Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (15): 2342-2348.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.15.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Pedicle screw fixation combined with posterior-lateral fusion with autogenous bone for thoracolumbar burst fractures
Dong You-jun, Wu Liang, Wu Guo-feng, Zhou Jian, Wang Kun, Sun Han, Sun Xiao-liang
- Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochw University, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Online:2017-05-28Published:2017-06-07 -
Contact:Sun Xiao-liang, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochw University, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Dong You-jun, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Orthopedics, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochw University, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dong You-jun, Wu Liang, Wu Guo-feng, Zhou Jian, Wang Kun, Sun Han, Sun Xiao-liang. Pedicle screw fixation combined with posterior-lateral fusion with autogenous bone for thoracolumbar burst fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(15): 2342-2348.
share this article
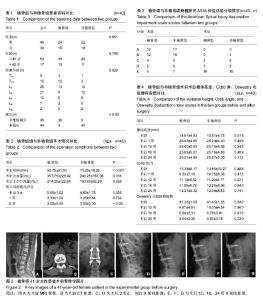
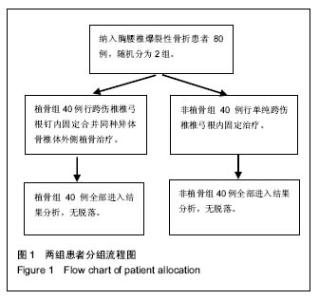
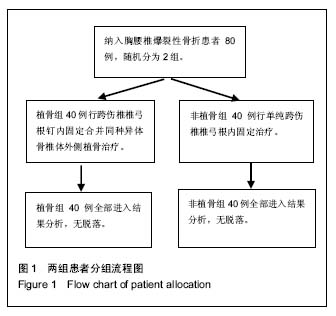
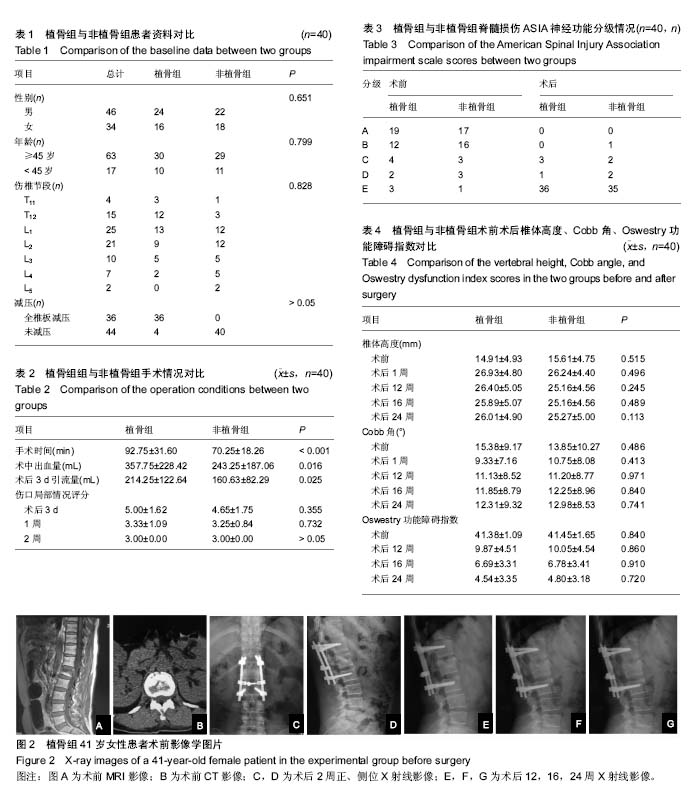
2.2 基线资料比较 植骨组男女性别比、年龄以及减压情况与非植骨组相比差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);植骨组的伤椎节段与非植骨组相比差异无显著性意义(P=0.828>0.05)。综上所述,2组基线资料比较差异无显著性意义,具有可比性,见表1。 2.3 手术情况对比 通过临床观察,植骨组40例患者的手术时间、术中出血量以及术后引流量均大于非植骨组(P < 0.05),2组患者伤口局部情况术后3 d后得到明显改善(P < 0.05),但在术后3 d、1周、2周的时间段内,2组患者之间差异并无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表2。 2.4 脊髓损伤ASIA神经功能分级变化 植骨组患者术前分级A级19例、B级12例、C级4例、D级2例、E级3例,术后改善到A级0例、B级0例、C级3例、D级1例、E级36例;而非植骨组患者术前分级A级17例、B级16例、C级3例、D级3例、E级1例,术后改善为A级0例、B级1例、C级2例、D级1例、E级35例。2组患者神经功能均明显改善,但2组间差异无显著性意义,见表3。 2.5 术后随访对比 与术前相比,植骨组与非植骨组患者术后随访过程中椎体高度、Cobb角均有显著改善(P < 0.01),椎体高度矫正率分别为45%,41%;Cobb角矫正率为65%,29%;但术后随访过程中椎体高度、Cobb角均有轻度丢失,椎体高度丢失4%,4%;Cobb角丢失32%,21%,2组患者之间对比差异仍无显著性意义(P=0.741)。根据Steinman脊椎融合标准,植骨组术后12周左右植骨椎体后外侧均出现融合,大部分移植骨被新骨代替,16周左右评分均达到满分4分,植骨椎体100%全部融合。Oswestry功能障碍指数结果表明,与术前相比2组患者术后运动功能障碍有显著好转,且随着时间推移,功能恢复进一步改善(P < 0.01),但植骨与否并未对此评分有明显影响(P > 0.05),见表4。 2.6 典型病例 女性患者,41岁,因车祸摔伤致腰背部疼痛、活动受限2 h入院,根据病史、查体及相关影像资料检查,诊断为L1椎体爆裂性骨折。治疗方案:腰椎后路减压术+腰椎后路内固定+椎体后外侧植骨融合术。随访24个月,结果显示患者术后椎体高度及Cobb角较术前明显改善,且末次随访植骨部位已全部融合,椎体高度及Cobb角仅有轻度丢失,无不良事件发生,见图2。 2.7 不良事件 所有随访病例均无不良事件发生,同种异体骨与人体组织有较好的相容性,安全性等级为Ⅰ级。"
| [1] Tropiano P, Huang RC, Louis CA, et al. Functional and radiographic outcome of thoracolumbar and lumbar burst fractures managed by closed orthopaedic reduction and casting. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2003;28(21):2459-2465.[2] 凌仕勇,陈军. 经伤椎与跨伤椎椎弓根螺钉复位固定治疗单节段胸腰椎骨折疗效比较[J]. 中国现代医生, 2016,54(12):58-61.[3] Scheer JK, Bakhsheshian J, Fakurnejad S, et al. Evidence-Based Medicine of Traumatic Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review of Operative Management across 20 Years. Global Spine J. 2015;5(1): 73-82.[4] Fakurnejad S, Scheer JK, Patwardhan AG, et al. Biomechanics of thoracolumbar burst fractures: methods of induction and treatments. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(12): 2059-2064.[5] Anghel S, Petrisor M, Buicu CF, et al. Predictive factors for postoperative deformity in thoracolumbar burst fractures: a statistical approach. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49 (2):133-138.[6] Deng Z, Zou H, Cai L. The retrospective analysis of posterior short-segment pedicle instrumentation without fusion for thoracolumbar burst fracture with neurological deficit. Scientific World J. 2014;2014:457634.[7] Kim KW, Cho KJ, Kim SW, et al. A nation-wide, outpatient-based survey on the pain, disability, and satisfaction of patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Asian Spine J. 2013;7 (4):301-307.[8] Chen D, An ZQ, Song S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with conservative treatment in patients with chronic painful osteoporotic spinal fractures. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21 (3):473-477.[9] Oner FC, Wood KB, Smith JS, et al. Therapeutic decision making in thoracolumbar spine trauma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35 (21 Suppl):S235-244.[10] Vaccaro AR, Lehman RA Jr, Hurlbert R J, et al. A new classification of thoracolumbar injuries: the importance of injury morphology, the integrity of the posterior ligamentous complex, and neurologic status. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30 (20):2325-2333.[11] Krappinger D, Kastenberger TJ, Schmid R. [Augmented posterior instrumentation for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral body fractures]. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2012;24 (1):4-12.[12] Javadi SA, Naderi F. The long-term efficacy of pedicular screw fixation at patients suffering from thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurological deficit. Asian J Neurosurg. 2015;10 (4):286-289.[13] Tomii M, Mizuno J, Takeda M, et al. Thoracolumbar extradural arachnoid cyst--three surgical case reports. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2013;53 (2):129-133.[14] McCormack T, Karaikovic E, Gaines RW. The load sharing classification of spine fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19(15):1741-1744.[15] 孙天胜. 《新鲜胸腰段脊柱脊髓损伤评估与治疗》的专家共识[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21 (11):963-968.[16] Knop C, Fabian HF, Bastian L, et al. Late results of thoracolumbar fractures after posterior instrumentation and transpedicular bone grafting. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26 (1):88-99.[17] Chou PH, Ma HL, Wang ST, et al. Fusion may not be a necessary procedure for surgically treated burst fractures of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spines: a follow-up of at least ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96 (20):1724-1731.[18] Defino HL, Canto FR. Low thoracic and lumbar burst fractures: radiographic and functional outcomes. Eur Spine J. 2007;16 (11):1934-1943.[19] Liu CL, Wang ST, Lin HJ, et al. AO fixateur interne in treating burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 1999;62 (9):619-625.[20] Kim YM, Kim DS, Choi ES, et al. Nonfusion method in thoracolumbar and lumbar spinal fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36 (2):170-176.[21] Jindal N, Sankhala SS, Bachhal V. The role of fusion in the management of burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine treated by short segment pedicle screw fixation: a prospective randomised trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(8): 1101-1106.[22] Sanderson PL, Fraser RD, Hall DJ, et al. Short segment fixation of thoracolumbar burst fractures without fusion. Eur Spine J. 1999;8 (6):495-500.[23] Lakshmanan P, Jones A, Mehta J, et al. Recurrence of kyphosis and its functional implications after surgical stabilization of dorsolumbar unstable burst fractures. Spine J. 2009;9 (12):1003-1009.[24] Yaldiz C, Asil K, Ozkal B, et al. Thoracolumbar burst fractures requiring instrumented fusion: Should reducted bone fragments be removed? A retrospective study. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2015;49 (6):358-366.[25] Muller U, Berlemann U, Sledge J, et al. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic deficit by indirect reduction and posterior instrumentation: bisegmental stabilization with monosegmental fusion. Eur Spine J. 1999;8 (4):284-289.[26] Chang KW, Chen HC, Chen YY, et al. Sagittal translation in opening wedge osteotomy for the correction of thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity in ankylosing spondylitis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31 (10):1137-1142.[27] Toyone T, Tanaka T, Kato D, et al., The treatment of acute thoracolumbar burst fractures with transpedicular intracorporeal hydroxyapatite grafting following indirect reduction and pedicle screw fixation: a prospective study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31 (7):E208-214.[28] Alanay A, Acaroglu E, Yazici M, et al. Short-segment pedicle instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures: does transpedicular intracorporeal grafting prevent early failure? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26 (2):213-217.[29] Knop C, Fabian HF, Bastian L, et al. Fate of the transpedicular intervertebral bone graft after posterior stabilisation of thoracolumbar fractures. Eur Spine J. 2002;11 (3):251-257.[30] Ma Y, Li X, Dong J. Is it useful to apply transpedicular intracorporeal bone grafting to unstable thoracolumbar fractures? A systematic review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 154(12):2205-2213.[31] 史晓林,张昊,刘磊,等. 椎弓根置钉修复胸腰椎骨折合并脊髓损伤:选择性损伤节段及全部固定节段植骨融合的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20 (17):2488-2495.[32] Leferink VJ, Zimmerman KW, Veldhuis EF, et al. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures: radiological results of transpedicular fixation combined with transpedicular cancellous bone graft and posterior fusion in 183 patients. Eur Spine J. 2001;10 (6):517-523.[33] 贾金龙,杨庆国,张银顺,等.椎体减压植入物内固定修复胸腰椎爆裂性骨折:随访验证后路途径更安全[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(22):3531-3537.[34] Wang L, Wang Y, Yu B, et al. Comparison of cranial facet joint violation rate between percutaneous and open pedicle screw placement: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94 (5):e504.[35] Ito Z, Imagama S, Kanemura T, et al. Bone union rate with autologous iliac bone versus local bone graft in posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF): a multicenter study. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 (5):1158-1163.[36] Myeroff C, Archdeacon M. Autogenous bone graft: donor sites and techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(23): 2227-2236.[37] Tomford WW. Bone allografts: past, present and future. Cell Tissue Bank. 2000;1(2):105-109.[38] Miller LE, Block JE. Safety and effectiveness of bone allografts in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36 (24):2045-2050.[39] Bakhsheshian J, Dahdaleh NS, Fakurnejad S, et al. Evidence-based management of traumatic thoracolumbar burst fractures: a systematic review of nonoperative management. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;37(1):E1.[40] 高峰,张智达,任应清,等. 胸腰椎爆裂性骨折后路内固定手术中融合与非融合手术疗效的比较研究[J]. 中国现代医生, 2017, 55(2):56-59. |
| [1] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [2] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [3] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [4] | Jiang Huanchang, Zhang Zhaofei, Liang De, Jiang Xiaobing, Yang Xiaodong, Liu Zhixiang. Comparison of advantages between unilateral multidirectional curved and straight vertebroplasty in the treatment of thoracolumbar osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1407-1411. |
| [5] | Li Wei, Zhu Hanmin, Wang Xin, Gao Xue, Cui Jing, Liu Yuxin, Huang Shuming. Effect of Zuogui Wan on bone morphogenetic protein 2 signaling pathway in ovariectomized osteoporosis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1173-1179. |
| [6] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [7] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [8] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [9] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [10] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [13] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [14] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [15] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||