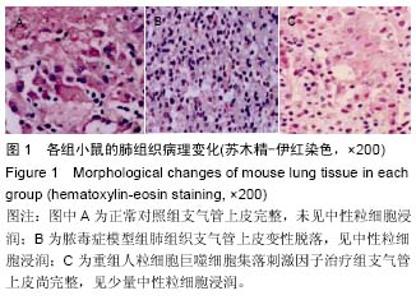
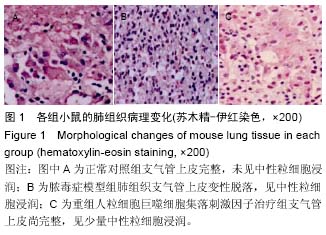
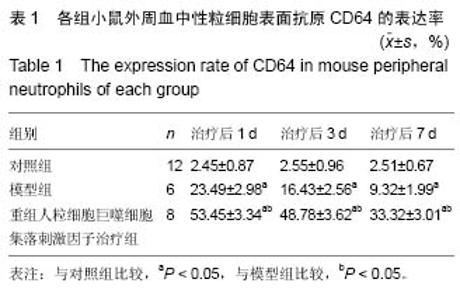
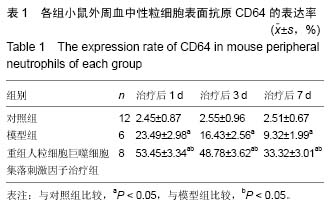
| [1] 王正国.当前脓毒症研究的思考[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2012,37(1)1:1011-1014.
[2] Ou SM, Chu H, Chao PW, et al. Long-Term Mortality and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Sepsis Survivors. A Nationwide Population-based Study.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;194(2):209-217.
[3] Kaynar AM, Bakalov V, Laverde SM, et al. Cost of surviving sepsis: a novel model of recovery from sepsis in Drosophila melanogaster. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2016;4(1):4.
[4] 王静,李熙鸿.脓毒症发病机制的研究进展[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2012,27(10):786-789.
[5] 石岩.严重脓毒症发病机制新认识[J].中国实用外科杂志, 2012,32(11):956-958.
[6] 于景敏,孟志云,窦桂芳. 粒细胞集落刺激因子的研究新进展[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志,2008,16(2):452-456.
[7] 宋媛媛. 重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子长效制剂Ⅰ期临床药代动力学和药效学研究[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院, 2013.
[8] Hashemzaei M, Imen Shahidi M, Moallem SA, et al. Modulation of JAK2, STAT3 and Akt1 proteins by granulocyte colony stimulating factor following carbon monoxide poisoning in male rat. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2016;39(4):375-379.
[9] Matsushita K, Takeno A, Tamura S, et al. A Case of Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor-Producing Gastric Cancer Successfully Treated with Trastuzumab. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2015;42(12): 1968-1970.
[10] 朱英,周琪,黄淮,等. 脓毒症患者死亡危险因素分析[J]. 中国急救医学,2008,28(1):24-27.
[11] 刘相德. 脓毒症和感染性休克治疗进展[J]. 创伤与急危重病医学,2014,2(1):14-17.
[12] 李成荣. 脓毒症免疫功能紊乱及免疫调节治疗[J]. 临床儿科杂志,2010,28(1):13-17.
[13] 肖为,杨明施. 脓毒症治疗的现状与新进展[J]. 医学综述, 2014,20(8):1425-1429.
[14] Ansari S, Paudel P, Gautam K, et al. Chromobacterium violaceum Isolated from a Wound Sepsis: A Case Study from Nepal. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2015;2015: 181946.
[15] Spec A, Shindo Y, Burnham CA, et al. T cells from patients with Candida sepsis display a suppressive immunophenotype. Crit Care. 2016;20:15.
[16] 唐丽群. 脓毒症不合并肾功能障碍时持续肾替代治疗的时机探讨[D]. 广州:广州中医药大学,2012.
[17] 黄顺伟,管向东,陈娟,等. 免疫调理治疗改善脓毒症炎症因子、体液和细胞免疫以及预后的作用[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2009,3(10):1645-1652.
[18] 任建安,张学文. 外科脓毒症病人的液体治疗[J]. 中国实用外科杂志,2010,30(6):460-462.
[19] 章志丹. 脓毒症与免疫营养治疗[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2010,30(11):919-923.
[20] 姚咏明,孟海东. 严重脓毒症抗凝治疗的新认识[J]. 中华儿科杂志,2006,44(8):569-572.
[21] 白冰心,吴言为,张路瑶,等. 脓毒症的免疫治疗进展[J]. 中国新药与临床杂志,2015,34(3):161-166.
[22] Mäenpää J, Varthalitis I, Erdkamp F, et al. The use of granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) and management of chemotherapy delivery during adjuvant treatment for early-stage breast cancer--further observations from the IMPACT solid study. Breast. 2016;25:27-33.
[23] Pettengell R, Bias P, Mueller U, et al. Clinical safety of tbo-filgrastim, a short-acting human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Support Care Cancer. 2016; 24(6):2677-2684.
[24] 薛耀辉. 重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子在化疗后白细胞减少的应用[J]. 中国现代医生,2008,46(28):76-77.
[25] Nakamura Y, Ishikawa K, Kai Y, et al. Case of malignant melanoma that developed the ability to secrete granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Dermatol. 2016;43(5):580-582.
[26] Cetean S, C?inap C, Constantin AM, et al. The importance of the granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in oncology. Clujul Med. 2015;88(4):468-472.
[27] Khanlarkhani N, Pasbakhsh P, Mortezaee K, et al. Effect of human recombinant granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on rat busulfan-induced testis injury. J Mol Histol. 2016;47(1):59-67.
[28] Yang JZ, Zhang JQ, Sun LX. Mechanisms for T cell tolerance induced with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Mol Immunol. 2016;70:56-62.
[29] 马玉杰,梁辉.粒细胞集落刺激因子与血液病[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(14):2755-2758.
[30] 李娇,张晟,张瑾. 重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子预防乳腺癌化疗后骨髓抑制的疗效分析[J].中国癌症杂志, 2014, 24(12):925-930.
[31] 何忠杰.重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子的临床应用进展[J]. 中国全科医学,2010,13(11):1252-1253,1257.
[32] 李培,席亚明,徐建旺,等. 粒细胞集落刺激因子治疗急性淋巴细胞白血病疗效和安全性的系统评价[J]. 中国循证医学杂志,2010,10(8):985-990.
[33] 郭少鹭. 重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子改善胃癌患者化疗后骨髓抑制的临床观察[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
[34] 莫红楠,石远凯,孙燕. 重组人粒细胞集落刺激因子在肿瘤化疗中应用20年回顾[J].中国新药杂志, 2013,22(17): 2027-2032.
[35] 王洁洁,徐家丽. 粒细胞集落刺激因子的神经保护作用机制[J]. 临床儿科杂志,2011,29(4):389-392.
[36] 杨茗.粒细胞集落刺激因子动员自体骨髓干细胞治疗急性心肌梗死的研究[D].上海:复旦大学,2011.
[37] 徐玉辉.粒细胞集落刺激因子(G-CSF)对脓毒症小鼠免疫功能的影响[D]. 南昌:南昌大学医学院, 2013. |