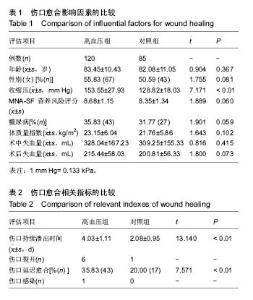
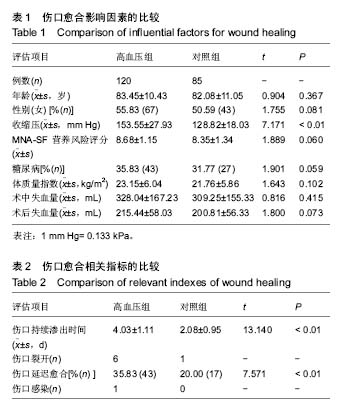
| [1] Guillemin Y, Le Broc D, Segalen C, et al. Efficacy of a collagen-based dressing in an animal model of delayed wound healing.J Wound Care.2016;25(7):406-413.[2] Tada M, Inui K, Sugioka Y, et al. Delayed wound healing and postoperative surgical site infections in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with or without biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs.Clin Rheumatol.2016;35(6):1475-1481.[3] Ishie S, Ito H, Azukizawa M, et al. Delayed wound healing after forefoot surgery in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol.2015;25(3):367-372.[4] Ahmed AA, Mooar PA, Kleiner M, et al. Hypertensive patients show delayed wound healing following total hip arthroplasty. PLoS One.2011;6(8):e23224.[5] Rubenstein LZ, Harker JO, Salva A,et al.Screening for undernutrition in geriatric practice:developing the short-form mini-nutritional assessment (MNA-SF). J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.2001;56(6):M366-M372.[6] Chu CS, Liang CK, Chou MY, et al. Short-Form Mini Nutritional Assessment as a useful method of predicting the development of postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing orthopedic surgery. Gen Hosp Psychiatry.2016;38:15-20.[7] 郭炯炯,唐天驷,杨惠林,等. 老年人营养状况对髋部骨折术后切口愈合的影响[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(2):112-114.[8] James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al.2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA.2014;311(5):507-520.[9] 张党锋,马巍,戈朝晖,等. 老年股骨头置换后1年内生存状况的相关因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(26):4127-4131.[10] Galat DD, Mcgovern SC, Larson DR, et al.Surgical treatment of early wound complications following primary total knee arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009;91(1):48-54.[11] Saleh K,Olson M, Resig S, et al.Predictors of wound infection in hip and knee joint replacement: results from a 20 year surveillance program.J Orthop Res.2002;20(3):506-515.[12] Ahmed AA, Mooar PA, Kleiner M, et al. Hypertensive patients show delayed wound healing following total hip arthroplasty. PLoS One.2011;6(8):e23224.[13] 王培丞,曹力,杨德盛,等. 双侧全膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成与高血压的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(9):1335-1339.[14] Myint MW,Wu J,Wong E,et al.Clinical benefits of oral nutritional supplementation for elderly hip fracture patients: a single blind randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing.2013;42(1):39-45.[15] Rostagno C, Buzzi R, Campanacci D, et al. In Hospital and 3-Month Mortality and Functional Recovery Rate in Patients Treated for Hip Fracture by a Multidisciplinary Team. PLoS One.2016;11(7):e158607.[16] Boddaert J, Raux M, Khiami F, et al. Perioperative management of elderly patients with hip fracture. Anesthesiology.2014;121(6):1336-1341.[17] Bartha E,Davidson T,Hommel A,et al.Cost-effectiveness analysis of goal-directed hemodynamic treatment of elderly hip fracture patients: before clinical research starts. Anesthesiology.2012;117(3):519-530.[18] Patel VP, Walsh M, Sehgal B, et al. Factors associated with prolonged wound drainage after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2007;89(1):33-38.[19] Mondini A, Bianchi L, Zagra L. Wound closure and wound monitoring in total hip arthroplasty. An overview. Hip Int.2012; 22 Suppl 8:S15-S18.[20] Villatte G, Engels E, Erivan R, et al. Effect of local anaesthetic wound infiltration on acute pain and bleeding after primary total hip arthroplasty: the EDIPO randomised controlled study. Int Orthop.2016;40(11):2255-2260.[21] Watts CD, Houdek MT, Wagner ER, et al. High Risk of Wound Complications Following Direct Anterior Total Hip Arthroplasty in Obese Patients. J Arthroplasty.2015;30(12):2296-2298.[22] Christensen CP,Karthikeyan T,Jacobs CA.Greater prevalence of wound complications requiring reoperation with direct anterior approach total hip arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty.2014, 29(9):1839-1841.[23] Newman ET,Watters TS,Lewis JS,et al.Impact of perioperative allogeneic and autologous blood transfusion on acute wound infection following total knee and total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2014;96(4):279-284.[24] Siddiqui M, Bidaye A, Baird E, et al. Wound dressing following primary total hip arthroplasty: a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Wound Care.2016;25(1):40, 42-45.[25] Nanni M, Perna F, Calamelli C, et al. Wound drainages in total hip arthroplasty: to use or not to use? Review of the literature on current practice. Musculoskelet Surg.2013;97(2):101-107.[26] Andersen LJ,Poulsen T,Krogh B,et al.Postoperative analgesia in total hip arthroplasty: a randomized double-blinded, placebo-controlled study on peroperative and postoperative ropivacaine, ketorolac, and adrenaline wound infiltration. Acta Orthop.2007;78(2):187-192.[27] Dora C, von Campe A, Mengiardi B, et al. Simplified wound care and earlier wound recovery without closed suction drainage in elective total hip arthroplasty. A prospective randomized trial in 100 operations. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2007;127(10):919-923.[28] Pachowsky M, Gusinde J, Klein A, et al. Negative pressure wound therapy to prevent seromas and treat surgical incisions after total hip arthroplasty.Int Orthop.2012;36(4): 719-722.[29] 朱冬梅,刘国印,王梦茹,等. 老年人营养状况与关节置换术后切口愈合的关系研究[J]. 实用老年医学,2016,30(4):281-284.[30] 佘树松,周波,徐顺才. 不同通气方式对髋关节置换高血压患者应激反应的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(35):5588- 5592.[31] Kim D, Jules-Elysee K, Turteltaub L, et al. Clinical outcomes in patients with pulmonary hypertension undergoing total hip arthroplasty. HSS J.2014;10(2):131-135.[32] Gaston MS, Amin AK, Clayton RA, et al. Does a history of cardiac disease or hypertension increase mortality following primary elective total hip arthroplasty?. Surgeon.2007;5(5): 260-265. |