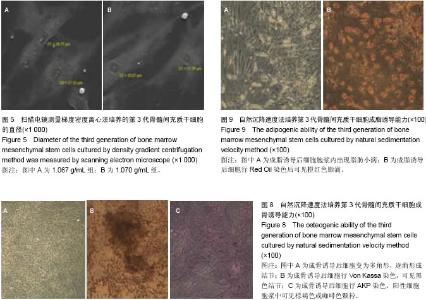
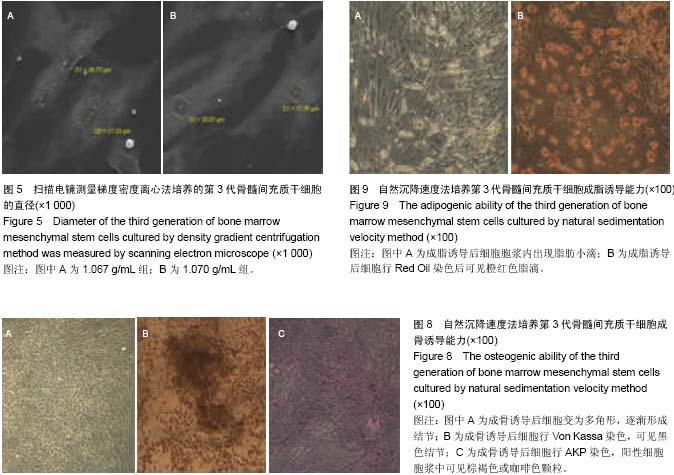
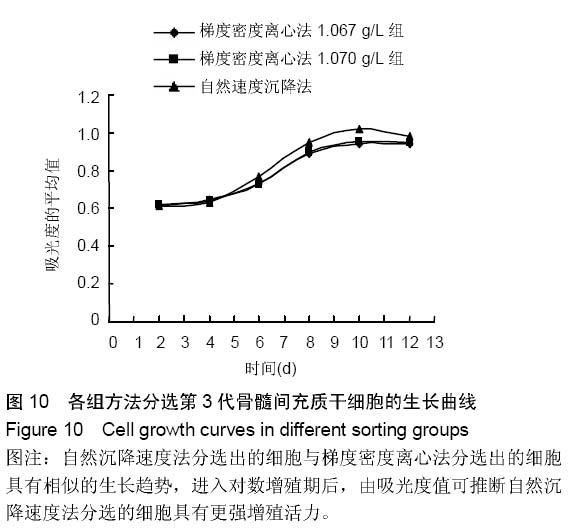
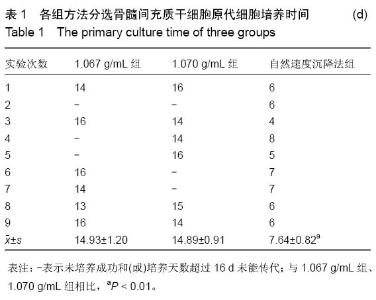
| [1] 林春博,杨渊,陈维平.低渗结合自然沉降法分离兔骨髓间充质干细胞及其鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(1): 12-16.
[2] Liu L, Zhao X, Li P, et al. A novel way to isolate MSCs from umbilical cords. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42(8):2190-2193.
[3] Lee KS, Nah JJ, Lee BC, et al. Maintenance and characterization of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells isolated from canine umbilical cord matrix by collagenase digestion. Res Vet Sci. 2013;94(1):144-151.
[4] Han YF, Tao R, Sun TJ, et al. Optimization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell isolation and culture methods. Cytotechnology. 2013;65(5):819-827.
[5] Castro-Malaspina H, Gay RE, Resnick G, et al. Characterization of human bone marrow fibroblast colony-forming cells (CFU-F) and their progeny. Blood. 1980;56(2):289-301.
[6] Lindsay SL, Johnstone SA, Mountford JC, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells isolated from olfactory biopsies but not bone enhance CNS myelination in vitro. Glia. 2013;61(3): 368-382.
[7] Chang Y, Hsieh PH, Chao CC. The efficiency of Percoll and Ficoll density gradient media in the isolation of marrow derived human mesenchymal stem cells with osteogenic potential. Chang Gung Med J. 2009;32(3):264-275.
[8] 肖盼,陈剑,王彦平,等.不同消化分离方法分离人羊膜间充质干细胞效果比较[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2010,26(5):1033-1037.
[9] 蔡金宏,林春博,杨渊.间充质干细胞分离方法的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(45): 7375-7380.
[10] Li X, Zhang Y, Qi G. Evaluation of isolation methods and culture conditions for rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotechnology. 2013;65(3):323-334.
[11] Trivanovi? D, Koci? J, Mojsilovi? S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells isolated from peripheral blood and umbilical cord Wharton's jelly. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2013;141(3-4):178-186.
[12] Tian X, Fu R, Deng L. Method and conditions of isolation and proliferation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2007;21(1):81-85.
[13] Lodie TA, Blickarz CE, Devarakonda TJ, et al. Systematic analysis of reportedly distinct populations of multipotent bone marrow-derived stem cells reveals a lack of distinction. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(5):739-751.
[14] 吴宁,张琪,曲占庆.固体颗粒在液体中沉降速度的计算方法评述[J].石油钻采工艺, 2000,22(2): 51-53,56.
[15] 李铭志,何炎平,诸葛玮,等.泥沙颗粒沉降速度计算方法比较分析[J].水运工程,2014(6): 6-9.
[16] Rosca AM, Burlacu A. Isolation of a mouse bone marrow population enriched in stem and progenitor cells by centrifugation on a Percoll gradient. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2010;55(4):199-208.
[17] Pham PV, Vu NB, Pham VM, et al. Good manufacturing practice-compliant isolation and culture of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Transl Med. 2014;12:56.
[18] Hendijani F, Sadeghi-Aliabadi H, Haghjooy Javanmard S. Comparison of human mesenchymal stem cells isolated by explant culture method from entire umbilical cord and Wharton's jelly matrix. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014;15(4):555-565.
[19] Zeng G, Lai K, Li J, et al. A rapid and efficient method for primary culture of human adipose-derived stem cells. Organogenesis. 2013;9(4):287-295.
[20] Hua J, Gong J, Meng H, et al. Comparison of different methods for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord matrix: proliferation and multilineage differentiation as compared to mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood and bone marrow. Cell Biol Int. 2013 Oct 7. [Epub ahead of print]
[21] Xia CS, Zuo AJ, Wang CY, et al. Isolation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells using density gradient centrifugation and adherence screening methods. Minerva Med. 2013;104(5):519-525. |