Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (5): 657-662.doi: 10.12307/2022.107
Feasibility of ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection in rabbit hip joint
Wang Shaoling, Wang Yanxue, Zheng Yaochao, Yu Shaojun, Ma Chao, Wu Shaoling
- Department of Rehabilitative Medicine, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2020-11-06Revised:2020-11-11Accepted:2020-12-14Online:2022-02-18Published:2021-10-28 -
Contact:Wu Shaoling, MD, Doctoral supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Rehabilitative Medicine, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Wang Shaoling, Master candidate, Department of Rehabilitative Medicine, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81671088 (to WSL) and 81972152 (to MC); Yat-sen Clinical Research and Cultivation Routine Project of Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, No. SYS-C-202002 (to WSL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Shaoling, Wang Yanxue, Zheng Yaochao, Yu Shaojun, Ma Chao, Wu Shaoling. Feasibility of ultrasound-guided intra-articular injection in rabbit hip joint[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 657-662.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

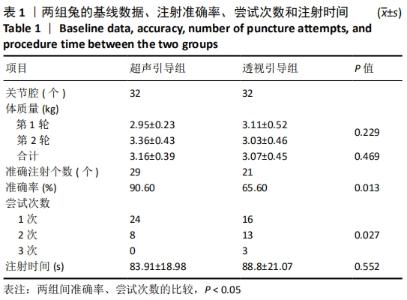
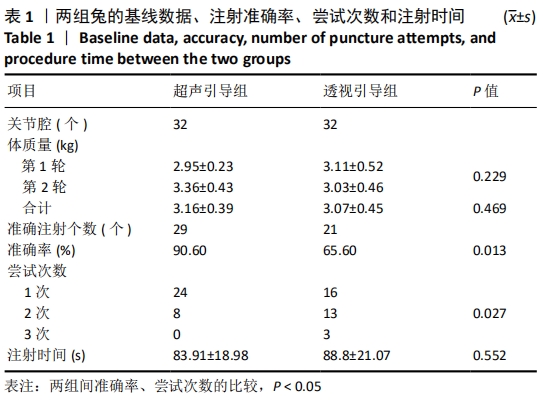
2.3.1 两组基线数据分析 两组实验动物第1轮,第2轮注射的体质量比较差异无统计学意义。 2.3.2 两组注射准确率比较结果 超声引导组注射准确的髋关节为29个,准确率为90.6%,透视引导组注射准确个数为21个,准确率为65.6%,两组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.3.3 两组尝试注射次数比较结果 超声引导组1次、2次和3次尝试注射的髋关节个数分别为24,8和0个;透视引导组1次、2次和3次尝试注射的个数分别为16,13和3个。超声引导组的2次、3次尝试次数明显少于透视引导组(P < 0.05)。 2.3.4 两组注射花费时间比较结果 超声引导组的注射时间与透视引导组比较差异无显著性意义(P=0.552)。"

| [1] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [2] DALLARI D, STAGNI C, RANI N, et al. Ultrasound-Guided Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid, Separately and in Combination, for Hip Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Controlled Study. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(3):664-671. [3] HARADA Y, NAKASA T, MAHMOUD EE, et al. Combination therapy with intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells and articulated joint distraction for repair of a chronic osteochondral defect in the rabbit. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(10):1466-1473. [4] FILARDO G, KON E, DI MATTEO B, et al. Leukocyte-poor PRP application for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Joints. 2013;3:112-120. [5] NAREDO E, CABERO F, BENEYTO P, et al. A Randomized Comparative Study of Short Term Response to Blind Injection versus Sonographic-Guided Injection of Local Corticosteroids in Patients with Painful Shoulder. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(2):308-314. [6] KUYINU EL, NARAYANAN G, NAIR LS, et al. Animal models of osteoarthritis: classification, update, and measurement of outcomes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11:19 [7] ARZI B, WISNER ER, HUEY DJ, et al. A proposed model of naturally occurring osteoarthritis in the domestic rabbit. Lab Anim (NY). 2011; 41(1):20-25. [8] RIVERA F. Can viscosupplementation be used in the hip? An Italian perspective. Orthopedics. 2014;37(1):48-55. [9] VÁZQUEZ-PORTALATÍN N, BREUR GJ, PANITCH A, et al. Accuracy of ultrasound-guided intraarticular articular. Bone Joint Res. 2015;4(1):1-5. [10] DIRAÇOĞLU D, ALPTEKIN K, DIKICI F, et al. Evaluation of needle positioning during blind intra-articular hip injections for osteoarthritis: fluoroscopy versus arthrography. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;90(12): 2112-2115. [11] BATTISTA DJ, SCHAEFFER MA, TYMKO CM, et al. An Alternative Approach to the Fluoroscopically Guided Intra-Articular Hip Injection. PM R. 2019;11(7):783-785. [12] SCHMIDT-BRAEKLING T, WALDSTEIN W, RENNER L, et al. Ultrasound and fluoroscopy are unnecessary for injections into the arthritic hip. 2015;39(8):1495-1497. [13] HOEBER S, ALY AR, ASHWORTH N, et al. Ultrasound-guided hip joint injections are more accurate than landmark-guided injections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2016;50(7): 392-396. [14] RUIZ A, BRAVO D, DUARTE A, et al. Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided versus Landmark-Guided Intra-articular Injection for Rat Knee Joints. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019;45(10):2787-2796. [15] JONES JC, GONZALEZ LM, LARSON MM, et al. Feasibility and accuracy of ultrasound-guided sacroiliac joint injection in dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2012;53(4):446-454. [16] LEVY M, GASCHEN L, RADEMACHER N, et al. Technique for ultrasound-guided intraarticular cervical articular process injection in the dog. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2014;55(4):435-440. [17] SCHNEEWEISS W, PUGGIONI A, DAVID F. Comparison of ultrasound-guided vs. ‘blind’ techniques for intra-synovial injections of the shoulder area in horses: scapulohumeral joint, bicipital and infraspinatus bursae. Equine Vet J. 2012;44(6):674-678. [18] IAGNOCCO A, NAREDO E. Ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection in rheumatology: accuracy or efficacy?. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49(8):1427-1428. [19] BYRD JW, POTTS EA, ALLISON RK, et al. Ultrasound-Guided Hip Injections: A Comparative Study With Fluoroscopy-Guided Injections. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(1):42-46. [20] SHARPE RE JR, NAZARIAN LN, LEVIN DC, et al. The increasing role of nonradiologists in performing ultrasound-guided invasive procedures. J Am Coll Radiol. 2013;11:859-863. [21] KRUSE DW.Intraarticular cortisone injection for osteoarthritis of the hip. Is it effective? Is it safe?. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2008;1(3-4): 227-233. [22] BUM PARK Y, AH CHOI W, et al. Accuracy of blind versus ultrasound-guided suprapatellar bursal injection. J Clin Ultrasound. 2012;40(1):20-25. [23] SMITH J, HURDLE MF. Office-based ultrasound-guided intra-articular hip injection: technique for physiatric practice. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006;87(2):296-298. [24] COLE BJ, KARAS V, HUSSEY K, et al. Hyaluronic Acid Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma: A Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes and Effects on Intra-articular Biology for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(2):339-346. [25] MONTAÑEZ-HEREDIA E, IRÍZAR S, HUERTAS PJ, et al. Intra-Articular Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Hyaluronic Acid in the Treatment of Osteoarthritic Knee Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial in the Context of the Spanish National Health Care System. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(7):1064. [26] 郭玉冬,马良彧,王善正,等. 富血小板血浆治疗骨性关节炎的现状[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(15):1396-1399. [27] BENNELL KL, HUNTER DJ, PATERSON KL. Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Management of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(5):24. [28] ORNETTI P, NOURISSAT G, BERENBAUM F, et al. Does platelet-rich plasma have a role in the treatment of osteoarthritis?. Joint Bone Spine. 2016;83(1):31-36. [29] 张波,韦冰丹,甘坤宁. 富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞对兔股骨头坏死BMP-2/Smads通路的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2016,22(2):131-134. [30] 杨富强,杨晓明,葛建健. 髓芯减压植骨联合富血小板血浆治疗股骨头缺血性坏死的前瞻随机对照研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志, 2016,10(2):22-25. [31] DI SANTE L, VILLANI C, SANTILLI V, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid vs platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of hip osteoarthritis. Med Ultrason. 2016;18(4):463-468. [32] 王鹏志,李盛华. 骨髓间充质干细胞治疗股骨头坏死的研究进展[J]. 实用中西医结合临床,2020,20(1):179-182. [33] KURUP H, WARD P. Do we need radiological guidance for hip joint injections?. Acta Orthop Belg. 2010;2:205-207. [34] LEOPOLD SS, BATTISTA V, OLIVERIO JA. Safety and efficacy of intraarticular hip injection using anatomic landmarks. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; (391):192-197. [35] JONES A, REGAN M, LEDINGHAM J, et al. Importance ofplacement of intra-articular steroid injections. BMJ. 1993;307(6915):1329-1330. [36] SIBBITT WL JR, PEISAJOVICH A, MICHAEL AA, et al. Does sonographic needle guidance affect the clinical outcome of intraarticular injections?. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(9):1892-902. [37] BERKOFF DJ, MILLER LE, BLOCK JE. Clinical utility of ultrasound guidance for intra-articular knee injections: a review. Clin Interv Aging. 2012;7:89-95. [38] WANG D, TIAN W, LI Y. A study on Puncturing the Temporomandibular Joint Cavity of Rabbits and Withdrawing Synovia. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003;21(1):64-66. [39] 戴亚辉,梅炯.家兔与人股骨近端的解剖学对照研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2018,35(2):312-314. |
| [1] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [2] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [3] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [4] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [5] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [6] | Xu Kuishuai, Zhang Liang, Chen Jinli, Ren Zhongkai, Zhao Xia, Li Tianyu, Yu Tengbo. Effect of force line changes on lower limb joints after medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 821-826. |
| [7] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [8] | Song Yuxin, Zhang Tongtong, Niu Jianxiong, Wang Zengping, Wen Jie, Zhang Qunli, Xue Wen, Liu Lin. Precise screw placement of 3D printing model and orthopedic robot in spinal deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 904-907. |
| [9] | He Junjun, Huang Zeling, Hong Zhenqiang. Interventional effect of Yanghe Decoction on synovial inflammation in a rabbit model of early knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 694-699. |
| [10] | Wang Shihui, Cheng Yang, Zhu Yunjie, Cheng Shaodan, Mao Jianying. Effect of arc edge needle-scalpel therapy on inflammatory factors and histomorphology of the frozen shoulder in rabbit models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 706-711. |
| [11] | Yang Xue, Wang Baoqun, Jiang Xiaowen, Zou Shengcan, Ming Jinfa, Lin Shasha. Preparation and properties of biodegradable plant polysaccharide hemostatic microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2487-2491. |
| [12] | Li Shijie, Ma Liqiong, Xiong Xianmei, Zhang Yan, Chen Zijie, Feng Junming, Gao Yijia, Zeng Zhanpeng. Effect of panax notoginseng saponins on platelet-rich plasma promoting bone defect healing in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2155-2160. |
| [13] | Gao Xixin, Wang Xi, Fan Xuhui, Cui Yi, Yang Wei, Zhao Yunzhuan. Platelet-rich fibrin combined with induced bone matrix repairs bone defects around oral implants in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2207-2213. |
| [14] | Yang Xiaoxiao, Xu Yuanjing, Li Wentao, Wang Wenhao, Ma Zhenjiang, Wang Jinwu. Treatment of Achilles tendinitis with an ultrasonic device for emulsification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2259-2264. |
| [15] | Li Zhi, Hua Yongyong, Zhang Jianquan, Fu Zhen. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by inducing cyclin D1 up-regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(13): 2006-2011. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||