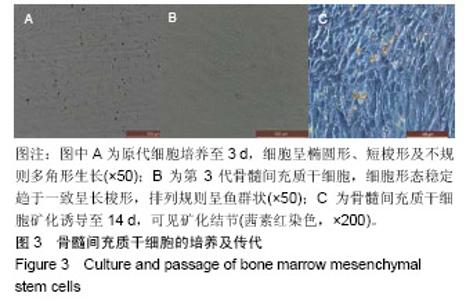
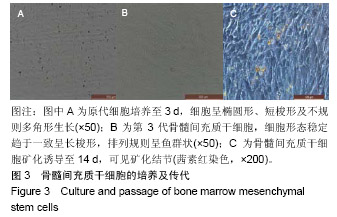
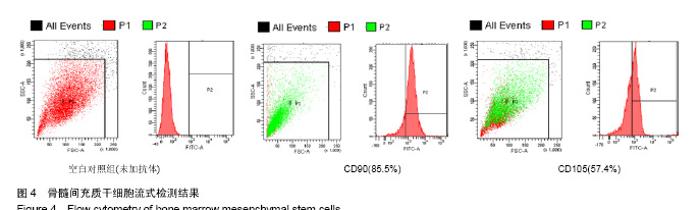
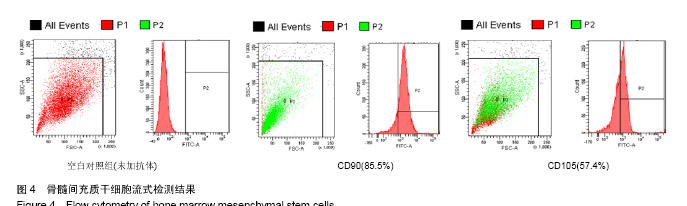
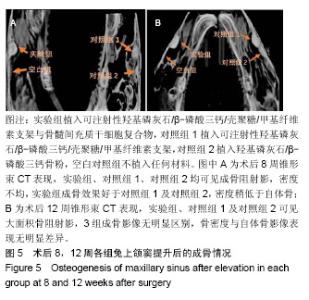
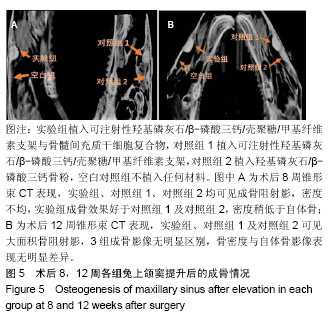
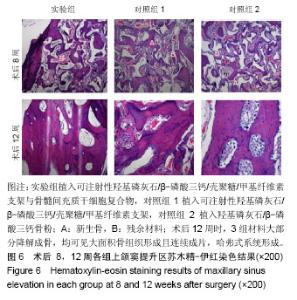
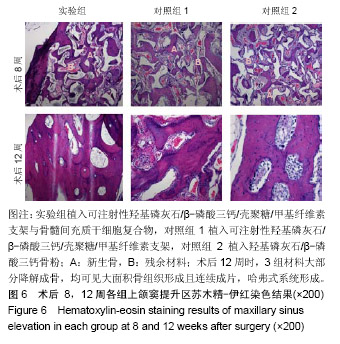
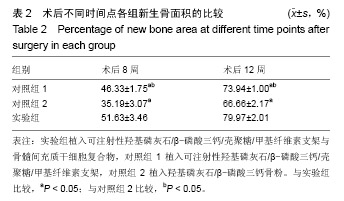
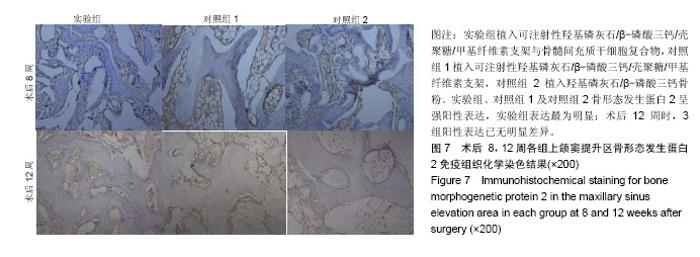
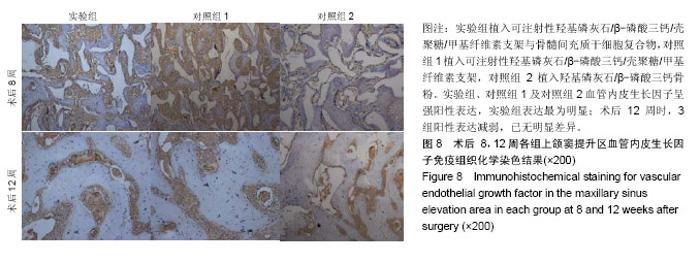
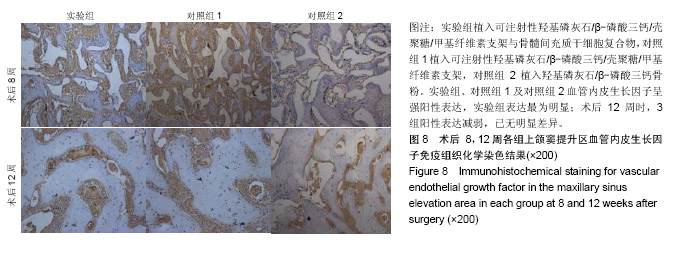
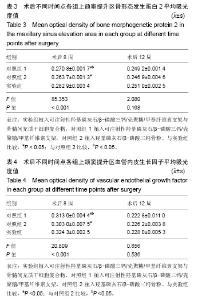
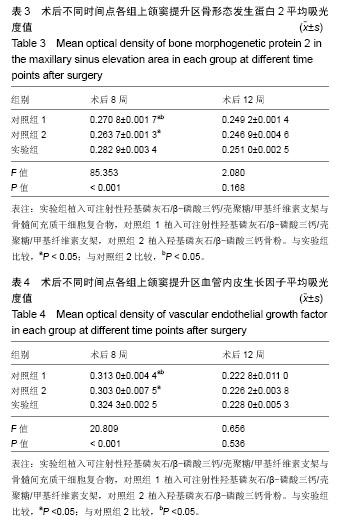
| [1]Kaufman E.Maxillary sinus elevation surgery: an overview.J Esthet Restor Dent.2003;15(5): 272-282.[2]Nandi SK,Kundu B,Ghosh SK,et al. Efficacy of nano-hydroxyapatite prepared by an aqueous solution combustion technique in healing bone defects of goat.J Vet Sci.2008;9(2):183-191.[3]Nishida J,Shimamura T.Methods of reconstruction for bone defect after tumor excision: a review of alternatives. Med Sci Monit.2008;14(8):RA107-113.[4]Grassi L,Isaksson H.Extracting accurate strain measurements in bone mechanics: A critical review of current methods.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2015;50:43.[5]李雅梅.HA/β-TCP/CS/MC可注射组织工程支架材料的制备与分析[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2017.[6]Han TY, Liu XW,Liang N,et al.In vitro effects of recombinant adenovirus-mediated bone morphogenetic protein 2/vascular endothelial growth factor 165 on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol.2017;45(1):108-114.[7]肖仕辉,韦庆军,赵劲民,等.全骨髓贴壁法培养兔骨髓间充质干细胞体外定向成骨诱导分化及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(6):1069-1074.[8]Abdallah BM,Kassem M.The use of mesenchymal (skeletal) stem cells for treatment of degenerative diseases: current status and future perspectives.J Cell Physiol. 2009;218(1): 9-12.[9]曾嘉芙,吴涛,郑文龙,等.SDF-1α复合Pluronic F-127对兔上颌窦底提升术成骨影响的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志, 2016, 26(5):339-345.[10]Rabah N,Nathalie N,Marc EH,et al.Osteotome sinus floor elevation procedure for first molar single-gap implant rehabilitation: a case series.Implant Dent. 2014;23(6): 760-767.[11]Boyne PJ,James RA.Boyne PJ,et al.Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone.J Oral Surg. 1980;38(8):613-616.[12]Dos Santos Pereira R,Boos FB,Gorla LF,et al.Maxillary Sinus Elevation Surgery with ChronOS and Autogenous Bone Graft: Immunohistochemical Assessment of RUNX2, VEGF, TRAP, and Osteocalcin.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2017; 37(6):e321-e327.[13]Nauth A,Lane J,Watson JT,et al.Bone Graft Substitution and Augmentation. J Orthop Trauma.2015;29 Suppl 12:S34.[14]Gupta P,Adhikary M,Jc M,et al.Biomimetic, Osteoconductive Non-mulberry Silk Fiber Reinforced Tricomposite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(45):30797-30810.[15]Pu Y,Wu H,Lu S,et al.Adiponectin Promotes Human Jaw Bone Marrow Stem Cell Osteogenesis.J Dent Res. 2016; 95(7):769-775.[16]刘洪亚.壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石骨复合支架修复关节软骨损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(2):244-248.[17]王松,杨函,杨剑,等.多孔磷酸钙/骨基质明胶复合骨水泥修复兔腰椎骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017,(12): 1462-1467.[18]PLOS ONE Staff.Correction: Decellularized Wharton's Jelly from human umbilical cord as a novel 3D scaffolding material for tissue engineering applications.PLoS One. 2017;12(3): e0172098.[19]de Oliveira Gonçalves JB,Buchaim DV,de Souza Bueno CR,et al.Effects of low-level laser therapy on autogenous bone graft stabilized with a new heterologous fibrin sealant.J Photochem Photobiol B.2016;162:663-668.[20]Patrick O,Ana RR,Venkatesan JK,et al.Current perspectives in stem cell research for knee cartilage repair. Stem Cells Cloning.2014;7:1-17.[21]Grgurevic L,Macek B,Mercep M,et al.Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)1-3 enhances bone repair. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2011;408(1):25-31.[22]Kuzaka B,Janiak M,W?odarski KH,et al. Expression of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and -7 in urinary bladder cancer predicts time to tumor recurrence.Arch Med Sci. 2015;11(2): 378-384.[23]Deckers MM,van Bezooijen RL,van der Horst G,et al.Bone morphogenetic proteins stimulate angiogenesis through osteoblast-derived vascular endothelial growth factor A.Endocrinology.2002;143(4):1545-1553.[24]Maes C,Carmeliet P,Moermans K,et al.Impaired angiogenesis and endochondral bone formation in mice lacking the vascular endothelial growth factor isoforms VEGF164 and VEGF188.Mech Dev. 2002;111(1):61-73.[25]孙丽君,吴大明,杨路,等.不植骨上颌窦内提升术种植的临床疗效观察[J].口腔医学,2018,38(4):324-328.[26]张耀升,周知航,王烨欣,等.犬上颌窦内提升植骨与不植骨的成骨效果比较[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2018,16(4):317-321. |