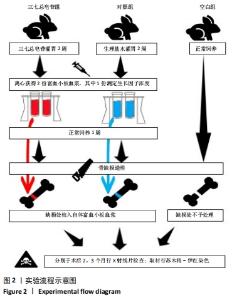
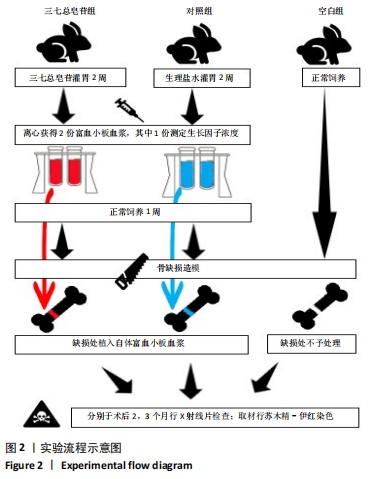
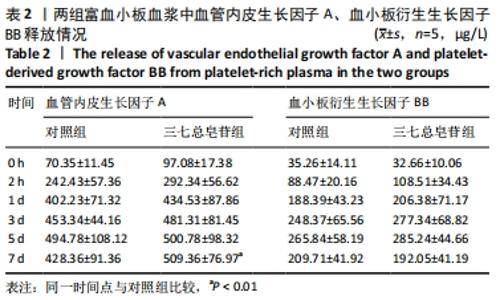
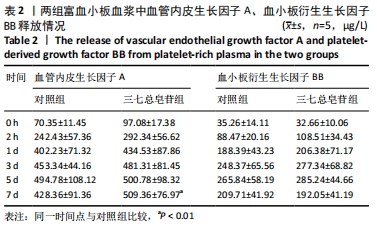
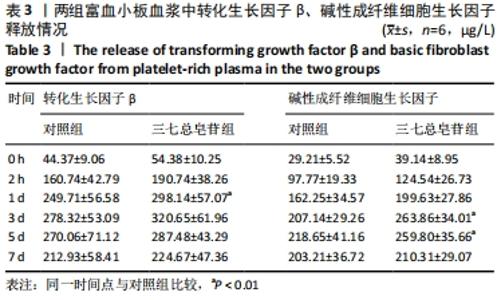
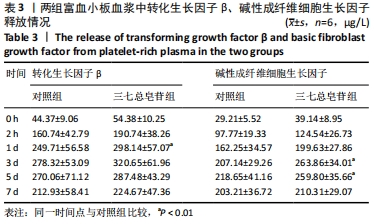
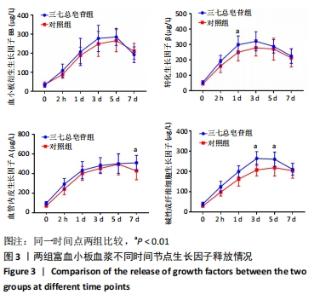
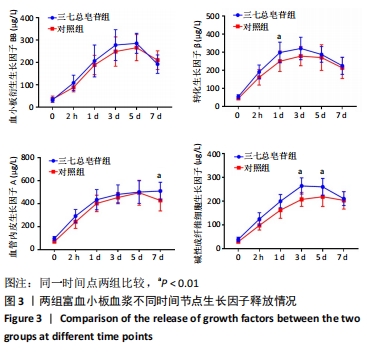
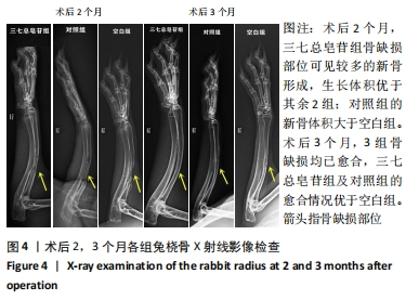
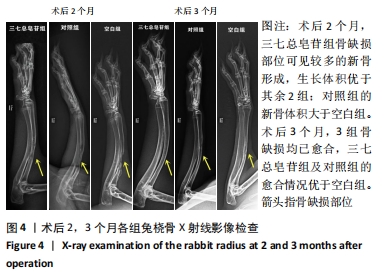
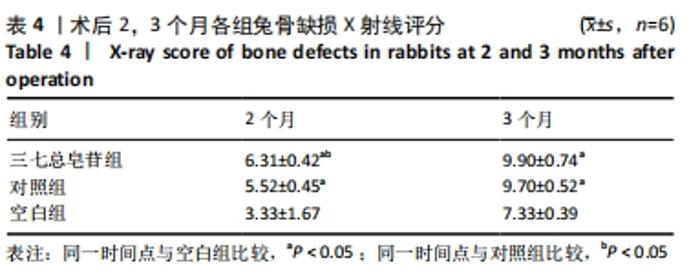
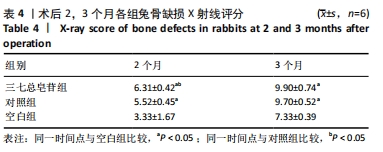
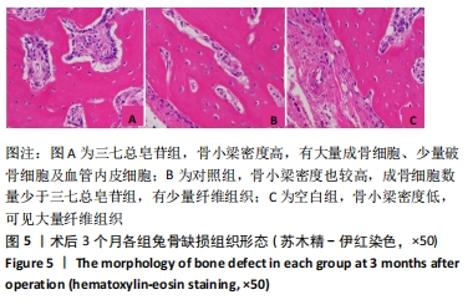
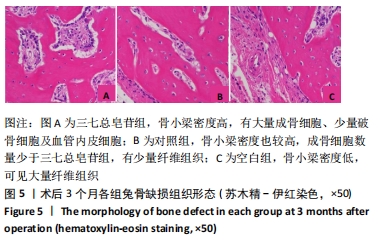
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (14): 2155-2160.doi: 10.12307/2022.476
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of panax notoginseng saponins on platelet-rich plasma promoting bone defect healing in rabbits
Li Shijie, Ma Liqiong, Xiong Xianmei, Zhang Yan, Chen Zijie, Feng Junming, Gao Yijia, Zeng Zhanpeng
- The First Clinical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-22Revised:2021-06-29Accepted:2021-07-24Online:2022-05-18Published:2021-12-21 -
Contact:Gao Yijia, Master, Associate chief physician, the First Clinical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Li Shijie, Master candidate, the First Clinical School of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 2018A030313369 (to GYJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Shijie, Ma Liqiong, Xiong Xianmei, Zhang Yan, Chen Zijie, Feng Junming, Gao Yijia, Zeng Zhanpeng. Effect of panax notoginseng saponins on platelet-rich plasma promoting bone defect healing in rabbits[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2155-2160.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] DHILLON MS, BEHERA P, PATEL S, et al.Orthobiologics and platelet rich plasma. Indian J Orthop. 2014;48(1):1-9. [2] MARIANI E, PULSATELLI L.Platelet Concentrates in Musculoskeletal Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1328. [3] EPPLEY BL, WOODELL JE, HIGGINS J.Platelet Quantification and Growth Factor Analysis from Platelet-Rich Plasma: Implications for Wound Healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114(6):1502-1508. [4] FRANKLIN SP, BURKE EE, HOLMES SP.The effect of platelet-rich plasma on osseous healing in dogs undergoing high tibial osteotomy. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0177597. [5] 陈红艳,陈安,卢芳国,等.三七总皂苷的药理研究进展[J]. 湖南中医杂志,2019,35(1):154-157. [6] 周海辛.三七总皂甙对创伤性下肢骨折大鼠碱性成纤维细胞因子和血管内皮生长因子表达的影响[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2018, 34(20):2431-2434. [7] 柳毅,陈建治. 三七总皂苷及其诱导成骨的试验和机制[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志,2015,42(1):75-78. [8] BOLLAND BJ, PARTRIDGE K, TILLEY S,et al.Biological and mechanical enhancement of impacted allograft seeded with human bone marrow stromal cells: potential clinical role in impaction bone grafting. Regen Med. 2006;1(4):457-467. [9] 秦宇星, 任前贵,沈佩锋.组织工程骨技术治疗骨缺损的优越性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,24(24):3877-3882. [10] 陈柏行.含中药富血小板血浆干预骨不连的实验研究与临床回顾[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2019. [11] 何翠欢.富血小板血浆联合仙灵骨葆胶囊治疗KOA的疗效观察及网络药理学研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2019. [12] 马浩哲.富血小板血浆联合一盘珠汤促进兔腱骨结合部损伤后的修复[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2019. [13] 彭钦.补肾生精法联合富血小板血浆干预兔骨缺损模型研究[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2020. [14] 陈修, 徐叔云,卞如濂.药理实验方法学[M]. 2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2002:1203. [15] AGHALOO TL, MOY PK, FREYMILLER EG.Investigation of platelet-rich plasma in rabbit cranial defects: A pilot study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2002;60(10):1176-1181. [16] 宋子鉴,郑欣,王进,等.成年兔桡骨骨缺损模型的骨缺损长度探讨[J]. 实验动物与比较医学,2018,38(3):182-187. [17] LANE JM, SANDHU HS.Current approaches to experimental bone grafting. Orthop Clin North Am. 1987;18(2):213-225. [18] ZHANG L, MU W, CHEN S, et al.The enhancement of osteogenic capacity in a synthetic BMP-2 derived peptide coated mineralized collagen composite in the treatment of the mandibular defects. Biomed Mater Eng. 2016;27(5):495-505. [19] ROFFI A, DI MATTEO B, KRISHNAKUMAR GS, et al.Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of bone defects: from pre-clinical rational to evidence in the clinical practice. Int Orthop. 2017;41(2):221-237. [20] DHILLON RS, SCHWARZ EM, MALONEY MD.Platelet-rich plasma therapy-future or trend? Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(4):219. [21] FERNÁNDEZ-BARBERO JE, GALINDO-MORENO P, AVILA-ORTIZ G, et al.Flow cytometric and morphological characterization of platelet-rich plasma gel. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(6):687-693. [22] BETSHOLTZ C, JOHNSSON A, HELDIN CH, et al.cDNA sequence and chromosomal localization of human platelet-derived growth factor A-chain and its expression in tumour cell lines. Nature. 1986; 320(6064):695-699. [23] XIE H, CUI Z, WANG L, et al. PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis. Nature Med. 2014;20(11):1270-1278. [24] CRANE JL, CAO X.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and TGF-βsignaling in bone remodeling. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(2):466-472. [25] CHEN G, DENG C, LI YP.TGF-β and BMP Signaling in Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2):272-288. [26] HARRY LE, PALEOLOG EM. From the cradle to the clinic: VEGF in developmental, physiological, and pathological angiogenesis. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2003;69(4):363-374. [27] HU K, OLSEN BR.Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):509-526. [28] ALDRIDGE SE, LENNARD TW, WILLIAMS JR, et al.Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in osteoclast differentiation and function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;335(3):793-798. [29] FELBER K, ELKS PM, LECCA M,et al.Expression of osterix Is Regulated by FGF and Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling during Osteoblast Differentiation. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0144982. [30] 任前贵,王瞾,张坤.仿生控释BMP-2和VEGF的PELA微球支架对骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的Wnt/β-catenin通路的影响[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志,2018,31(10):1118-1121+1125. [31] 秦宇星,任前贵,沈佩锋,等, 组织工程技术治疗骨缺损:应用于临床还有多远?[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(29):4703-4708. [32] TANG R, WANG S, YANG J,et al.Application of platelet-rich plasma in traumatic bone infections. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021;19(7):867-875. [33] 任军,赵岩,肖彬,等.富血小板血浆促进胫骨骨折模型兔的骨愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(35):5595-5599. [34] MALHOTRA A, PELLETIER M, OLIVER R, et al.Platelet-Rich Plasma and Bone Defect Healing. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(19-20):2614-2633. [35] KOBAYASHI E, FLÜCKIGER L, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, et al.Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20(9):2353-2360. [36] 庄雅雯,曾奕明,陈云峰,等.不同激活剂对人富血小板血浆释放曲线的影响[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志,2018,41(11):868-872. [37] 张猛,谢松涛,贺西京,等.富血小板血浆复合移植骨用于肱骨髁部骨缺损修复治疗的临床探索[J].局解手术学杂志,2018,27(1):20-24. [38] FERNANDEZ DE GRADO G, KELLER L, IDOUX-GILLET Y, et al., Bone substitutes: a review of their characteristics, clinical use, and perspectives for large bone defects management. J Tissue Eng. 2018;9: 2041731418776819. [39] MIJIRITSKY E, ASSAF HD, PELEG O, et al.Use of PRP, PRF and CGF in Periodontal Regeneration and Facial Rejuvenation-A Narrative Review. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(4):317. |
| [1] | Xue Yadong, Zhou Xinshe, Pei Lijia, Meng Fanyu, Li Jian, Wang Jinzi . Reconstruction of Paprosky III type acetabular defect by autogenous iliac bone block combined with titanium plate: providing a strong initial fixation for the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1424-1428. |
| [2] | Kong Yamin, Yan Juntao, Ma Bingxiang, Li Huawei. Massage vibration intervenes with MyoD expression and proliferation and differentiation of muscle satellite cells in rats with sciatic nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1160-1166. |
| [3] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [4] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [5] | Wang Qin, Shen Cheng, Liao Jing, Yang Ye. Dapagliflozin improves renal injury in diabetic nephropathy rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [6] | Xiao Yang, Gong Liqiong, Fei Jing, Li Leiji. Effect of electroacupuncture on nerve growth factor and its receptor expression in facial nerve nucleus after facial nerve injury in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1253-1259. |
| [7] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [8] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [9] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [10] | Peng Kun. Improvement of the treatment effect of osteoporotic fractures: research status and strategy analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 980-984. |
| [11] | Xu Jing, Yan Yongmin, Cai Mengjie . miR-373 inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by downregulating transforming growth factor beta type II receptor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 756-761. |
| [12] | Tan Guozhong, Tu Xinran, Guo Liyang, Zhong Jialin, Zhang Yang, Jiang Qianzhou. Biosafety evaluation of three-dimensional printed gelatin/sodium alginate/58S bioactive glass scaffolds for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(4): 521-527. |
| [13] | Wang Hailong, Li Long, Yilihamu Tuoheti, Liu Xu, Nacikedaoerji, Chen Hongtao, Cui Yong. Molecular network of miR-106b-5p regulating osteoporotic fracture in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(2): 239-244. |
| [14] | Chen Yuting, He Feiming, Xiang Wei, Wang Chao, Cao Weiwei, Wang Weishan, Liu Wei . Effects of transforming growth factor beta1 and Ras homolog gene family member A on cell morphology and cytoskeleton during chondrocyte differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2144-2149. |
| [15] | Gao Xixin, Wang Xi, Fan Xuhui, Cui Yi, Yang Wei, Zhao Yunzhuan. Platelet-rich fibrin combined with induced bone matrix repairs bone defects around oral implants in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(14): 2207-2213. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||