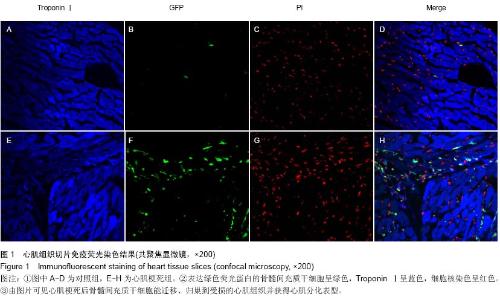
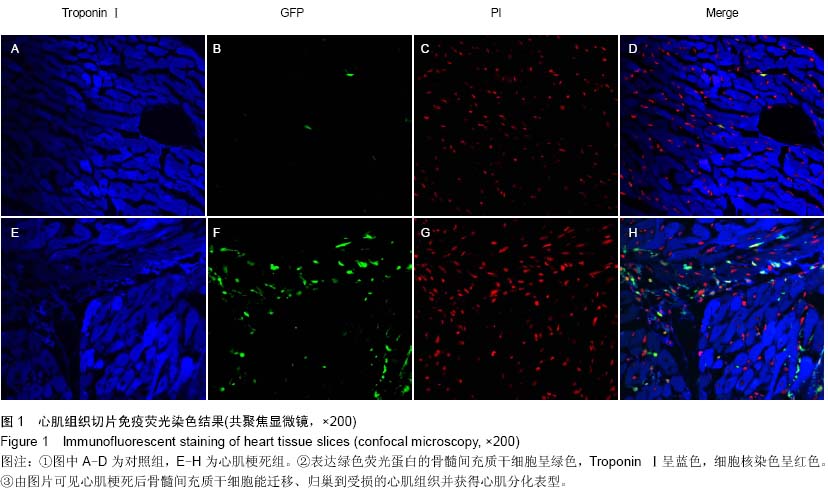
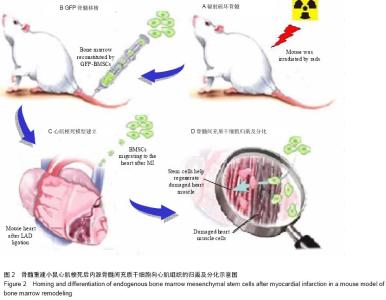
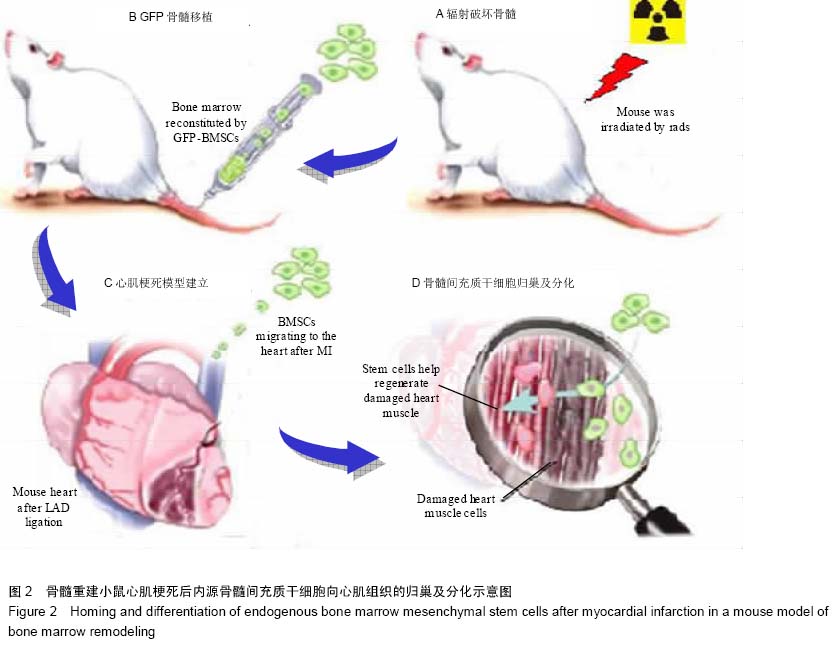
| [1] He XQ, Chen MS, Li SH, et al. Co-culture with cardiomyocytes enhanced the myogenic conversion of mesenchymal stromal cells in a dose-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biochem. 2010;339(1-2):89-98.
[2] 曾春雨.诱导多能干细胞和心脏干/祖细胞对心肌修复作用的研究进展[J].解放军医药杂志,2012,24(7):1-4.
[3] Rangappa S, Makkar R, Forrester J. Review article: current status of myocardial regeneration: new cell sources and new strategies. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2010;15(4): 338-343.
[4] Senyo SE, Lee RT, Kühn B. Cardiac regeneration based on mechanisms of cardiomyocyte proliferation and differentiation. Stem Cell Res. 2014;13(3 Pt B):532-541.
[5] Cho GS, Fernandez L, Kwon C. Regenerative medicine for the heart: perspectives on stem-cell therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;21(14):2018-2031.
[6] Zamilpa R, Navarro MM, Flores I, et al. Stem cell mechanisms during left ventricular remodeling post-myocardial infarction: Repair and regeneration. World J Cardiol. 2014;6(7):610-620.
[7] Odörfer KI, Walter I, Kleiter M, et al. Role of endogenous bone marrow cells in long-term repair mechanisms after myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(6B): 2867-2874.
[8] Kanellakis P, Slater NJ, Du XJ, et al. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and stem cell factor improve endogenous repair after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;70(1):117-125.
[9] Schuh A, Konschalla S, Kroh A, et al. Effect of SDF-1 α on endogenous mobilized and transplanted stem cells in regeneration after myocardial infarction. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(12):1964-1970.
[10] Oh H, Bradfute SB, Gallardo TD, et al. Cardiac progenitor cells from adult myocardium: homing, differentiation, and fusion after infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(21): 12313-12318.
[11] Rajantie I, Ilmonen M, Alminaite A, et al. Adult bone marrow-derived cells recruited during angiogenesis comprise precursors for periendothelial vascular mural cells. Blood. 2004;104(7):2084-2086.
[12] Ozerdem U, Alitalo K, Salven P, et al. Contribution of bone marrow-derived pericyte precursor cells to corneal vasculogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46(10): 3502-3506.
[13] Kuramochi Y, Fukazawa R, Migita M, et al. Cardiomyocyte regeneration from circulating bone marrow cells in mice. Pediatr Res. 2003;54(3):319-325.
[14] 雷俊霞,郭振宇,赵东长,等.大鼠骨髓间质干细胞对同种骨髓移植后造血重建和免疫重建的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2006, 22(6): 1129-1132.
[15] 刘凡凤,邱慧颖,解琳娜,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植重建极重度放射损伤小鼠造血功能[J].第二军医大学学报,2008,29(9): 1015-1019.
[16] 郑晓丽,高磊,宋宁霞,等.异基因骨髓源间充质干细胞对极重度放射损伤小鼠造血功能重建的影响[J].解放军医学杂志,2010, 35(10):1187-1191.
[17] Chiu RC. Adult stem cell therapy for heart failure. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2003;3(2):215-225.
[18] Kawada H, Fujita J, Kinjo K, et al. Nonhematopoietic mesenchymal stem cells can be mobilized and differentiate into cardiomyocytes after myocardial infarction. Blood. 2004; 104(12):3581-3587.
[19] Fukuda K, Fujita J. Mesenchymal, but not hematopoietic, stem cells can be mobilized and differentiate into cardiomyocytes after myocardial infarction in mice. Kidney Int. 2005;68(5):1940-1943.
[20] Terada N, Hamazaki T, Oka M, et al. Bone marrow cells adopt the phenotype of other cells by spontaneous cell fusion. Nature. 2002;416(6880):542-545.
[21] Ying QL, Nichols J, Evans EP, et al. Changing potency by spontaneous fusion.Nature. 2002;416(6880):545-548.
[22] Alvarez-Dolado M, Pardal R, Garcia-Verdugo JM, et al. Fusion of bone-marrow-derived cells with Purkinje neurons, cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Nature. 2003;425(6961): 968-973. |