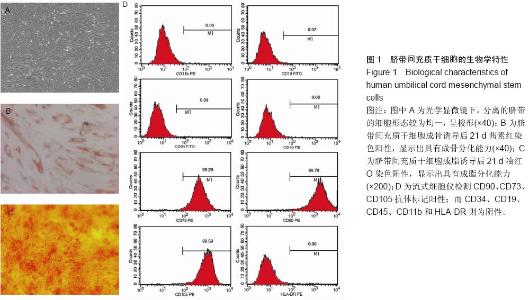
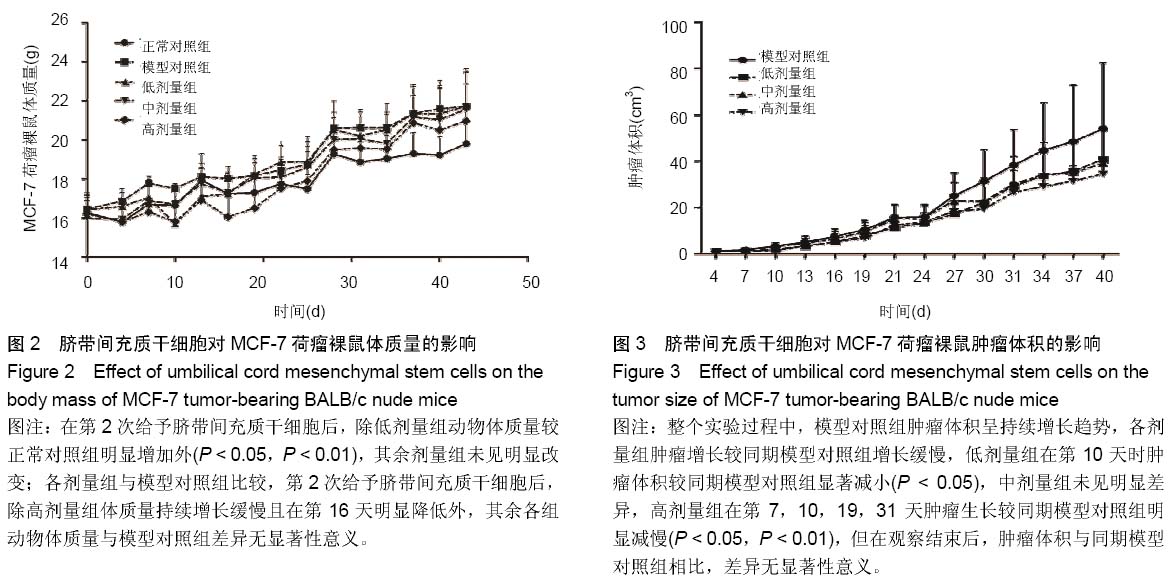
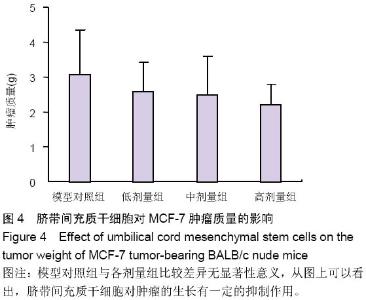
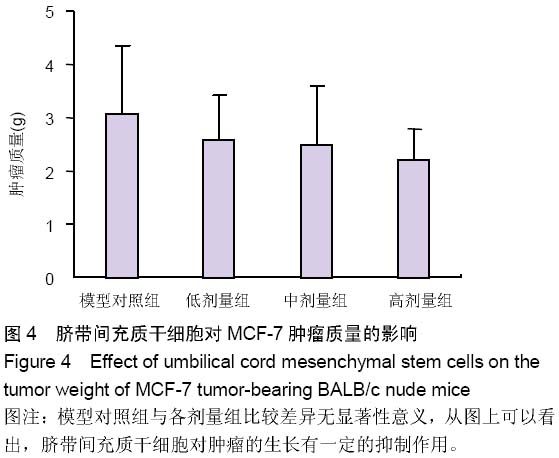
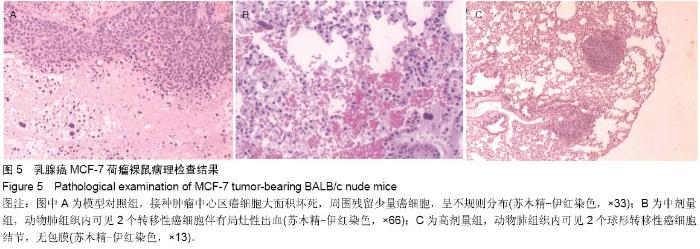
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (19): 2986-2992.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.19.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on the growth of human breast cancer MCF-7 xenograft in a nude mouse
Han Li-xin1, Han Zhi-bo1, Geng Jie2, Wang Bin2, Yan Shu-ling2, Mao Ai-bin2, Han Zhong-chao1, 2
- 1State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, Institute of Hematology and Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Tianjin 300020, China; 2National Engineering Research Center of Cell Products, Tianjin 300457, China
-
Online:2015-05-06Published:2015-05-06 -
Contact:Corresponding author: Han Zhong-chao, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, Institute of Hematology and Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Tianjin 300020, China; National Engineering Research Center of Cell Products, Tianjin 300457, China -
About author:Han Li-xin, Master, State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, Institute of Hematology and Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College, Tianjin 300020, China -
Supported by:the National Science and Technology Supporting Plan of China, No. 2013BAI01B09
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Li-xin, Han Zhi-bo, Geng Jie, Wang Bin, Yan Shu-ling, Mao Ai-bin, Han Zhong-chao. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on the growth of human breast cancer MCF-7 xenograft in a nude mouse [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(19): 2986-2992.
share this article
| [1] Fan CG, Tang FW, Zhang QJ, et al. Characterization and neural differentiation of fetal lung mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2005;14(5):311-321.
[2] Wu Y, Wang Z, Cao Y, et al. Cotransplantation of haploidentical hematopoietic and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with a myeloablative regimen for refractory/relapsed hematologic malignancy. Ann Hematol. 2013;92(12):1675-1684.
[3] Liang J, Zhang H, Hua B, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in treatment of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2009;15(5):644-646.
[4] Jiang R, Han Z, Zhuo G, et al. Transplantation of placenta- derived mesenchymal stem cells in type 2 diabetes: a pilot study. Front Med. 2011;5(1):94-100.
[5] 韩忠朝,李宗金,韩之波.围产期干细胞[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014:260-262.
[6] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69-90.
[7] Croce CM. Oncogenes and cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358(5):502-511.
[8] Devarajan E, Song YH, Krishnappa S, et al. Epithelial- mesenchymal transition in breast cancer lines is mediated through PDGF-D released by tissue-resident stem cells. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(5):1023-1031.
[9] Mailliez A, Decanter C, Bonneterre J. Adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer and fertility: estimation of the impact, options of preservation and role of the oncologist. Bull Cancer. 2011;98(7):741-751.
[10] Anders CK, Johnson R, Litton J, et al. Breast cancer before age 40 years. Semin Oncol. 2009;36(3):237-249.
[11] Colleoni M, Rotmensz N, Robertson C, et al. Very young women (<35 years) with operable breast cancer: features of disease at presentation. Ann Oncol. 2002;13(2):273-279.
[12] Althuis MD, Brogan DD, Coates RJ, et al. Breast cancers among very young premenopausal women (United States). Cancer Causes Control. 2003;14(2):151-160.
[13] Anders CK, Hsu DS, Broadwater G, et al. Young age at diagnosis correlates with worse prognosis and defines a subset of breast cancers with shared patterns of gene expression. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(20):3324-3330.
[14] Winchester DP, Osteen RT, Menck HR. The National Cancer Data Base report on breast carcinoma characteristics and outcome in relation to age. Cancer. 1996;78(8):1838-1843.
[15] Nixon AJ, Neuberg D, Hayes DF, et al. Relationship of patient age to pathologic features of the tumor and prognosis for patients with stage I or II breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12(5):888-894.
[16] Murk W, Seli E. Fertility preservation as a public health issue: an epidemiological perspective. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2011;23(3):143-150.
[17] Lu LL, Liu YJ, Yang SG, et al. Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica. 2006;91(8):1017-1026.
[18] Hu Y,Liang J,Cui HP,et al.Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into retinal progenitor cells.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (19): 1783-1792.
[19] Liu XY,Li DH,Jiang D,et al.Acetylcholine secretion by motor neuron-like cells from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(22): 2086-2092.
[20] Nagano M, Kimura K, Yamashita T, et al. Hypoxia responsive mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood are effective for bone repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2010; 19(8): 1195-1210.
[21] Bieback K, Kern S, Klüter H, et al. Critical parameters for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells. 2004;22(4):625-634.
[22] Ciavarella S, Dominici M, Dammacco F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a new promise in anticancer therapy. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(1):1-10.
[23] Wang Y, Zhang Z, Chi Y, et al. Long-term cultured mesenchymal stem cells frequently develop genomic mutations but do not undergo malignant transformation. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4:e950.
[24] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[25] Yang X, Li Z, Ma Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells promote carcinoma growth and lymph node metastasis when co-injected with esophageal carcinoma cells in nude mice. Cancer Cell Int. 2014;14(1):93.
[26] Ozawa K, Sato K, Oh I, et al. Cell and gene therapy using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). J Autoimmun. 2008;30(3): 121-127.
[27] Studeny M, Marini FC, Dembinski JL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: potential precursors for tumor stroma and targeted-delivery vehicles for anticancer agents. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96(21):1593-1603.
[28] Ahn JO, Chae JS, Coh YR, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit T-cell lymphoma growth in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(9):4839-4847.
[29] Akimoto K, Kimura K, Nagano M, et al. Umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit, but adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote, glioblastoma multiforme proliferation. Stem Cells Dev. 2013; 22(9):1370-1386.
[30] Nakamizo A, Marini F, Amano T, et al. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of gliomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65(8):3307-3318.
[31] Ahn Jo, Lee Hw, Seo Kw, et al. Anti-tumor effect of adipose tissue derived-mesenchymal stem cells expressing interferon-β and treatment with cisplatin in a xenograft mouse model for canine melanoma. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74897.
[32] Hou L, Wang X, Zhou Y, et al. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells on liver cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(2):1239-1250.
[33] Khakoo AY, Pati S, Anderson SA, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells exert potent antitumorigenic effects in a model of Kaposi's sarcoma. J Exp Med. 2006;203(5):1235-1247.
[34] Duan X, Guan H, Cao Y, et al. Murine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells as vehicles for interleukin-12 gene delivery into Ewing sarcoma tumors. Cancer. 2009;115(1): 13-22.
[35] Menon LG, Picinich S, Koneru R, et al. Differential gene expression associated with migration of mesenchymal stem cells to conditioned medium from tumor cells or bone marrow cells. Stem Cells. 2007;25(2):520-528.
[36] Komarova S, Kawakami Y, Stoff-Khalili MA, et al. Mesenchymal progenitor cells as cellular vehicles for delivery of oncolytic adenoviruses. Mol Cancer Ther. 2006;5(3): 755-766.
[37] Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2007;449(7162):557-563.
[38] Ramasamy R, Lam EW, Soeiro I, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation and apoptosis of tumor cells: impact on in vivo tumor growth. Leukemia. 2007;21(2):304-310.
[39] Zimmerlin L, Park TS, Zambidis ET, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome and regenerative therapy after cancer. Biochimie. 2013;95(12):2235-2245.
[40] Sasser AK, Mundy BL, Smith KM, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells enhance breast cancer cell growth rates in a cell line-dependent manner when evaluated in 3D tumor environments. Cancer Lett. 2007;254(2):255-264.
[41] Leng L, Wang Y, He N, et al. Molecular imaging for assessment of mesenchymal stem cells mediated breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(19):5162-5170.
[42] Spaeth EL, Dembinski JL, Sasser AK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transition to tumor-associated fibroblasts contributes to fibrovascular network expansion and tumor progression. PLoS One. 2009;4(4):e4992.
[43] Short B, Brouard N, Occhiodoro-Scott T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells. Arch Med Res. 2003;34(6):565-571.
[44] Beckermann BM, Kallifatidis G, Groth A, et al. VEGF expression by mesenchymal stem cells contributes to angiogenesis in pancreatic carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2008; 99(4):622-631.
[45] Papetti M, Herman IM. Mechanisms of normal and tumor-derived angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;282(5):C947-970.
[46] Hsieh JY, Wang HW, Chang SJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord express preferentially secreted factors related to neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72604.
[47] Matsuo Y, Raimondo M, Woodward TA, et al. CXC-chemokine/CXCR2 biological axis promotes angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(5):1027-1037.
[48] Arenberg DA, Keane MP, DiGiovine B, et al. Epithelial-neutrophil activating peptide (ENA-78) is an important angiogenic factor in non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Invest. 1998;102(3):465-472.
[49] Wang SW, Sun YM. The IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway: potential therapeutic strategies in treating colorectal cancer (Review). Int J Oncol. 2014;44(4):1032-1040.
[50] Rattigan Y, Hsu JM, Mishra PJ, et al. Interleukin 6 mediated recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells to the hypoxic tumor milieu. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(20):3417-3424.
[51] Lazarus HM, Koc ON, Devine SM, et al. Cotransplantation of HLA-identical sibling culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cells and hematopoietic stem cells in hematologic malignancy patients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11(5):389-398.
[52] Wang Y, Han ZB, Ma J, et al. A toxicity study of multiple-administration human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in cynomolgus monkeys. Stem Cells Dev. 2012; 21(9):1401-1408. |
| [1] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Liu-Gao Miyang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Wang Jinxiang, Pan Xinghua. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for traumatic systemic inflammatory response syndrome in tree shrews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3994-4000. |
| [2] | Han Ningning, Zuo Jinfu, Sun Miao, Tang Shengjian, Liu Fangjun. Application and progress of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2079-2086. |
| [3] | Jing Yucheng, Wang Le, Wang Xianyun, Wei Mei, Li Min, Ji Lishuang, Ma Fangfang, Liu Gang , Zheng Mingqi. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic heart disease: a 3-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 6-12. |
| [4] | Gu Jingjing, Zhou Rui, Yang Tingting, Yang Xiaoping, Xu Fei, Zheng Bo. Supporting effect of human skeletal muscle-derived myoendothelial cells on hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 50-55. |
| [5] | Zhu Bingbing, He Haibin, Deng Jianghua, Wang Wenqiang, Mu Xiaoling. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing interleukin 8 receptor inhibit inflammation and promote vascular repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 61-66. |
| [6] | Guo Xuan, Xie Jun, Suo Jinrong, Li Yingrui, Huang Lei, Ma Munan, Li Jingjing, Fu Songtao. Transplantation of islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 78-83. |
| [7] | Ruan Guangping, Yao Xiang, Cai Xuemin, Li Zian, Pang Rongqing, Pan Xinghua. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for treating systemic lupus erythematosus in a tree shrew model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 90-95. |
| [8] | Zang Jing, Luan Zuo, Wang Qian, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wu Youjia, Guo Aisong. Two kinds of stem cell nasal transplantation for treating white matter injury in premature rat infants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 101-107. |
| [9] | Huang Yongming, Huang Qiming, Liu Yanjie, Wang Jun, Cao Zhenwu, Tian Zhenjiang, Chen Bojian, Mai Xiujun, Feng Enhui. Proliferation and apoptosis of chondrocytes co-cultured with TDP43 lentivirus transfected-human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1016-1022. |
| [10] | Liu Mengting, Rao Wei, Han Bing, Xiao Cuihong, Wu Dongcheng. Immunomodulatory characteristics of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1063-1068. |
| [11] | Zhang Xuhan, Wang Li, Tang Baolin, Wan Xiang, Yao Wen, Song Kaidi, Sun Zimin. Pretreatment of unrelated umbilical cord blood transplantation without antithymocyte globulin for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia: follow-up evaluation of 306 cases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4986-4993. |
| [12] | Chen Jianglong, Shi Xinyu, Cheng Jun, Ye Yichao, Zhang Zhenwen, Li Xiaohong, Sun Hongtao. Protective effect of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells on the rat’s blood-brain barrier after traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3947-3952. |
| [13] | Zhao Yilang, Liu Tao, Yang Huilin, He Fan. Extracellular matrix improves antioxidant capacity of human umbilical cord stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3953-3958. |
| [14] |
Gao Kunli, Xing Hongyun, Bian Tierong, Han Liying.
Transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in the repair of hematopoietic injury in bone marrow [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 3966-3972. |
| [15] | Yu Heng, Zhou Tao. Effects of umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on recovery of nerve function and telomerase reverse transcriptase expression in brain tissue of cerebral infarction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 2972-2977. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||