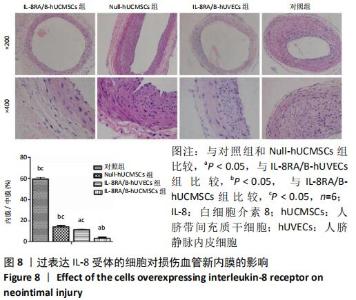
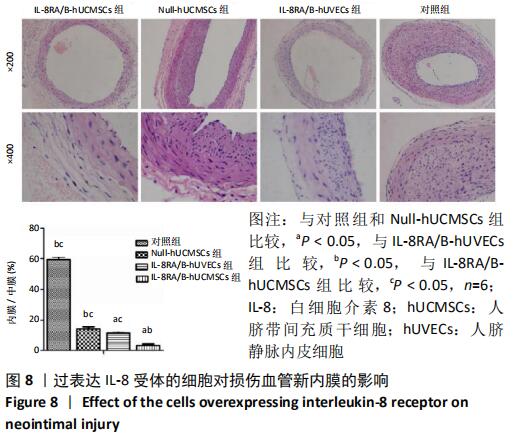
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 61-66.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2124
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin 8 receptor inhibit inflammation and promote vascular repair
Zhu Bingbing, He Haibin, Deng Jianghua, Wang Wenqiang, Mu Xiaoling
- School of Medicine, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China