Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (33): 5393-5398.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0655
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism and application of stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke
Zhang Dong-lin1, Li Dan1, Wang Min-juan2
- 1Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710021, Shaanxi Province, China; 2the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2018-07-22Online:2018-11-28Published:2018-11-28 -
Contact:Wang Min-juan, Doctorate candidate, Associate chief physician, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhang Dong-lin, Master candidate, Xi’an Medical University, Xi’an 710021, Shaanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Dong-lin, Li Dan, Wang Min-juan. Mechanism and application of stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(33): 5393-5398.
share this article
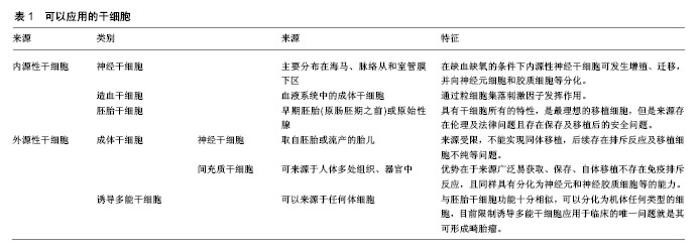
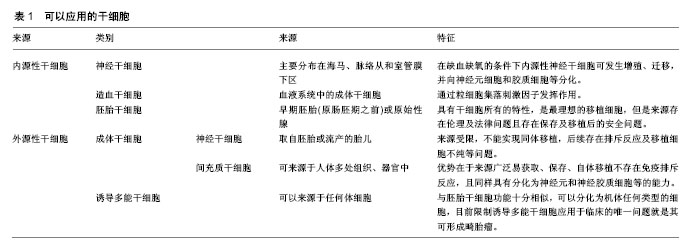
2.1 干细胞的特殊性 干细胞是一类具有多向分化和自我更新潜能的细胞。在适当的条件下,其可以分化成各种功能细胞,如神经元和少突胶质细胞。这使得干细胞基础及转化医学相关研究成为当前国际上最受关注的领域之一,随着干细胞技术的不断发展,干细胞应用于越来越多疾病的治疗,包括中枢神经系统疾病、心肌损伤、骨关节炎、糖尿病、肝脏疾病、肿瘤等[6]。缺血性脑卒中发病后对于不同种(系)的神经细胞都有影响,这种复杂和广泛的神经元-胶质细胞-内皮细胞相互作用并影响,这就要求用于治疗缺血性脑卒中损伤的移植细胞需要具有干细胞的特性,即分化潜能,可在特定的条件下分化、增殖为成熟的体细胞,如神经细胞、胶质细胞、内皮细胞等。因此,细胞移植只能利用干细胞作为主要的移植细胞治疗缺血性脑卒中。 2.2 干细胞移植治疗缺血性脑卒中可能的机制 干细胞移植治疗缺血性脑卒中可能的作用机制:①细胞替代:移植的干细胞进入脑组织结构中,代替损伤的神经元,促进神经传导通路和连接结构的重建;来源于骨髓的骨髓间充质干细胞可分泌碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、胎盘生长因子、血管内皮生长因子等多种细胞因子,可诱导大脑缺血边界区形成新的血管[7-11];②神经保护和营养:移植的干细胞可分泌神经营养分子、酶、细胞因子等;如脑源性神经营养因子、神经生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子、胶质细胞源性神经营养因子、肝细胞生长因子、表皮生长因子、干细胞因子等,这些因子在脑损伤的保护和促进已损伤神经功能的恢复中起着重要的作用[12-13]。以脑源性神经营养因子为例,脑源性神经营养因子可与其具有高亲和力的酪氨酸激酶受体B蛋白结合启动膜受体酪氨酸蛋白激酶信号传导途径和磷脂酶C信号传导途径等细胞内信号传导途径,发挥促进神经再生和保护作用[14]。在大鼠实验中证实干细胞分泌的神经营养因子可增强神经细胞发生,并减少卒中大鼠模型脑中的小胶质细胞/巨噬细胞浸润,促进卒中后功能恢复[15]。此外,Jablonska等[16]将人脐血衍生神经干细胞移植入缺血性卒中大鼠模型中的研究证实缺血事件可促进内源性神经再生,这可能是通过激活内源性干细胞从而促进内源性神经发生,促进脑损伤区域的内源性神经营养因子表达增加;③炎症和免疫调节:移植的干细胞可以通过抑制炎症局部T淋巴细胞和巨噬细胞的分化阶段发挥免疫调节减轻炎症反应,M1型巨噬细胞或小胶质细胞可分泌破坏性的炎性介导因子,而M2型巨噬细胞或小胶质细胞则能够分泌营养因子对组织起到保护作用,还可以清除损伤的细胞或细胞碎片可促进预后恢复[17-18]。而干细胞可通过分泌因子作用于巨噬细胞,使其由M1型转变为M2型,影响免疫分泌的细胞因子图谱,从而抑制和极化胶质细胞[19-20]。 2.3 可以应用的干细胞类别 治疗缺血性脑卒中的干细胞中可分为内源性和外源性2种类型。前者是应用自身的干细胞,包括神经干细胞和造血干细胞。内源性神经干细胞存在于人类和其他哺乳动物中枢神经系统中,主要分布在海马、脉络从和室管膜下区,在缺血缺氧的条件下内源性神经干细胞细胞可发生增殖、迁移,并向神经元细胞和胶质细胞等分化,进而修复中枢神经系统[21-22],造血干细胞则是通过粒细胞集落刺激因子发挥作用,但由于条件不足且数量有限没有能形成足够的细胞来完全修复缺血损伤区[23-24]。 可用于移植的外源性干细胞主要有胚胎干细胞、成体干细胞和诱导多能干细胞[8]。胚胎干细胞具有干细胞所有的特性,具有在适当的环境、条件下转换为任何神经细胞的潜能,是最理想的移植细胞,但是由于其来源存在伦理及法律问题且存在保存及移植后的安全问题[25-26]。虽然胚胎干细胞移植在缺血性脑卒中动物模型研究中表现出理想的效果,但要应用于人类治疗还受到多方面限制[27-28]。 外源性成体干细胞包括神经干细胞和间充质干细胞,外源性神经干细胞一般取自胚胎或流产的胎儿,Huang等[29]在动物实验中证实神经干细胞治疗效果显著,但是由于来源受限,不能实现同体移植,且后续存在排斥反应及移植细胞不纯等问题,目前难以应用于临床。间充质干细胞属于成体干细胞中的一大类,其研究最多、使用最广,可来源于人体多处组织、器官中[30]。根据来源不同可分为骨髓间充质干细胞、脐血间充质干细胞、脐带间充质干细胞以及脂肪间充质干细胞等[31]。间充质干细胞的优势在于来源广泛易获取、保存、自体移植不存在免疫排斥反应,且同样具有分化为神经元和神经胶质细胞等的能力。已经开始应用于临床试验,Honmou等[32]应用自体人间充质干细胞进行移植,首次评估了干细胞治疗缺血性脑卒中的可行性与安全性,在其后5年的随访中虽然患者的神经功能恢复的不理想,但并没有发现不良反应。Honmou等[33]在其另一试验中经静脉注射自体骨髓间充质干细胞,对12例缺血性脑损伤患者进行试验,在移植后一周患者的NIHSS评分持续改善,MRI显示梗死体积减小,且无不良反应。 诱导多能干细胞最早是由Kazutoshi Takahashi和Shinya Yamanaka报道,由于其可以来源于任何体细胞,所以被认为是过去的十余年中干细胞领域中最令人兴奋的突破之一[34]。诱导多能干细胞与胚胎干细胞功能十分相似,可以分化为机体任何类型的细胞,目前限制诱导多能干细胞应用于临床的唯一问题就是其可形成畸胎瘤,如果这一问题得以解决,那么诱导多能干细胞在细胞移植方面拥有巨大潜力[35-36]。除了上述几种干细胞外,目前在研究的可应用于移植治疗缺血性脑卒中的细胞还包括人畸胎瘤衍生的细胞、源自人类第3磨牙的成人牙髓干细胞、内皮祖细胞等[37-38]。见表1。"
| [1] O'Neill D. Global burden of stroke: an underestimate. Lancet. 2014; 383(9924): 1205-1206.[2] Borlongan CV, Jolkkonen J, Detante O. The future of stemcell therapy for stroke rehabilitation. Future Neurol. 2015;10(4): 313-319.[3] Hara T, Abo M, Kakita K, et al.Does a combined intervention program of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and intensive occupational therapy affect cognitive function in patients with post-stroke upper limb hemiparesis?Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(12):1932-1939.[4] Liu X, Ye R, Yan T, et al. Cell based therapies for ischemic stroke: from basic science to bedside. ProgNeurobiol. 2014; 115:92-115.[5] Zhang Z, Michael C. Neural stem cells and ischemic brain. Stroke.2016; 18(3):267-272.[6] Trounson A, Mcdonald C. Stem cell therapies in clinicaltrials: Progress andchallenges. Cell Stem Cell.2015;17(1):11-22. [7] Wakabayashi K, Nagai A, Sheikh AM, et al. Transplantation of humanmesenchymal stem cells promotes functional improvement and increasedexpression of neurotrophic factors in a rat focal cerebral ischemia model. NeurosciRes. 2010;88(5):1017-25.[8] 张倩,胡荣,郑江,等.干细胞移植治疗脑出血的关键影响因素研究进展[J].中国卒中杂志,2015,10(10):890-895.[9] 李芸,王昭君,谢怡,等.间充质干细胞移植治疗缺血性卒中的临床研究进展[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2014, 11(3):165-168.[10] 涂雪松.干细胞移植治疗缺血性脑血管病实验研究进展[J].中国脑血管病杂志, 2014,11(8):440-445.[11] 裴远,靳令经,聂志余.不同类型干细胞移植治疗缺血性脑卒中的研究现状[J].上海医学, 2012,35(1):84-87.[12] Ishizaka S, Horie N, Satoh K, et al. Intra-arterial cell transplantation provides timing-dependent cell distribution and functional recovery afterstroke. Stroke. 2013;44(3): 720-726. [13] Aboody K,Capela A,Niazi N,et al.Translating stemcell studies to the clinic for CNS repair: current state ofthe art and the need for a Rosetta stone. Neuron.2011;70(4): 597-613. [14] 师佳,戴丹,李洋洋,等.脑卒中后抑郁大鼠海马小胶质细胞脑源性神经营养因子及酪氨酸激酶受体B蛋白的表达[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2018,20(01):83-87.[15] Tsai MJ, Tsai SK, Hu BR, et al. Recovery of neurological function of ischemic stroke by application of conditioned medium of bone marrowmesenchymal stem cells derived from normal and cerebral ischemia rats. Biomed Sci, 2014; 21(1):5.[16] Jablonska A, Drela K, Wojcikstanaszek L, et al. Shortlived human umbilical cord-blood-derived neural stemcells influence the endogenous secretome and increase thenumber of endogenous neural progenitors in a rat model oflacunar stroke. Mol Neurobiol.2016;53(9):1-13.[17] Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12): 958-969.[18] David S, Kroner A. Repertoire of microglial and macrophage responses after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011; 12(7):388-399.[19] Omi M, Hata M, Nakamura N, et al. Transplantation of dental pulp stem cells suppressed inflammation in sciatic nerves by promoting macrophage polarization towards anti-inflammation phenotypes and ameliorated diabetic polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Investig. 2016;7(4):485-496. [20] Hu X, Leak RK, Shi Y, et al. Microglial and macrophage polarization-new prospects for brain repair. Nature Rev Neurol. 2015;11(1):56-64.[21] Zheng W, Zhu GQ, Zhong M, et al. Neurogenesis in adult human brain after traumatic brain injury. Neurotrauma, 2013; 30(22):1872-1880.[22] Christian KM, Song H, Ming GL. Functions and dysfunctions of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2014;37:243-262.[23] Popa-Wagner A, Stocker K, Balseanu AT, et al. Effects of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor after stroke in aged rats. Stroke, 2010;41(5):1027-1031.[24] Erlandsson A, Lin A, Yu FG, Morshead C. Immunosuppression promotes endogenous neural stem and progenitor cell migration and tissue egeneration after ischemic injury. Exp Neurol. 2011;230(1):48-57. [25] Trounson A. The production and directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Endocr Rev.2006;7(2):208-219.[26] Seminatore C, Polentes J, Ellman D, et al. The postischemic environment differentially impacts teratoma or tumor formation after transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors. Stroke. 2010;41(1):153-159.[27] Martino G, Pluchino S. The therapeutic potential of neural stem cells.Nat Rev Neurosci.2006;7:395-406.[28] Zhang P, Li J, Liu Y, et al. Human embryonic neural stem cell transplantation increases subventricular zone cell proliferation and promotesperi-infarct angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. Neuropathology.2011;31(4):384-391.[29] Huang L, Wong S, Snyder EY, et al. Human neural stem cells rapidly ameliorate symptomatic inflammation in early-stage ischemic-reperfusion cerebral injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(6):129.[30] 邱小华,戴育成,胡葵葵.脐带间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2012,6(06):1494-1497.[31] Zhang L, Wang LM, Chen WW,et al.Neural differentiation of human Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves the recovery of neurological function after transplantation in ischemic stroke rats.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(7):1103-1110.[32] Honmou O, Onodera R, Sasaki M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: thera- peutic outlook for stroke. Trends Mol Med.2012; 18( 5) : 292-7.[33] Honmou O, Houkin K, Matsunaga T, et al. Intravenous administration of auto serum-expanded autologous mesenchymalstem cells in stroke. Brain. 2011;134(Pt6): 1790-1807.[34] Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, et al. Induction of pluripotentstem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.2007;131(5):861-872. [35] Nishimura K, Nakagawa T, Ono K, et al. Transplantation of mouseinduced pluripotent stem cells into the cochlea. Neuro Report.2009;20 (14):1250-1254. [36] Abe K, Yamashita T, Kawai H, et al. iPS cell transplantation for ischemic brain.Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2012;52(11): 1143-1146. [37] Leong WK, Henshall TL. Human adult dental pulp stem cells enhance poststroke functional recovery through non-neural replacement mechanisms. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012; 1(3):177-187. [38] Fan Y,Sben F, Frcnzel T, et al. Endothelial progenitor Cen transplantation improves long-term stroke outcomein mice. Ann Neuroi. 2010;67(4):488-497. [39] Yang B, Strong R, Sharma S, et al. Therapeutic time window and dose response of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells for ischemic stroke. J Neurosci Res.2011;89(6):833-839.[40] Diez-TejedorE, Gutier-Fernandez M, MartinezsanchezP, et al. Reparative therapy for acute ischemic strokewith allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue: asafety assessment: a phase II randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled, single-center, pilot clinical trial. Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis.2014;23(10): 2694-2700. [41] Leong WK, Lewis MD, Kpblar SA. Concise review: preclinical studies on human cell-based therapy in rodent ischemicstroke models: where are we now after a decade.Stem Cells. 2013; 31(6):1040-1043. [42] Dulamea AO. The potential use of mesenchymal stem cells instroke therapy: from bench to bedside. Neurol Sci. 2015; 352(1 /2):1-11.[43] Yang Z, Zhu L, Li F, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells as a therapeutic treatment for ischemic stroke. Neurosci Bull. 2014;30(3) : 524-534. [44] Liu DD, Shyu WC, Lin SZ. Stem cell therapy in stroke: strategies in basic study and clinical application. ActaNeurochir Suppl. 2006;99:137-139.[45] Wang W, Jiang Q, Zhang H, et al. Intravenous administration of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells is safe for the lung in a chronic myocardial infarction model. Regen Med. 2011;6(2):179-190.[46] Jiang Y, Zhu W, Zhu J, et al. Feasibility of delivering mesenchymal stem cells via catheter to the proximal end of the lesion artery in patients with stroke in the territory of the middle cerebral artery. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(12): 2291-2298.[47] Gonzalez FF, McQuillen P, Mu D, et al. Erythropoietin enhances long-term neuroprotection and neurogenesis in neonatal stroke. Dev Neurosci. 2007;29(4-5):321-330.[48] 刘慧纯,张培培,王世民,等.脐带间充质干细移植治疗大鼠脑缺血损伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(19):3471-3475.[49] Zhao LR, Berra HH, Duan WM, et al. Beneficial effects of hematopoietic growth factor therapy in chronic ischemic stroke in rats. Stroke. 2007; 38(10): 2804- 2811.[50] 郭燕宁,王雪笠.不同干细胞移植途径治疗脑缺血的示踪及效果评定[J].脑与神经疾病杂志, 2013,21(04):316-318.[51] 魏建强.不同途径移植骨髓间充质干细胞促进创伤性脑损伤大鼠功能恢复和神经再生的研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2013.[52] Rabadi MH. Randomized clinical stroke rehabilitation trials in2005.Neurochem Res. 2007;32(4-5): 807-821.[53] 王亮,崔维韻,王新平,王世民,尉辉杰,王东.不同数量神经干细胞移植治疗实验性脑梗死[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(1): 90-94.[54] Kim S J, Moon G J, Chang W H, et al. Intravenous transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells preconditioned with early phasestroke serum: current evidence and study protocol for a randomized trial. Trials.2013;14(1):317. [55] Wakabayashi K, Nagai A, Sheikh AM, et al. Transplantationof human mesenchymal stem cells promotes functionalimprovement and increased expression of neurotrophicfactors in a rat focal cerebral ischemia model. Neurosci Res.2010;88(5):1017-1025. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [5] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [7] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [8] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [9] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [10] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [11] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [12] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [13] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [14] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [15] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||