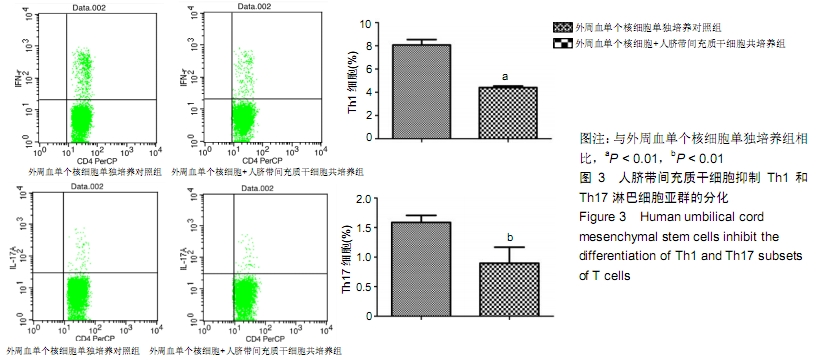
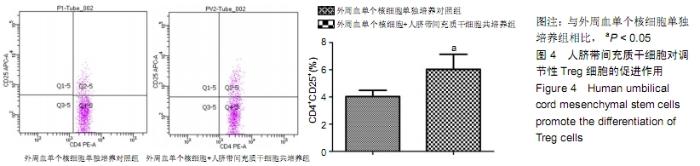
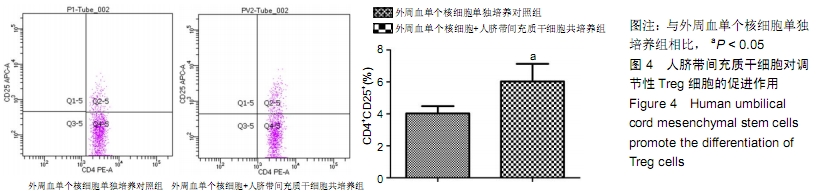
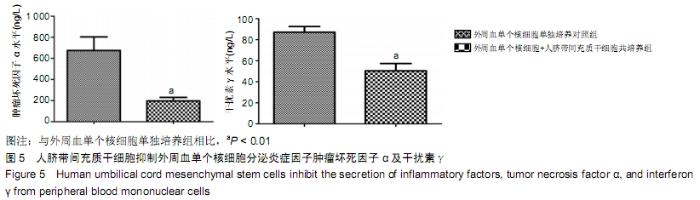
[1] PHINNEY DG, PROCKOP DJ. Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair--current views. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(11):2896-2902.
[2] EL OMAR R, BEROUD J, STOLTZ JF, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: the new gold standard for mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(5):523-544.
[3] AGGARWAL S, PITTENGER MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815-1822.
[4] UCCELLI A, DE ROSBO NK. The immunomodulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells: mode of action and pathways. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1351:114-126.
[5] NASSEREDDINE S, RAFEI H, ELBAHESH E, et al. Acute Graft Versus Host Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(4):1547-1555.
[6] BERNARDO ME, LOCATELLI F. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1416:3-20.
[7] FATHOLLAHI A, GABALOU NB, ASLANI S. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in systemic lupus erythematous, a mesenchymal stem cell disorder. Lupus. 2018;27(7): 1053-1064.
[8] CHEN C, LIANG J, YAO G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells upregulate Treg cells via sHLA-G in SLE patients. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;44:234-241.
[9] HU J, YU X, WANG Z, et al. Long term effects of the implantation of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells from the umbilical cord for newly-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. Endocr J. 2013;60(3):347-357.
[10] MOREIRA A, KAHLENBERG S, HORNSBY P. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for diabetes. J Mol Endocrinol. 2017;59(3):R109-R120.
[11] WANG L, WANG L, CONG X, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell therapy for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: safety and efficacy. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(24):3192-3202.
[12] ANSBORO S, ROELOFS AJ, DE BARI C. Mesenchymal stem cells for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: immune modulation,repair or both. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2017;29(2): 201-207.
[13] LIEW A, O'BRIEN T, EGAN L. Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for Crohn’s disease. Dig Dis. 2017;35(1-2):115-122.
[14] ZHANG XM, ZHANG YJ, WANG W, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Treat Crohn’s Disease with Fistula. Hum Gene Ther. 2017;28(7):534-540.
[15] CHAE HK, SONG WJ, AHN JO, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of soluble factors secreted by feline adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2017;191:22-29.
[16] WANG Q, YANG Q, WANG Z, et al. Comparative analysis of human mesenchymal stem cells from fetal-bone marrow, adipose tissue, and Warton's jelly as sources of cell immunomodulatory therapy. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016; 12(1):85-96.
[17] 张权,张亚奇,饶巍.长期传代培养对人脐带间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2019,41(1):42-52.
[18] POLTAVTSEV AM, POLTAVTSEVA RA, YUSHINA MN, et al. Proliferation of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes and Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived from Wharton's Jelly in Mixed and Membrane-Separated Cultures. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2017;163(4):542-549.
[19] TSE WT, PENDLETON JD, BEYER WM, et al. Suppression of allogeneic T-cell proliferation by human marrow stromal cells: implications in transplantation. Transplantation. 2003; 75(3):389-397.
[20] 徐志娟,盛立霞,欧阳桂芳.脐血间充质干细胞抑制外周淋巴细胞增殖的作用[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2014,30(9):968-971.
[21] RASMUSSON I, RINGDÉN O, SUNDBERG B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit lymphocyte proliferation by mitogens and alloantigens by different mechanisms. Exp Cell Res. 2005;305(1):33-41.
[22] ALIKARAMI F, YARI F, AMIRIZADEH N, et al. The Immunosuppressive Activity of Amniotic Membrane Mesenchymal Stem Cells on T Lymphocytes. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2015;7(3):90-96.
[23] SHENG H, WANG Y, JIN Y, et al. A critical role of IFNgamma in priming MSC-mediated suppression of T cell proliferation through up-regulation of B7-H1. Cell Res. 2008;18(8): 846-857.
[24] YANG H, SUN J, LI Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells suppress proliferation of PHA-activated lymphocytes in vitro by inducing CD4(+) CD25(high)CD45RA(+) regulatory T cell production and modulating cytokine secretion. Cell Immunol. 2016;302: 26-31.
[25] PIANTA S, BONASSI SIGNORONI P, MURADORE I, et al. Amniotic membrane mesenchymal cells-derived factors skew T cell polarization toward Treg and downregulate Th1 and Th17 cells subsets. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(3):394-407.
[26] WANG D, HUANG S, YUAN X, et al. The regulation of the Treg/Th17 balance by mesenchymal stem cells in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017;14(5): 423-431.
[27] GHANNAM S, PÈNE J, MOQUET-TORCY G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit human Th17 cell differentiation and function and induce a T regulatory cell phenotype. J Immunol. 2010;185(1):302-312.
[28] SUN L, AKIYAMA K, ZHANG H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation reverses multiorgan dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus mice and humans. Stem Cells. 2009; 27(6):1421-1432.
[29] LI L, LIU S, XU Y, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells downregulate inflammatory responses by shifting the Treg/Th17 profile in experimental colitis. Pharmacology. 2013;92(5-6):257-264.
|