Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (14): 2266-2273.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3113
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanisms of inflammatory cytokines and related signaling pathways in osteoarthritis
Wang Guoxiang1, Zhang Xiaoyun1, 2
- 1Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2020-05-21Revised:2020-05-23Accepted:2020-06-17Online:2021-05-18Published:2020-12-31 -
Contact:Zhang Xiaoyun, MD candidate, Attending physician, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Wang Guoxiang, Master, Attending physician, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960908 (to WGX [project participant]); Chinese Medicine, Zhuang & Yao Pharmaceutical Preparation Upgrading Project of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. GZZJ16-07 (to WGX [project participant]); First-class Discipline Projects of Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2019XK026 (to ZXY [project participant]) and 2019XK029 (to ZXY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Guoxiang, Zhang Xiaoyun. Mechanisms of inflammatory cytokines and related signaling pathways in osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2266-2273.
share this article
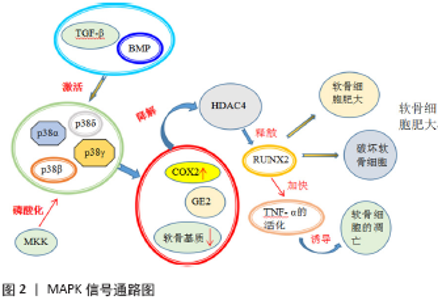
2.1 相关炎症细胞因子在骨关节炎中的作用机制 炎性细胞因子在骨关节炎的发病过程中有至关重要的地位,它参与了众多的生理代谢及功能调节,并维持其组织结构及功能的正常。目前发现骨关节炎相关的炎性细胞因子主要有促炎细胞因子(白细胞介素1、白细胞介素17、肿瘤坏死因子α等)、合成性细胞因子(骨形态发生蛋白、转化生长因子β、胰岛素样生长因子)、抗炎细胞因子(白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10、白细胞介素13)等。 2.1.1 促炎细胞因子 促炎细胞因子包括白细胞介素1、白细胞介素17、肿瘤坏死因子α等。白细胞介素1家族成员主要包括白细胞介素1α和白细胞介素1β两种类型,目前发现其与先天免疫和炎症密切相关,在骨关节炎的滑膜、软骨、软骨下骨以及滑液中均发现其处于高水平的表达。 白细胞介素1β上调炎性递质的产生和基质金属蛋白酶的表达,在骨关节炎的发病机制中发挥重要作用[5]。目前发现其通过激活炎症相关信号通路,从而刺激软骨降解酶(包括基质金属蛋白酶和ADAMTS5)的表达,诱导炎症递质如诱导型一氧化氮合酶和环氧化酶2的过度释放和软骨细胞分解代谢,抑制细胞外基质的合成,促进软骨钙化及软骨下骨重塑过程中所涉及的退化,最终促进了骨关节炎的发展[6]。此外白细胞介素1β在刺激其他促炎因子和趋化因子如白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的基因表达和蛋白分泌的情况下,促进了一氧化氮和前列腺素E2的过度表达,将会诱导软骨细胞发生再次严重损伤[7]。周炎等[8]的实验结果与大多数以往的研究结果一致,进一步证实了白细胞介素1β在骨关节炎发生发展中的作用。他发现在膝骨关节炎患者的关节中白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6 及肿瘤坏死因子α等的活性明显提高,表达水平明显过量;并且这些细胞因子的表达水平与炎症的严重程度呈正相关,能够用来作为衡量膝骨关节炎病情发展的参考指标,提示抑制白细胞介素1β诱导的炎症反应可延缓或阻止骨关节炎的发展。目前白细胞介素1β被认为是骨关节炎的主要诱因,在软骨降解和骨再生中起着关键作用,通过抑制白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素1β诱导的炎症递质的过表达可能为骨关节炎的治疗提供有效的方法。 白细胞介素17是由淋巴细胞和单核细胞所分泌的细胞因子,它包含6个蛋白成员(白细胞介素17A、17B、17C、17D、17E和17F),其成员通过诱导软骨细胞和滑膜成纤维细胞中基质金属蛋白酶和其他促炎细胞因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6)的表达而参与组织炎症和破坏,引起关节软骨塌陷和滑膜浸润,最终造成骨关节炎的发生[9-10]。此外骨关节炎涉及软骨的降解和关节软骨下骨的重建,包括骨赘生物的形成,目前发现高水平表达的白细胞介素17可能通过改变成骨细胞的分化对骨赘生物产生影响,从而加快骨关节炎的发生。据报道,白细胞介素17编码基因的多态性与骨关节炎风险有关。LEE等[11]在研究中证实白细胞介素17A rs2275913和白细胞介素17F rs763780多态性与骨关节炎易感性密切相关。与健康对照者相比,骨关节炎患者血液中的白细胞介素17水平明显升高,提示T17细胞参与骨关节炎发病。因此阻断白细胞介素17信号通路可能是控制骨关节炎症状和防止骨关节破坏的一种新的治疗途径。 肿瘤坏死因子α被认为是炎性细胞因子中最强的抗肿瘤效应因子,目前发现肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β可控制关节软骨的退化。肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β等通过抑制软骨细胞的合成代谢活动来激活软骨细胞产生基质金属蛋白酶,特别是基质金属蛋白酶13(软骨破坏的关键调节因子),从而对软骨造成严重的破坏作用。除了它们的破坏性作用,这些炎性细胞因子也倾向于诱导软骨细胞凋亡。目前肿瘤坏死因子α的上调和Bcl-2的下调被认为是骨关节炎发病过程中的基础机制,在骨关节炎过程中,软骨细胞大量凋亡可促进白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α调节骨关节炎的进展,其中Bcl-2家族中Bcl-2和Bax的平衡是最重要的调控机制[12]。此外,肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1和白细胞介素6可诱导许多炎症及其他细胞因子、基质金属蛋白酶和前列腺素的产生,并抑制蛋白多糖和Ⅱ型胶原的合成,在骨关节炎的软骨基质降解和骨吸收中起着关键作用[13]。LIAO等[14]在前交叉韧带断裂诱导的动物骨关节炎模型中发现,外源性注射高级氧化蛋白产物可上调软骨中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的表达,而这种表达可以通过使用SB202190 (p38-MAPK抑制剂)或罗布麻宁(NADPH氧化酶抑制剂)预处理或者NOX4基因敲除起到抑制作用,从而增加了Ⅱ型胶原和糖胺聚糖,并最终延缓骨关节炎进程中的软骨退变。目前肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β被认为是导致骨关节炎发病的关键细胞因子,这两种细胞因子大部分由骨关节炎关节中的软骨细胞产生,可诱导许多炎症和分解代谢因子的产生。因此调节细胞因子合成的化合物可能是骨关节炎治疗的有利靶点。 2.1.2 合成性细胞因子 合成性细胞因子主要包括骨形态发生蛋白、转化生长因子β、胰岛素样生长因子等。 骨形态发生蛋白是一类结构相似的高度保守蛋白,属于转化生长因子β超级家族。众所周知,骨形态发生蛋白家族成员对软骨内成骨有着重要的影响,是促进成骨和诱导软骨分化的重要生长因子[15]。研究表明软骨细胞能够产生骨形态发生蛋白,从而诱导和促进异位部位新的软骨形成,并且骨形态发生蛋白能通过加强转化生长因子β、胰岛素样生长因子等的活性,显著降低白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6等炎性细胞的表达,使关节软骨细胞受到的破坏减少[16]。但是最近的研究发现,在骨关节炎患者的软骨细胞中,骨形态发生蛋白细胞因子在各种病理因素刺激下表达水平显著提高,此时骨形态发生蛋白对软骨细胞的保护作用遭到破坏,促进软骨形成的Sox9及Ⅱ型胶原表达水平被抑制,从而诱导软骨细胞退形性变,促进骨关节炎的发生发展[17]。此外CHIEN等[18]在动物骨关节炎模型实验中发现,白细胞介素1β通过MEK、ERK和Sp1信号途径促进软骨细胞中骨形态发生蛋白2的表达,在小鼠膝关节中诱导骨赘形成。通过向关节内注射Noggin可以降低骨形态发生蛋白2、白细胞介素1β和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,有效减轻了炎症的发生及关节软骨降解和软骨下骨破坏。这也进一步证实了骨形态发生蛋白2在软骨细胞中的表达增加,将参与骨关节炎软骨下骨及软骨细胞的病理改变;并且骨形态发生蛋白2具有强大的合成代谢作用,在骨关节炎软骨中呈现处高水平的表达时,其可以通过与其他降解酶的相互作用导致蛋白聚糖的降解并触发骨关节炎的软骨改变。因此使用骨形态发生蛋白抑制剂或者类似药物靶向病理性骨重塑和炎症可能是治疗骨关节炎的一种潜在治疗方法。 转化生长因子β超家族由30多个成员组成,包括转化生长因子、激活素、骨形态发生蛋白和生长分化因子,这些因子具有特征性的四元二聚体结构,并通过在两种类型(Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型)的丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶受体之间形成异聚物来传递信号[19]。转化生长因子β由软骨细胞分泌并储存在基质中,发挥着调节软骨细胞的代谢、分化、增殖和存活,并调节细胞外基质的产生和周转的作用,对维持关节软骨及软骨细胞的内环境稳定至关重要[20],并且通过机械负荷快速上调,刺激蛋白多糖合成,阻断软骨细胞肥大基因的表达[21]。樊志强等[22]在动物实验中发现,在骨关节炎关节腔内注射转化生长因子β1可以起到保护关节软骨的作用,其促进了软骨细胞的增殖,加快受损关节软骨的修复。此外转化生长因子β信号转导在软骨中具有重要的抗炎作用,转化生长因子β1在体内外均能对抗促炎细胞因子白细胞介素1的表达,并有助于在经过炎症诱导耗竭后的软骨蛋白多糖含量的恢复。研究发现,在兔关节软骨细胞中,转化生长因子β1和转化生长因子β3显著降低了白细胞介素1受体在蛋白和mRNA水平上的表达,另外转化生长因子β还通过下调人和牛软骨细胞中的白细胞介素6受体水平来抵消促炎细胞因子白细胞介素6的表达[23]。但是实验发现转化生长因子β在骨关节炎中的异常表现会加剧骨关节炎的进展。高水平的转化生长因子β激活SMAD1/5/8途径,引起与纤维生成和肥大相关的基因上调,从而导致滑膜纤维化,此时位于骨膜中的间充质干细胞的软骨细胞终末分化,诱导骨赘形成[24]。此外转化生长因子β能够加速血管的生成,进而侵润软骨下骨,加重骨关节炎的发展。降低转化生长因子β在软骨下骨中的表达,能够对软骨下骨起到保护作用,并阻止了关节软骨的退变,有效延缓骨关节炎的发生[25]。总之基于转化生长因子β对软骨作用的双重性还需要进一步的探讨,期待为靶向转化生长因子治疗骨关节炎提供新的研究方向。 胰岛素样生长因子包括胰岛素样生长因子1和胰岛素样生长因子2两种调节软骨基因表达的多肽生长因子。目前发现软骨组织在受到损害时,基质蛋白发生溶解并且引起蛋白酶活化,此时胰岛素样生长因子1和 转化生长因子β的表达得到增强,显著刺激软骨细胞外基质成分的产生,从而加快软骨细胞的生成、胶原蛋白和蛋白多糖的合成,以维持软骨的稳态。胰岛素样生长因子1是软骨细胞的已知合成代谢因子,它促进软骨细胞的增殖和分化,并调节胚胎中的骨骼发育[26],事实上胰岛素样生长因子1在体外也还具有减少白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨基质减少的能力。因此,胰岛素样生长因子1被认为是软骨合成代谢和维持软骨表型的关键因素,胰岛素样生长因子1及其下游通路如PI3K/AKT通路的缺陷可能导致关节软骨发育不良。有实验将软骨细胞放在胶原支架上进行培育,在添加胰岛素样生长因子1后发现软骨细胞的基质合成及分解代谢的能力得到提升,并增加了Ⅱ型胶原的表达水平,利用胰岛素样生长因子1维持软骨细胞的功能联合生物支架对骨关节损伤的治疗可以起良好的效果[27]。此外胰岛素样生长因子2也在软骨中表达,目前发现胰岛素样生长因子2促进正常人软骨细胞软骨基质基因表达并抑制核因子κB活化。UCHIMURA等[28]在动物骨关节炎造模实验中发现,关节腔内注射胰岛素样生长因子2后,高水平表达的胰岛素样生长因子2将导致软骨基质基因如Agg、Ⅱ型胶原和IX型胶原表达升高,而白细胞介素1β水平及基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白的表达明显降低,从而减少骨赘形成和软骨下骨的硬化,证实了胰岛素样生长因子2可以促进软骨的完整性以及阻止膝骨关节的破坏。 2.1.3 抗炎细胞因子 抗炎细胞因子包括白细胞介素10、白细胞介素4、白细胞介素13等。 白细胞介素10由非免疫细胞如关节软骨细胞和软骨肉瘤细胞分泌,是一种具有软骨保护作用及促进软骨细胞增殖的细胞因子。目前发现白细胞介素10通过抑制白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达、基质金属蛋白酶的合成以及前列腺素E2的分泌,以此达到保护关节软骨免受退化的影响[29]。此外它还稳定了软骨细胞的特定表型,保护其免受机械损伤引起的细胞死亡和细胞外基质降解[30]。实验中发现关节内注射白细胞介素10有助于保护关节软骨细胞免于凋亡,同时保持软骨细胞增殖,显著减轻小鼠的关节软骨退化[31]。 白细胞介素4是一种由辅助性T淋巴细胞2(Th2)、嗜酸性粒细胞和肥大细胞分泌的有效免疫调节细胞因子。它对关节软骨起到一定的保护作用,通过抑制诱导型一氧化氮合酶和一氧化氮的表达,进而抑制白细胞介素1β等促炎性细胞因子的表达及基质金属蛋白酶的合成来保护软骨,是最有效的抗炎细胞因子之一。目前骨髓间充质干细胞疗法被认为是治疗骨关节炎的一种有前途的细胞再生药物。有实验证明,白细胞介素4基因转染通过延长植入的骨髓间充质干细胞的存活时间和促进软骨保护和抗炎的作用,增强了骨髓间充质干细胞对骨关节炎的治疗作用[32]。 白细胞介素13在治疗骨关节炎中有着重要的潜在用途,它能够抑制骨关节炎滑膜上白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和基质分解素1的合成和基质分解素的活性,同时增加白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂(白细胞介素1Ra)的产生。这无疑为减少白细胞介素1β对软骨细胞的刺激创造了有利条件。 2.2 相关信号通路在骨关节炎中的作用机制 2.2.1 MAPK信号通路 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPKs)是一类广泛存在于真核细胞中的丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,可被细胞外信号、物理刺激、炎性细胞因子如白细胞介素1和白细胞介素6、细菌或肿瘤生长因子激活,将细胞外信号逐步传递至细胞核,从而调节转录因子的活性、控制相关基因的表达,进一步引起细胞反应[33],目前被认为是调节骨关节炎的主要信号通路。MAPKs信号通路在被破坏的情况下会加速炎症反应,从而引起软骨基质降解酶大量外释,加重软骨退变。因此,它在软骨退行性变和骨关节炎进展中起着重要作用。 MAPK亚家族包括p38mapk、细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases, ERK)、ERK5和c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal kinase,JNK)等,其中与关节炎主要相关的是P38mapk及JNK信号通路。p38 MAPK家族有4个成员:p38α、p38β、p38γ 和 p38δ,分别有各自的基因编码,其在骨组织的稳态和发育中起重要作用,并且在炎症和肿瘤转化过程中控制细胞分化、增殖及细胞因子的产生、衰老以及凋亡[34]。在软骨细胞发育和分化过程中,由于生长因子如转化生长因子β和骨形态发生蛋白的作用,p38 MAPK被激活,所有的p38成员被上游的MAPK激酶(MKK)作为双重磷酸化的目标,并且在骨关节炎或骨质疏松的背景下,p38MApk信号传导途径也发生了改变,其抑制软骨基质的合成,增加环氧化酶2和前列腺素E2的表达,促进组蛋白去乙酰化酶4的降解,并在去乙酰化酶4的抑制作用下释放RUNX2,导致软骨细胞肥大,加快软骨细胞的破坏,并且加速肿瘤坏死因子 α的活化,促进了软骨细胞的凋亡(见图2)。 JNK-MAPKs通路与P38mapk通路相似,在肿瘤坏死因子a诱导的软骨细胞凋亡过程中,JNK-MAPKs的激活是非常重要的,它可以提高基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶13、aggrecanase-1和aggrecanase-2的表达,其同样通过活化肿瘤坏死因子 α和相关炎性因子,加快软骨细胞的凋亡。 "
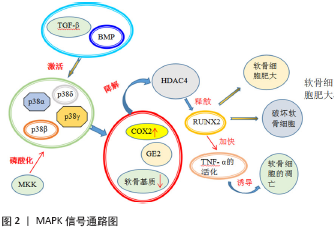
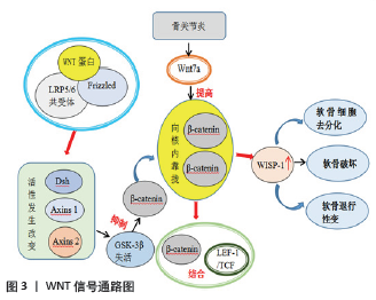
SUN等[35]在实验中发现通过抑制p38MAPK信号通路能够降低促炎性细胞因子的活性,并提高了软骨细胞修复骨性关节炎损伤能力。PRASADAM等[36]在实验中证实了透明质酸联合 U0126的使用,能够显著减少ERK磷酸化的发生,并且降低了RUNX2 及基质金属蛋白酶13的活性,改善了软骨细胞的损伤及软骨退行性变。总之MAPK是一种调节炎性细胞因子和基质金属蛋白酶下游表达的介质,它也可以作为疼痛的调节剂。因此这一信号通路可能是发现新药阻止骨关节炎进展的潜在途径,值得更多的关注。 2.2.2 Wnt信号通路 Wnt信号通路是一种高度保守的途径,决定着胚胎的多个发育过程,至少涉及19种不同的配体和3种途径:一个典型的Wnt/β-catenin途径和一个包括Wnt/PCP和Wnt/Ca2+途径在内的非典型Wnt途径。近年来,Wnt信号调节异常在老年性疾病中的作用越来越明显,尤其是骨关节炎[37]。研究表明滑膜中紊乱的Wnt信号通路会加速骨关节炎中的软骨退化,并且在控制软骨细胞、成骨细胞和滑膜细胞功能的关节组织中发挥着独特的作用[38]。 目前Wnt/β-catenin 信号通路作为Wnt信号转导中的经典通路,其信号转导失调被认为是骨关节炎的主要机制之一。β-catenin是经典Wnt信号通路中的一个中心分子,它维持骨骼和关节发育的多个发展过程,并且在软骨细胞分化、增殖、肥大和凋亡中起重要作用,与骨关节炎的发生发展密切相关。在通路形成过程中,当Wnt与膜卷曲受体(Frizzled)和LRP5/6共受体结合时,下游信号蛋白Disheveled(Dsh)和Axins 1、2的活性发生改变,这导致丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶GSK-3β失活,从而抑制由GSK-3β触发的β-catenin泛素化和降解。β-catenin随后在细胞质中积累并转运至细胞核,与转录因子LEF-1/TCF结合以调节下游靶基因的转录,参与细胞增殖,发挥刺激骨细胞的发育及防止细胞凋亡的调控作用(见图3)。但是目前众多研究表明抑制Wnt信号通路在软骨降解中起到了保护作用,被认为能减缓骨关节炎的进展[39]。据先前的报道,骨关节炎患者或软骨组织在受到损伤的情况下,软骨细胞中β-catenin蛋白水平显著上调,其转录活性通过Wnt7a激发后将引发关节软骨细胞去分化,从而加快软骨退化[40]。唐萌芽等[41]经过实验发现膝骨关节炎患者在接受治疗前,Wnt/5a、β-catenin等表达水平较高,通过治疗后出现显著的降低状态。BLOM等[42]在动物实验中发现,骨关节炎小鼠的关节软骨中Wnt及相关基因的活性发生变化,其中Wnt诱导的信号蛋白1 (WISP-1)的活性明显增强,而过度表达也导致软骨破坏,诱导关节软骨退行性变。同时LIETMAN等[43]通过实验发现β-catenin在骨关节炎和人骨关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞中的表达水平均明显增加,并且发现用β-catenin抑制剂XAV-939抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的表达可减轻骨关节炎的进展。总之,这些研究提供了明确的证据表明Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在关节软骨细胞中的过度表达,将导致关节软骨细胞异常成熟,加快软骨破坏,从而加重骨关节炎的进展。 "
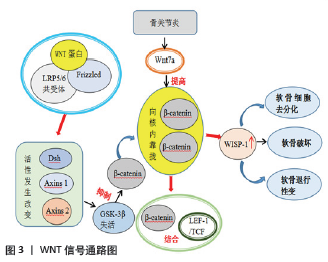
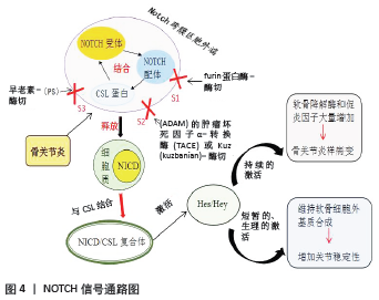
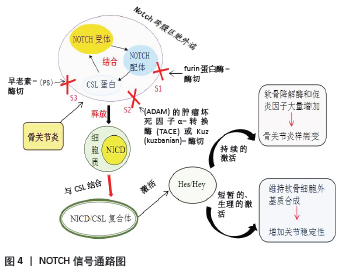
Wnt信号通路是关节内稳态和骨关节炎等关节疾病中一个重要的生物级联通路,在级联的各个层次都受到严格的调控,从而为药物开发提供了许多机会。期待在未来的治疗中,能够通过调节 Wnt信号转导途径来预防或缓解骨关节炎的发生。 2.2.3 NOTCH信号通路 NOTCH信号通路作为一种被广泛研究的信号通路,是进化过程中一种高度保守的机制,广泛表达于从无脊椎动物到脊椎动物的各种物种之间,决定细胞在发育过程中的命运,并维持成熟组织的内稳态。目前被认为是软骨细胞外基质在发育过程中分解代谢和合成代谢分子的潜在调节因子,负责维持细胞的增殖状态和集落形成能力[44]。 NOTCH信号主要由3个部分组成,即NOTCH受体(Notch1,Notch2,Notch3和Notch4)、它们的配体(Delta1,Delta3,Delta4和Jagged1,Jagged2)和CSL蛋白。在该通路过程中,细胞表面的NOTCH受体与跨膜配体在胞外区域结合后被激活,经过γ-分泌酶等的作用下经过3次剪切,最终将NOTCH胞内结构域(Notch intracellular domain,NICD)释放到细胞质中,随后转移到细胞核并与CSL结合形成NICD/CSL复合体,参与目标基因的转录,激活下游如Hes/Hey家族的靶基因的表达[45],启动一系列的细胞内事件(见图4)。目前大量研究表明,NOTCH信号通路在骨关节炎的进展中扮演着双重的调节作用,即关节软骨中NOTCH信号经过持续的激活将导致严重的、进行性的骨关节炎样病变,而短暂的、生理的NOTCH信号激活会起到维持软骨细胞外基质合成增加及关节稳定的作用[46-47],因此NOTCH信号通路对骨关节炎的发展至关重要。 MAHJOUB等[48]研究表明,他们通过免疫组织化学方法观察到,NOTCH1在健康的关节软骨中正常表达,但在病理性软骨中高度表达,其表达与骨关节炎等级成正比。同时吴绍军等[49]在实验中发现,抑制NOTCH信号的表达可下调Bax蛋白,并上调Bcl-2蛋白,可有效促进骨组织的早期发育和骨缺损的修复,加快骨和软骨的形成,从而抑制软骨细胞凋亡,尤其是有助于骨关节炎的治疗,对骨关节炎起到了重要的保护作用。此外LIU等[50]通过研究发现随着关节软骨中NOTCH的持续激活,软骨降解酶和促炎因子大量增加,出现了包括关节软骨退化、纤维化和滑膜扩张等在内的早期骨关节炎样病理。因此,必须实现NOTCH信号在软骨组织中的适当平衡,以维持正常的关节软骨稳定和关节完整性,进而有效控制骨关节炎的发展。 综上,根据NOTCH信号调节软骨合成代谢、分解代谢和纤维化基因调节的复杂性,靶向NOTCH通路和骨关节炎软骨细胞群可能是产生有效治疗该疾病的关键之一。期待未来的研究将致力于剖析这一复杂的调控机制,以揭示NOTCH诱导的骨关节炎的确切机制。 2.2.4 核因子κB信号通路 核因子κB是一种重要的转录因子,它可以通过影响凋亡相关蛋白(Bcl-2,Bax,Cyto-c,c-caspase3)的表达和分解代谢因子的合成,在调节骨关节炎诱导炎症基因、细胞因子和基质降解酶的表达中起重要作用。 核因子κB家族成员由RelA(p65)、RelB、C-Rel、核因子κB1(p105/p50)、核因子κB2(p100/p52)所组成,其中RelA(p65)和p50组成的异源二聚体是细胞内最常见、最具特异性的一种。目前大量研究发现核因子κB信号通路通过参与调节软骨细胞的增殖、分化及凋亡,在关节软骨发育及骨性关节炎的进展中起重要的作用。在稳定情况下,核因子κB在细胞质中以无活性形式与抑制蛋白 ( Inhibitor of κB,I-κB)相结合,在炎症递质(如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6等)的刺激下,上游的信号都传递至IκB 激酶,紧接着IκB 激酶使软骨细胞I-κB发生磷酸化,受到I-kB抑制的核因子κB得以暴露,此时活化的核因子κB从细胞质转移到细胞核,促进骨关节炎相关基因的表达,诱导关节软骨发生破坏并最终造成骨关节炎的发生[51]。同时核因子κB信号通路作为参与骨关节炎发病机制的主要分解代谢信号通路之一,其通过调节诱导型一氧化氮合酶,环氧化酶2,一氧化氮,前列腺素E2和基质金属蛋白酶等分解代谢因子的产生,进而加快了软骨炎症的发生及关节软骨细胞的凋亡[52]。 DAI等[53]在动物骨关节炎造模实验中的结果表明,治疗组在使用锦葵花色素后,核因子κB 信号通路受到了明显的抑制,从而引起白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α以及基质金属蛋白酶的表达降低,显著缓解了骨关节炎诱导的疼痛和炎症的发生。同时MA等[54]也在研究中发现,NLRX1通过抑制核因子κB信号通路激活从而减轻脂多糖诱导的软骨细胞凋亡和炎症,最终起到保护骨关节的作用,NLRX1可能是骨关节炎的潜在治疗靶点。PAN等[55]在评估大鼠骨关节炎的研究中发现,α-倒捻子素可以通过阻断核因子κB信号通路来降低白细胞介素1β诱导的大鼠软骨细胞凋亡,成功地抑制凋亡相关蛋白的表达和分解代谢因子的合成来保护软骨细胞,有效延缓了大鼠骨关节炎的进展。总之大量试验证实了核因子κB信号通路过度激活可导致软骨细胞凋亡和炎症的发生,因此通过抑制其活化,不仅可以达到治疗软骨炎症及骨细胞凋亡的目的,也可以有效地防止骨关节炎的发生,这为新药的开发和研究阐明了道路。"
| [1] 杨丰建,俞永林,夏军,等.基质金属蛋白酶-1/13与信号通路激酶ERKl/2在兔骨关节炎软骨中的表达[J].老年医学与保健,2007, 13(6):338-342. [2] LORIES RJ, MONTEAGUDO S. Review Article:Is Wnt Signaling an Attractive Target for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis?Rheumatol Ther. 2020;7(2):259-270. [3] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759. [4] XI Y, HUANG X, TAN G, et al. Protective effects of Erdosteine on interleukin-1β-stimulated inflammation via inhibiting the activation of MAPK,NF-κB,and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in rat osteoarthritis. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;873:172925. [5] LI H, PENG Y, WANG XI, et al. Astragaloside inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2019;41:497-503. [6] SCURUCHI M, D’ASCOLA A, AVENOSO A, et al. Serglycin as part of IL-1beta induced inflammation in human chondrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019;669:80-86. [7] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7:33–42. [8] 周炎,邓明,贺斌,等.大鼠诱发性骨关节炎模型构建研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2016,37(5):304-310. [9] ONISHI RM, GAFFEN SL. Interleukin-17 and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease.Immunology. 2010; 129:311-321. [10] LIU Y, PENG H, MENG Z, et al. Correlation of IL-17 Level in Synovia and Severity of Knee Osteoarthritis.Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1732-1736. [11] LEE J, LEE SY, KANG CM, et al. Interleukin-17 Enhances Germinal Center Formation and Immunoglobulin G1 Production in Mice.Rheum Dis. 2017;24:271-278. [12] ZHANG J, LI Q, CHANG S. The effects of particle density in moxa smoke on the ultrastructure of knee cartilage and expressions of TNF-α,IL-1b,BAX,and Bcl-2 mRNA in a rat model for osteoarthritis.J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(4):6589-6595. [13] 陈波,谢西梅,李佳霖.艾灸治疗对兔 KOA 软骨损伤及TNF-α、TGF-β1 和 IGF-1表达调节作用的实验研究[J].江苏中医药,2009, 41(6):69-71. [14] LIAO C, WANG S, ZHU S, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products increase TNF-α and IL-1β expression in chondrocytes via NADPH oxidase 4 and accelerate cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis progression. Redox Biol. 2020;28:101306. [15] MEDVEDEVA EV, GREBENIK EA, GORNOSTAEVA SN, et al. Repair of Damaged Articular Cartilage:Current Approaches and Future Directions. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8):2366. [16] 郭伟雄,魏波.炎症细胞因子及通路在骨关节炎中的研究进展[J].国际检验医学杂志,2015,36(15):2240-2241. [17] 李灿锋,陈卓,曾羿,等.骨形态发生蛋白信号通路在骨关节炎发病机制中的作用研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2017,11(5): 500-505. [18] CHIEN SY, TSAI CH, LIU SC, et al. Noggin Inhibits IL-1β and BMP-2 Expression,and Attenuates Cartilage Degeneration and Subchondral Bone Destruction in Experimental Osteoarthritis. Cells. 2020;9(4):E927. [19] THIELEN NGM, VAN DER KRAAN PM, VAN CAAM APM. TGFβ/BMP Signaling Pathway in Cartilage Homeostasis. Cells. 2019;8(9):969. [20] CHOI B, KIM S, FAN J, et al. Covalently conjugated transforming growth factor-β1 in modular chitosan hydrogels for the effective treatment of articular cartilage defects. Biomater Sci. 2015;3(5):742-752. [21] RUIZ M, MAUMUS M, FONTENEAU G, et al. TGFβi is involved in the chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and is dysregulated in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2019;27:493-503. [22] 樊志强,庞炜,杨连甲,等.白介素1受体拮抗剂及转化生长因子β1对兔膝关节骨性关节炎(OA)的治疗研究[J].现代生物医学进展, 2011,11(13):2447-2450. [23] WIEGERTJES R, VAN CAAM A, VAN BEUNINGEN H, et al. TGF-β dampens IL-6 signaling in articular chondrocytes by decreasing IL-6 receptor expression. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2019;27:1197-1207. [24] VAN DER KRAAN PM. The changing role of TGFbeta in healthy,ageing and osteoarthritic joints.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13:155-163. [25] CUNHA SI, PIETRAS K. ALK1 as an emerging target for antiangiogenic therapy of cancer. Blood. 2011;117:6999-7006. [26] TAN Y, LU K, LI J, et al. Prenatal caffeine exprosure increases adult female offspring rat’s susceptibility to osteoarthritis via low-functional programming of cartilage IGF-1 with histone acetylation. Toxicol Lett. 2018;295:229-236. [27] PASOLD J, ZANDER K, HESKAMP B, et al. Positive impact of IGF-1-coupled nanoparticles on the differentiation potential of human chondrocytes cultured on collagen scaffolds. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:1131-1143. [28] UCHIMURA T, FOOTE AT, SMITH EL, et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor II (IGF-II) Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Cartilage Matrix Loss and Promotes Cartilage Integrity in Experimental Osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2015; 116(12):2858-2869. [29] SCHWARZ S, MROSEWSKI I, SILAWAL S, et al. The interrelation of osteoarthritis and diabetes mellitus:considering the potential role of interleukin-10 and in vitro models for further analysis. Inflamm Res. 2018;67(4):285‐300. [30] BEHRENDT P, PREUSSE-PRANGE A, KLÜTER T, et al. IL-10 reduces apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation after injurious compression of mature articular cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(11):1981-1988. [31] VAN MEEGEREN ME, ROOSENDAAL G, COELEVELD K, et al. A single intra-articular injection with IL-4 plus IL-10 ameliorates blood-induced cartilage degeneration in haemophilic mice.Br J Haematol. 2013;160(4):515-520. [32] SONG SY, HONG J, GO S, et al. Interleukin-4 Gene Transfection and Spheroid Formation Potentiate Therapeutic Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteoarthritis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(5):e1901612. [33] WANG J, CHEN H, CAO P, et al. Inflammatory cytokines induce caveolin-1/β-catenin signalling in rat nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis through the p38 MAPK pathway. Cell Prolif. 2016;49(3):362-372. [34] Yao J, Weng Y, Yan S, et al. NOV inhibits proliferation while promoting apoptosis and migration in osteosarcoma cell lines through p38/MAPK and JNK/MAPK pathways. Oncology Reports. 2015;34(4): 2011-2021. [35] SUN HY, HU KZ, YIN ZS. Inhibition of the p38-MAPK signaling pathway suppresses the apoptosis and expression of proinflammatory cytokines in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Cytokine. 2017;90:135-143. [36] PRASADAM I, MAO X, SHI W, et al. Combination of MEK ERK inhibitor and hyaluronic acid has a synergistic effect on antihypertrophic and pro chondrogenic activities in osteoarthritis treatment. J Mol Med(Berl). 2013;91(3):369-380. [37] GARCÍA-VELÁZQUEZ L, ARIAS C. The emerging role of Wnt signaling dysregulation in the understanding and modification of age-associated diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2017;37:135-145. [38] ZHOU Y, WANG T, HAMILTON JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Osteoarthritis and in Other Forms of Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(9):53. [39] STAMPELLA A, MONTEAGUDO S, LORIES R. Wnt signaling as target for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2017;31(5):721-729. [40] SASSI L, LAADHAR M, ALLOUCHE B, et al. The roles of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling in human de-differentiated articular chondrocytes. Biotech Histochem. 2014;89(1):53-65. [41] 唐萌芽,倪慧英,张学民,等.补肾活血中药对膝骨关节炎患者经典 Wnt /β-catenin 通路调控作用的临床研究[J].中医正骨,2014, 26(8):12-14+17. [42] BLOM AB, BROCKBANK SM, VAN LENT PL, et al. Involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway in experimental and human osteoarthritis: prominent role of Wnt-induced signaling protein 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60( 2):501-512. [43] LIETMAN C, WU B, LECHNER S, et al. Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling ameliorates osteoarthritis in a murine model of experimental osteoarthritis. JCI Insight. 2018;3(3):e96308. [44] 张清,向明,陈杭,等.Notch 信号通路在骨关节炎软骨细胞中的表达及意义[J].局解手术学杂志,2018,27(4):240-245. [45] KOVALL RA, GEBELEIN B, SPRINZAK D, et al. The canonical notch signaling pathway:structural and biochemical insights into shape, sugar, and force. Developmental Cell. 2017;41(3):228. [46] LIU Z, REN Y, MIRANDO AJ, et al. Notch signaling in postnatal joint chondrocytes,but not subchondral osteoblasts,is required for articular cartilage and joint maintenance. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(4): 740-751. [47] ZHENG Y, LIU C, NI L, et al. Cell type-specific effects of Notch signaling activation on intervertebral discs:Implications for intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(7):5431-5440. [48] Mahjoub M, Sassi N, Driss M, et al. Expression patterns of Notch receptors and their ligands in osteoarthritic and healthy human knee cartilage. Tissue and Cell. 2012;44(3):182-194. [49] 吴绍军,刘俊才,左银龙,等.Notch信号通路在膝骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡中的作用研究[J].华西医学,2018,33( 9):1162 -1167. [50] Liu Z, Chen J, Mirando AJ, et al. A dual role for NOTCH signaling in joint cartilage maintenance and osteoarthritis. Sci Signal. 2015; 8(386):71-76. [51] Rigoglou S, Papavassiliou AG. The NF-κB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(11):2580-2584. [52] Ji B, Guo W, Ma H, et al. Isoliquiritigenin suppresses IL-1β induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocyte-like ATDC5 cells by inhibiting NF-κB and exerts chondroprotective effects on a mouse model of anterior cruciate ligament transection. Int J Mol Med. 2017; 40(6):1709-1718. [53] Dai T, Shi K, Chen G, et al. Malvidin attenuates pain and inflammation in rats with osteoarthritis by suppressing NF-κB signaling pathway. Inflamm Res. 2017;66(12):1075-1084. [54] Ma D, Zhao Y, She J, et al. NLRX1 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocytes by suppressing the activation of NF-κB signaling. International Immunopharmacology. 2019;71:7-13. [55] Pan T, Chen R, Wu D, et al. Alpha-Mangostin suppresses interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis in rat chondrocytes by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway and delays the progression of osteoarthritis in a rat model. International Immunopharmacology. 2017;52:156-162. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [4] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [5] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [6] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [7] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [8] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [9] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [10] | Gu Xia, Zhao Min, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Relationship between hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha and hypoxia signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1284-1289. |
| [11] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [12] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [13] | Wu Xun, Meng Juanhong, Zhang Jianyun, Wang Liang. Concentrated growth factors in the repair of a full-thickness condylar cartilage defect in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [14] | Shen Jinbo, Zhang Lin. Micro-injury of the Achilles tendon caused by acute exhaustive exercise in rats: ultrastructural changes and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1190-1195. |
| [15] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||