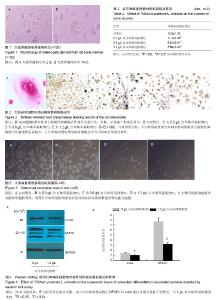
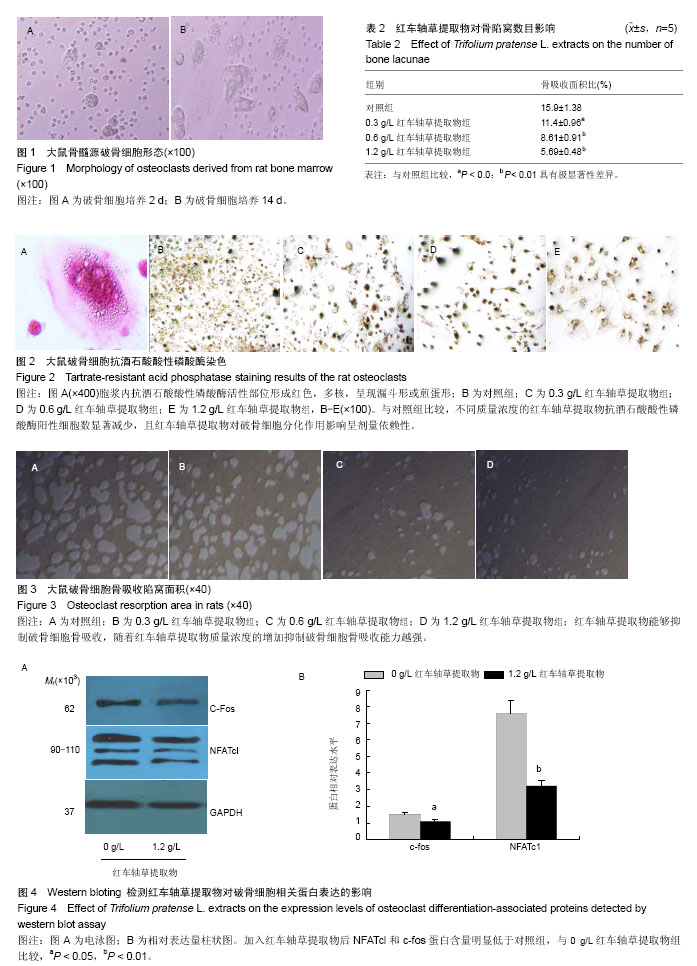
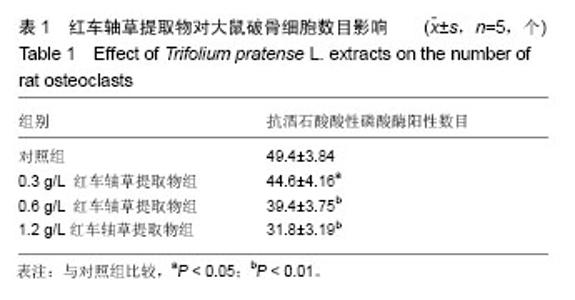
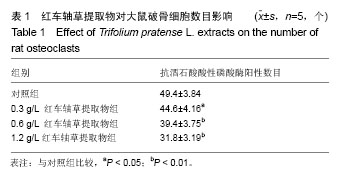
| [1] Clarke B. Normal bone anatomy and physiology. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol.2008;3(3): S131-139[2] Boyle WJ,Simonet WS,Lacey DL.Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature.2003;423:337-342.[3] Harada S, Rodan GA. Control of osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature.2003;423:349-355.[4] Decker CE,Yang Z, Rimer R,et al.Tmem178 acts in a novel negative feedback loop targeting NFATc1 to regulate bone mass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2015;112(51):15654-15659.[5] Brad B,Victoria S, Paul JK, et al.Osteoprotegerin , anendogenous antiosteoclast factor for protecting bone inrheumatoid arthritis. Aethritis Rheum.2002; 46(12): 3121-3135.[6] Bocyce BF, Xing L. Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008;473(2):139-146.[7] Soysa NS, Alles N.NF-KB functions in osteoclasts.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;378(1):1-5.[8] Naoko Y,Tohru T,Haruyasu U, et al.Down-regulation of osteoprotegerin production in bone marrow macrophages by macrophage colony stimulating factor. Cytokine.2005;31(28): 288- 297.[9] Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, et al. OPGL is a key regulator of osteoclastgenesis , lymphocyte development and lympya-node organogenesis.Nature.1999; 39(7): 315-323.[10] He Xiao-guo, Lin Lang-ze. Analysis of flavonoids from red Clover by liquid ch romatog raphy-electrosp ray mass spectrometry.J Chro mat ogr A.1996;755: 127-132.[11] 苏振宏,马红樱,喻格书,等. 红车轴草的化学成分与药理作用研究进展[J]. 黄石理工学院学报,2008,24(5):20-23.[12] Ming X, Ding M, Zhai B, et al. Biochanin A inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Life Sci. 2015;136:36-41.[13] 李颖,薛存宽,何学兵,等.红车轴草异黄酮对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松防治作用的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2005 , 11(4) :509-511.[14] Berlier JL, Kharroubi I, Zhang J, et al.Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Peptide Prevents Serum Deprivation-Induced Apoptosis in Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Osteoblastic Cells.Stem cell reviews.2015;11 (6):841-851.[15] Kwon JO, Jin WJ, Kim B , et al. Myristoleic acid inhibits osteoclast formation and bone resorption by suppressing theRANKL activation of Src and Pyk2. Eur J pharmacol. 2015 ;768:189-198. [16] 韩金祥. 骨分子生物学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010:55-91.[17] Zaidi M, Blair HC, Iqbal J, et al. New insights: elevated follicle-stimulating hormone and bone loss during the menopausal transition. Curr Rheumatol Rep.2009; 11(3): 191-195. [18] Takami M, Mochizuki A, Yamada A,et al.Osteoclast differentiation induced by synthetic octacalcium phosphate through receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand expression in osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(12):3991-4000.[19] Nozaki K, Kaku M, Yamashita Y, et al.Effect of cyclic mechanical loading on osteoclast recruitment in periodontal tissue. J Periodontal Res. 2010;45(1):8-15. [20] Scaramuzzo L, Messuti L, Manicone PF, et al.Clinical and histological modifications in osteopetrotic bone: a review.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2009;23(2):59-63. [21] Crabtree GR,Olson EN.NFAT signaling:Choreographing thesocial lives of cells . Cell.2002;109 Suppl: S67-79.[22] Takayanagi H.Osteoimmunology: Shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol.2007; 7(4): 292-304. [23] Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, et al. Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1(NFAT2) integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 2002; 3(6): 889-901.[24] Kim KJ,Yeon JT,Choi SW,et al.Decursin inhibits osteoclastogenesis by downregulating NFATc1 and blocking fusion of pre-osteoclasts.Bone.2015; 81:208-216.[25] Jeong BC, Kim JH, Kim K, et al. ATF3 modulates calcium signaling in osteoclast differentiation and activity by associating with c-Fos and NFATc1 proteins. Bone.2017;95: 33-40. [26] Murakami A, Matsuda M, Harada Y, et al.Phospholipase C-related, but catalytically inactive protein (PRIP) up-regulates osteoclast differentiation via calcium-calcineurin-NFATc1 signaling. J Biol Chem.2017; 292(19):7994-8006.[27] Yamasaki T, Ariyoshi W, Okinaga T, et al.The dectin 1 agonist curdlan regulates osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting nuclear factor of activated T cells cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1) through Syk kinase. J Biol Chem.2014;289(27):19191-19203.[28] Grigoriadis AE,Wang ZQ,Cecchini MG, et al. c-Fos: a key regulator of osteoclast- macrophage lineage determination and bone remodeling. Science.1994;266:443-448.[29] Matsuo K, Galson DL, Zhao C, et al. Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) rescues osteoclastogenesis in precursors lacking c-Fos.J Biol Chem.2004;279: 26475-26480.[30] Yamashita T,Yao Z,Li F, et al. NF-kappa B p50 and p52 regulate receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and tumor necrosis factor-induced osteoclast precursor differentiation by activating c-Fos and NFATc1.J Biol Chem . 2007;282:18245-18253 .[31] Raisz LG.Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts,and prospects. J Clin Invest.2005;115 (12) :3318-3325.[32] Vesprey A, Yang W.Pit Assay to Measure the Bone Resorptive Activity of Bone Marrow-derived Osteoclasts. Bio Protoc. 2016;6(12). pii: e1836..[33] Tanko LB, Christiansen C, Cox DA, et al. Relationship between osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease in postmenopausal women. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(11): 1912-1920.[34] 郑杰,刘艳平,宗永立,等.红车轴草提取物对胃癌BGC-823细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 生命科学研究,2006,10(2):178-182.[35] 刘岩,刘顺航,王平. 红车轴草的研究进展[J]. 中草药,2007, 38(5):801-804.[36] 陈封政,李书华,弓加文. 红三叶中总异黄酮含量测定[J]. 乐山师范学院学报,2005,20(5):49-50.[37] Roldan M, Islam A, Dinh PT, et al.Phosphate availability regulates ethylene biosynthesis gene expression and protein accumulation in white clover (Trifolium repens L.) roots. Biosci Rep.2016;36(6). pii: e00411.[38] Sands RJ, Rowntree JK.Interactions between the Bumblebee Bombus pascuorum and Red Clover (Trifolium pratense) Are Mediated by Plant Genetic Background. PLoS One.2016; 11(8):e0161327.[39] Yesil Y, Ulger Z, Halil M, et al. Coexistence of osteoporosis (OP) and coronary artery disease (CAD) in the elderly: it is not just a by chance event. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2012;54(3): 473-476.[40] Reyes-Garcia R, Rozas-Moreno P, Munoz-Torres M. Cardiovascular disease and bone metabolism. Endocrinol Nutr. 2011;58(7):353-359. [41] Kolodziejczyk-Czepas J, Nowak P, Kowalska I,et al.Antioxidant action of six Trifolium species in blood platelet experimental system in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015; 410(1-2):229-237. |