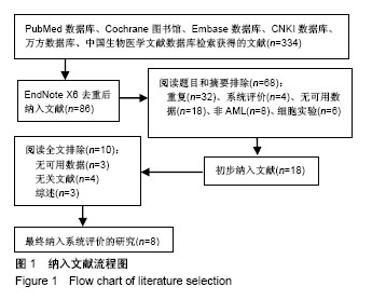
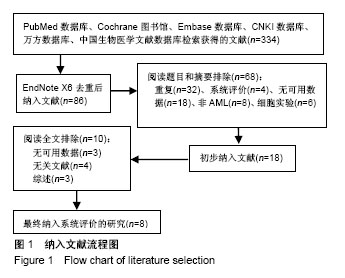
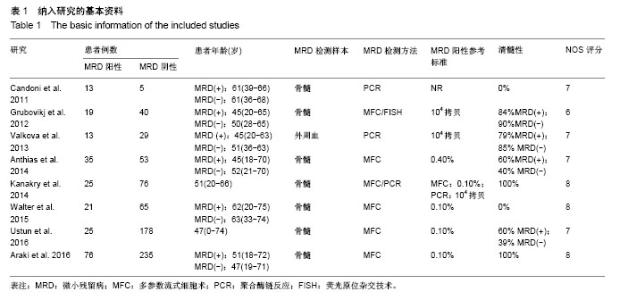
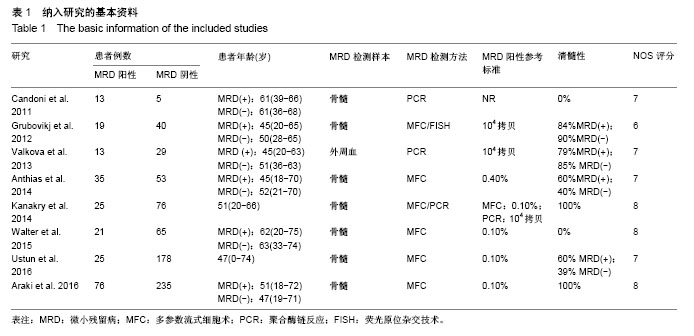
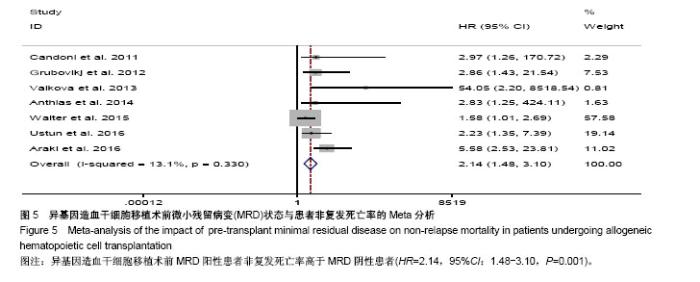
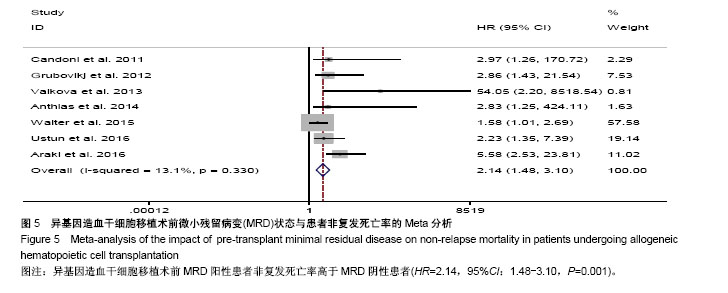
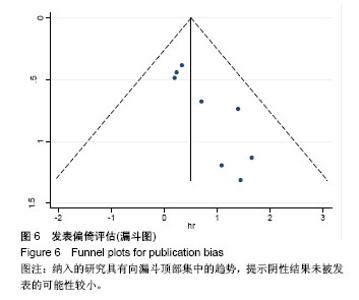
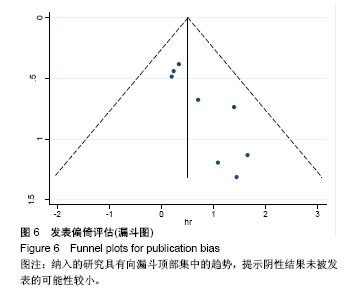
| [1] Krause A,Luciana M,Krause F,et al. Targeting the acute myeloid leukemia stem cells.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2010;10(2): 104-110.[2] Ivey A, Hills RK, Simpson MA,et al.Assessment of Minimal Residual Disease in Standard-Risk AML.N Engl J Med. 2016; 374(5):422-433.[3] El-Jawahri A, Li S, Ballen KK, et al. Phase II Trial of Reduced-Intensity Busulfan/Clofarabine Conditioning with Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Myelodysplastic Syndromes, and Acute Lymphoid Leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016; 22(1):80-85.[4] Ravandi F, Jorgensen JL, O'Brien SM, et al. Minimal residual disease assessed by multi-parameter flow cytometry is highly prognostic in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.Br J Haematol. 2016;172(3):392-400.[5] 郭青,金润铭. 微小残留病检测指导白血病治疗的研究进展[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志,2016, 31(4):264-268.[6] Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(9):603-605.[7] Candoni A, Toffoletti E, Gallina R, et al. Monitoring of minimal residual disease by quantitative WT1 gene expression following reduced intensity conditioning allogeneic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Transplant. 2011;25(2):308-316.[8] Grubovikj RM, Alavi A, Koppel A, et al. Minimal residual disease as a predictive factor for relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant in adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first and second complete remission. Cancers (Basel). 2012; 4(2):601-617.[9] Valkova V, Polak J, Markova M, et al. Minimal residual disease detectable by quantitative assessment of WT1 gene before allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients in first remission of acute myeloid leukemia has an impact on their future prognosis. Clin Transplant. 2013;27(1):E21-29.[10] Anthias C, Dignan FL, Morilla R, et al. Pre-transplant MRD predicts outcome following reduced-intensity and myeloablative allogeneic hemopoietic SCT in AML. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2014;49(5):679-683[11] Kanakry CG, Tsai HL, Bolanos-Meade J, et al. Single-agent GVHD prophylaxis with posttransplantation cyclophosphamide after myeloablative, HLA-matched BMT for AML, ALL, and MDS. Blood. 2014;124(25):3817-3827.[12] Walter RB, Gyurkocza B, Storer BE, et al. Comparison of minimal residual disease as outcome predictor for AML patients in first complete remission undergoing myeloablative or nonmyeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Leukemia. 2015;29(1):137-144[13] Ustun C, Courville EL, DeFor T, et al. Myeloablative, but not reduced-intensity, conditioning overcomes the negative dffect of flow-cytometric evidence of leukemia in acute myeloid leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016;22(4):669-675.[14] Araki D, Wood BL, Othus M, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: time to move toward a minimal residual disease-based definition of complete remission? J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(4):329-336.[15] 杨莉,何浩明. 急性髓细胞白血病患者外周血淋巴细胞亚群的检验分析[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2016,37(6):817-819.[16] 王昱,黄晓军. 单倍型移植治疗中高危急性髓系白血病第一次缓解期:指南与实践[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2016, 37(8):721-724.[17] 周慧,王建虹,闵捷. 老年急性髓系白血病治疗的研究进展[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志,2011, 18(10):816-820.[18] 卢晟晔,江浩. 老年急性髓系白血病危险度分层治疗[J]. 中国老年学, 2016, 36(12):3054-3057.[19] 陈喜填,夏维林. 老年急性髓系白血病治疗效果及预后因素分析[J].中国医学工程, 2016,(6):76-78.[20] 万岁桂,赵弘,孙雪静,等. 多参数流式细胞术对急性髓系白血病微小残留病变与疾病复发的监测[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2009,17(3): 557-562.[21] 朱勇梅,陈赛娟. 微小残留病检测方法及其临床应用[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志,2015, 13(6):1131-1136.[22] 李丽君,刘蓓,徐茜,等. 急性髓系白血病患者化疗后微小残留病与多药耐药基因表达相关[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2017,37(1):62-66.[23] 徐瑞琴,陆小云,张敏. 急性白血病缓解期微小残留病灶与预后的关系[J]. 临床血液学杂志, 2016(2):209-212.[24] van der Velden VH, van der Sluijs-Geling A, Gibson BE, et al. Clinical significance of flowcytometric minimal residual disease detection in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients treated according to the DCOG ANLL97/MRC AML12 protocol. Leukemia. 2010;24(9):1599-1606.[25] Rubnitz JE, Inaba H, Dahl G, et al. Minimal residual disease-directed therapy for childhood acute myeloid leukaemia: results of the AML02 multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(6): 543-552. |