Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (34): 5445-5451.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0679
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influence of additives on the tetragonal phase purity and grain size of zirconia
Zang Sitian1, Yang Qian1, He Ningxiang1, Ji Yang2, Yang Huazhe1
- 1School of Fundamental Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China; 2Department of Stomatology, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110840, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2018-07-31Online:2018-12-08Published:2018-12-08 -
Contact:Yang Huazhe, MD, Professor, School of Fundamental Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zang Sitian, Master candidate, School of Fundamental Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81500897; the grant from China Scholarship Council, No. 201408210385
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zang Sitian, Yang Qian, He Ningxiang, Ji Yang, Yang Huazhe. Influence of additives on the tetragonal phase purity and grain size of zirconia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(34): 5445-5451.
share this article
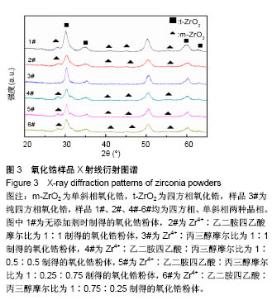
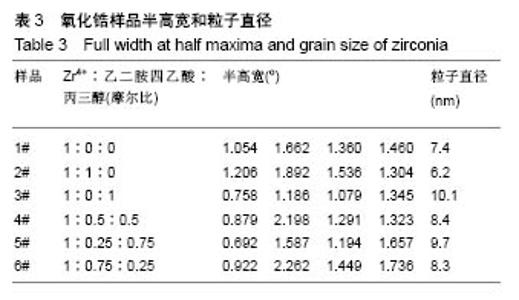
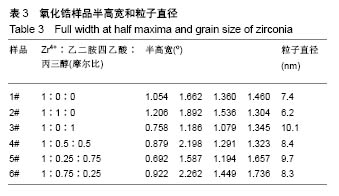
2.2 氧化锆样品X射线衍射图谱 图3为通过水热法所制备得到的含不同比例添加剂的粉末状样品X射线衍射图谱。分别对6个样品中4个最强衍射峰进行高斯拟合,分别得到半高宽为1.054°、1.662°、1.360°、1.460°(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0∶0);1.206°、1.892°、1.536°、1.304° (Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶1∶0);0.758°、1.186°、1.079 °、1.345°(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0∶1);0.879°、2.198°、1.291°、1.323°(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0.5∶0.5);0.692°、1.587°、1.194°、1.657°(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0.25∶0.75);0.922°、2.262°、1.449°、1.736°(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0.75∶0.25)。"
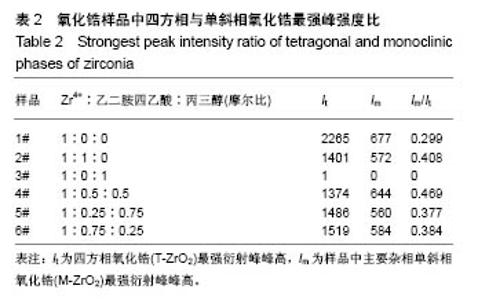
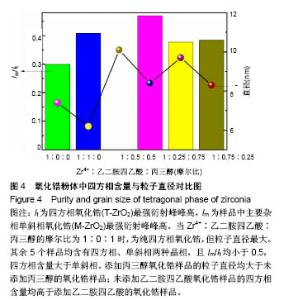
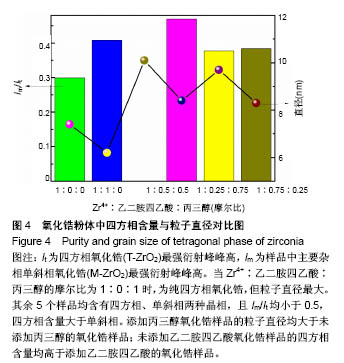
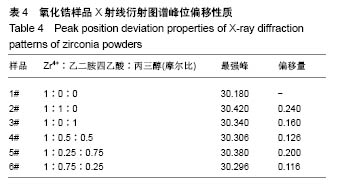
6个样品中Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇的值分别为1∶0∶0,1∶1∶0,1∶0∶1,1∶0.5∶0.5,1∶0.25∶0.75, 1∶0.75∶0.25,6个样品的X射线衍射图谱都出现了较为明显的4个衍射峰,说明样品均形成了晶体。从4个主要衍射峰的位置上来看,在20°-65°范围内,6个样品并无明显差别,但是从衍射峰强度来看却有较为明显的差别。与JCPDS库中标准卡片对比,确定了6个样品中均有四方相氧化锆,(101)峰位分别为30.180°、30.420°、30.340°、30.306°、30.380°、30.296°,(110)峰位分别为35.338°、35.518°、35.360°、35.302°、35.340°、35.381°,(112)峰位分别为50.300°、50.540°、50.680°、50.460°、50.480°、50.480°,(211)峰位分别为60.179°、60.398°、60.280°、60.099°、60.200°、60.281°,(202)峰位分别为62.940°、63.040°、63.120°、63.000°、63.240°、63.240°。其中,3#样品为纯四方相氧化锆,1#、2#、4#、5#、6#样品均出现了杂相峰,与标准卡片对比,确定了5个样品中均出现有单斜相氧化锆,(-111)峰位分别为28.197°、28.280°、28.241°、28.182°、28.320°,(-211)峰位分别为40.827°、40.911°、40.901°、40.834°、40.880°,(112)峰位分别为44.887°、45.017°、45.216°、45.221°、44.996°,(013)峰位分别为55.453°、55.540°、55.796°、55.561°、55.572°。所以,实验制得的样品均为氧化锆,X射线衍射图谱并未出现其他物质衍射峰,说明样品中不含有其他物质杂相。其中,3#样品为纯四方相氧化锆,1#、2#、4#、5#、6#样品为四方相氧化锆和单斜相氧化锆2种晶型结构。说明与其他样品相比,未添加EDTA、只添加丙三醇时可制得纯四方相氧化锆。 取It为四方相氧化锆(T-ZrO2)最强衍射峰峰高,Im为样品中主要杂相单斜相氧化锆(M-ZrO2)最强衍射峰峰高,根据公式(1)得出,1#、2#、4#、5#、6#样品单斜相与四方相氧化锆最强峰的峰高比值分别为0.299(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0∶0),0.408(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶1∶0),0(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0.5∶0.5),0.377(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0.25∶0.75),0.384(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0.75∶0.25),如表2和图3所示。Im/It值均< 1,说明样品中四方相氧化锆的含量大于单斜相氧化锆的含量,且两相比例与各添加剂的量无明显线性关系,说明此次实验条件更利于四方相氧化锆的形成。与无添加剂的1# (Im/It=0.299) 样品相比,2#只添加EDTA时四方相比例(Im/It=0.408)减小,3#只添加丙三醇时为纯四方相氧化锆。与1#、3#样品相比,其余4个样品,无论是单独添加EDTA还是同时添加EDTA和丙三醇,均会使四方相比例(Im/It分别为0.408、0.469、0.377、0.384)降低。"
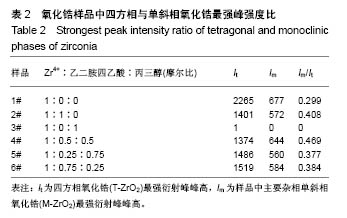
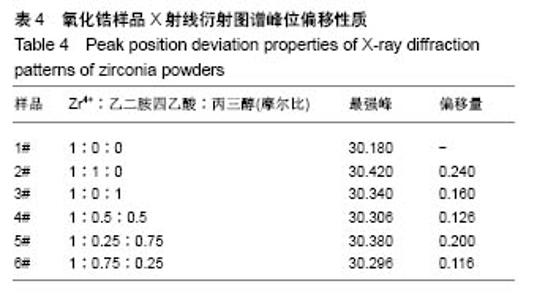
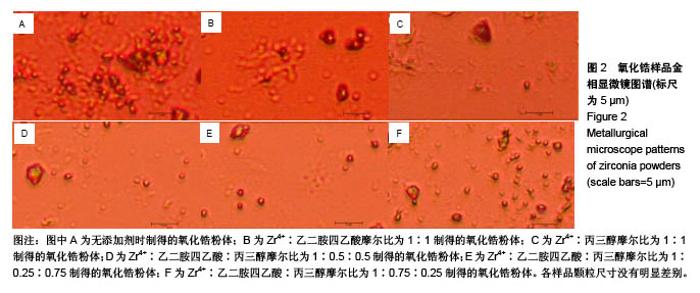
与无添加剂1#样品相比,2#只添加EDTA时粒子直径减小,但四方相比例也降低。3#只添加丙三醇时,粒子直径增大,且为6个样品中最大,但可制得纯四方相氧化锆。对于同时添加EDTA和丙三醇的4#、5#、6#样品与1#相比,同时添加EDTA和丙三醇会使粒子直径增大,四方相比例降低。5#、6#样品与只添加EDTA的2#相比,四方相含量提高,但粒子直径也增大;与只添加丙三醇的3#相比,粒子直径减小,但是四方相含量降低;其中5#样品,即Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇摩尔比值为1∶0.25∶0.75时四方相比例最高,但粒子直径也最大。Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇摩尔比值为1∶0.75∶0.25时,较1∶0.5∶0.5时四方相比例相对较高,且粒子直径相对较小。 与无添加剂的1#样品相比,其余5个样品的峰位均向右偏移,说明加入EDTA或丙三醇均使峰位右偏,偏移量分别为0.240(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶1∶0)、0.160 (Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0∶1)、0.126(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇= 1∶0.5∶0.5)、0.200(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0.25∶0.75)、0.116(Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇=1∶0.75∶0.25),见表4,且偏移量与各添加剂的量无明显线性关系。 综上所述,对于实验制备的氧化锆样品而言,EDTA主要的作用在于可降低粒子直径,但会降低四方相比例;丙三醇的主要作用在于提高四方相比例,但会增大粒子直径;加入EDTA或丙三醇均使峰位右偏,所以,Zr4+∶EDTA∶丙三醇的最合适比值还有待于进一步研究。 "
| [1] 王艳菊,张喜梅,陈玲,等.pH及浓度对微乳体系中溶胶—凝胶法制备氧化锆纳米粉体的影响[C]//海南全国粉体技术研讨会, 2001.[2] 郭振兴,张少锋,孙亚丽,等.齿科CAD/CAM氧化锆陶瓷的二体动态磨损行为研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2018,28(1):26-31.[3] 程竑,董聪,张富强.摩擦化学法硅涂层对氧化锆陶瓷粘接强度的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2018,27(3):248-251.[4] Veerachamy S, Hameed P, Sen D, et al. Studies on Mechanical, Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Activity of Plasma Sprayed Nano/Micron Ceramic Bilayered Coatings on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy for Biomedical Application. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;18(7):4515-4523. [5] Kim S, Kim MI, Shon M, et al. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Epoxy Composites Containing Zirconia-Impregnated Halloysite Nanotubes with Different Loadings. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;18(9):6152. [6] 杨倩,常世杰,王强,等.氧化锆全瓷冠修复体饰面瓷折裂影响因素的研究进展[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2015,29 (5):300-303.[7] You R, Hao X, Yu H, et al. High performance mixed-potential-type Zirconia-based NO 2, sensor with self-organizing surface structures fabricated by low energy ion beam etching. Sensor Actuat B Chem. 2018;263:445-451. [8] Garvie RC, Nicholson PS. Phase Analysis in Zirconia Systems. J Am Ceram Soc.2010;55(6):303-305. [9] Kim J, Dhital S, Zhivago P, et al. Viscoelastic finite element analysis of residual stresses in porcelain-veneered zirconia dental crowns.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;82: 202-209.[10] Pecharromán C, Bartolomé JF, Requena J, et al. Percolative Mechanism of Aging in Zirconia‐Containing Ceramics for Medical Applications. Adv Mater. 2018;15(6):507-511. [11] Kaliaraj GS, Vishwakarma V, Kirubaharan K, et al. Corrosion and biocompatibility behaviour of zirconia coating by EBPVD for biomedical applications. Surf Coat Technol. 2018;334: 336-343. [12] Shibata N, Yamamoto T, Ikuhara Y, et al. Structure of [110] tilt grain boundaries in zirconia bicrystals. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 2018;50(6):429-433. [13] 吴昊,史春燕,付晓辉,等.低温水热法制备纳米氧化锆粉体[J].硅酸盐通报,2015,34(11):3247-3250.[14] Yan Y, Chen W, Bai B, et al. Zirconia films prepared by sol-gel method on surface of ZrH1. 8 in different heat treatment atmospheres. Chin J Rare Metals. 2017;41; 179-183. [15] 张雄飞,王成峰.电化学合成氧化锆纳米粉体[J].硅酸盐学报, 2006,34(3):389-392.[16] Guilardi LF, Pereira GK, Gündel A, et al. Surface micro-morphology, phase transformation, and mechanical reliability of ground and aged monolithic zirconia ceramic. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2017;65:849-856. [17] Sutharsini U, Thanihaichelvan M, Ting CH, et al. Effect of two-step sintering on the hydrothermal ageing resistance of tetragonal zirconia polycrystals. Ceram Int. 2017;43(10): 7594-7599. [18] Peng MD, Wei JQ, Wang YN, et al. Microstructure and nanoindentation analyses of low-temperature aging on the zirconia-porcelain interface. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;66:119-126. [19] Yang H, Ji Y. Low-temperature Degradation of Zirconia-based All-ceramic Crowns Materials: A Mini Review and Outlook. J Mater Sci Technol. 2016;32(7):593-596. [20] Bahamirian M, Hadavi SMM, Rahimipour MR, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Nanoparticles Doped with Ytterbium and Gadolinium: ZrO 2, 9. 5Y 2 O 3, 5. 6Yb 2 O 3, 5. 2Gd 2 O 3. Metallu Mater Trans A. 2018;49(6):1-10. [21] Courtin E, Boy P, Rouhet C, et al. Optimized Sol–Gel Routes to Synthesize Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Thin Films as Solid Electrolytes for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells. Chem Mater. 2017; 24(23):4540. [22] Park SY, Kim JH, Kim MC, et al. Microscopic observation of degradation behavior in yttria and ceria stabilized zirconia thermal barrier coatings under hot corrosion. Surf Coat Technol. 2005;190(2):357-365. [23] Deville S, Attaoui HE, Chevalier J. Atomic force microscopy of transformation toughening in ceria-stabilized zirconia. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2017;25(13):3089-3096. [24] Nakonieczny DS, Paszenda ZK, Basiaga M, et al. Phase composition and morphology characteristics of ceria-stabilized zirconia powders obtained via sol-gel method with various pH conditions. Acta Bioengi Biomech. 2017;19(2): 21. [25] Yang H, Han L, Zhao L, et al. Optimization of Experimental Parameters to the Formation of ZrO2 Phase via Hydrothermal Method[C]// Advances in Engineering Materials and Applied Mechanics: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machinery, Materials Science and Engineering Application. 2015. [26] 孙笑非,宋秀芹.直接沉淀法制备棒状氧化锆[J].人工晶体学报, 2006,35(3):651-654.[27] 高龙柱,陈洪龄,徐南平.低温水热合成四方相纳米二氧化锆[J].化工学报,2005,56(3):551-554.[28] Yu H, Zhi Z, Zhang C, et al. Research on Literature Involving Zirconia-Based on Pubmed Database: A Bibliometric Analysis. Curr Sci. 2017;112(6):1134-1137. [29] Ji Y, Zhang X, Wang X, et al. Zirconia Bioceramics as All-Ceramic Crowns Materials: a Review. Rev Adv Mater Sci. 2013;34(1):72-78. [30] Ahmad I, Bashir M, Sadaqat A, et al. Effects of Temperature on Zirconia Nanoparticles During and after Synthesis. Mater Today Proc.2015;2(10):5786-5792. [31] Tana F, Serafini A, Lutterotti L, et al. Particle anisotropy and crystalline phase transition in one-pot synthesis of nano-zirconia: a causal relationship. Crystengcomm, 2017;20(Suppl). DOI: 10.1039/C7CE01949A[32] Hajizadeh-Oghaz M, Razavi RS, Ghasemi A. The Effect of Solution pH Value on the Morphology of Ceria–Yttria Co Stabilized Zirconia Particles Prepared Using the Polymerizable Complex Method. J Clust Sci. 2016;27(2): 469-483. [33] Abdelaal HM. “One-Pot Path for the Synthesis of Hollow Zirconia Sub-Microspheres Using Hydrothermal Approach”. Mater Lett. 2017;212. DOI: 10. 1016/j. matlet. 2017. 10. 083[34] Masoodiyeh F, Mozdianfard MR, Karimi-Sabet J. Modeling zirconia nanoparticles prepared by supercritical water hydrothermal synthesis using population balance equation. Powder Technol. 2017;317:264-274. [35] 舒展霞.二氧化锆纳米材料的水热/溶剂热法控制合成及性质表征[D].济南:山东大学,2012.[36] 刘力.纳米二氧化锆颗粒的合成及形成机理的研究[D].上海:东华大学, 2014.[37] Peng W, Wang K, Jin HU, et al. Research Progress on Preparation of Pure / Doped Nano-zirconia Powders by Hydrothermal. Mater Rev. 2013;27(19):146-149. [38] Ao H, Yu Y, Long Z, et al. A Brief Review on Synthesis Methods of Ultrafine Zirconia-Based Powders. ChinJ Rare Metals. 2013;39(5):1525-1526. [39] Gremillard L, Wei C, Chevalier J, et al. A fast, stepwise procedure to assess time-temperature equivalence for hydrothermal ageing of zirconia-based materials. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2018;38(1):181-186. [40] Pakma O, Özdemir C, Kariper A, et al. Wet chemical methods for producing mixing crystalline phase ZrO2 thin film. Appl Surf Sci. 2016;377:159-166. [41] Keizer K, Hemert MV, Van De Graaf MA, et al. Tetragonal zirconia: Wet chemical preparation, mechanical and electrical properties. Solid State Ionics. 1985;16(1-4):67-72. [42] Nath S, Biswas A, Kour PP, et al. Synthesis of Mesoporous Nanocrystalline Zirconia by Surfactant-Assisted Hydrothermal Approach. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;18(8):5390. [43] Gupta PK, Khan ZH, Solanki PR. Effect of Nitrogen Doping on Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Zirconia Nanoparticles. Adv Sci Lett. 2018;24(2):867-872. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Li Jing, Xie Jianshan, Cui Huilin, Cao Ximei, Yang Yanping, Li Hairong. Expression and localization of diacylglycerol kinase zeta and protein kinase C beta II in mouse back skin with different coat colors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1196-1200. |
| [3] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [4] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [6] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [7] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [8] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [9] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [10] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [11] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||