Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (17): 2762-2769.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1699
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes
Han Rui1, 2, Li Lin1, 2, Wang Runqing1, 2, Hou Zongliu1, 2
- 1Yan’an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650051, Yunnan Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Tumor Immunological Prevention and Treatment of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650051, Yunnan Province, China
-
Revised:2019-01-14Online:2019-06-18Published:2019-06-18 -
Contact:Hou Zongliu, Professor, Yan’an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650051, Yunnan Province, China; Key Laboratory of Tumor Immunological Prevention and Treatment of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650051, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Han Rui, Master, Yan’an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650051, Yunnan Province, China; Key Laboratory of Tumor Immunological Prevention and Treatment of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650051, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Research Plan Projects of Yunnan Province, No. 2017DG004 and 2018IA045 (both to HZL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Han Rui, Li Lin, Wang Runqing, Hou Zongliu. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2762-2769.
share this article
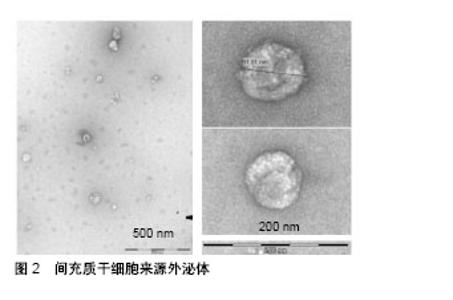
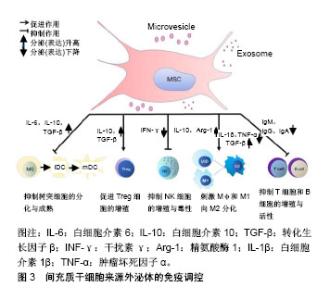
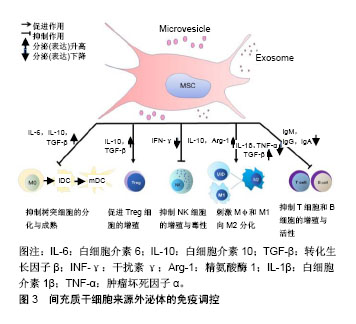
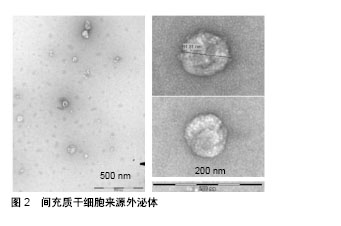
2.1 间充质干细胞来源外泌体概述 间充质干细胞是一种多分化潜能干细胞,具有自我更新和分化成间叶细胞谱系的能力,包括成骨细胞、软骨细胞和脂肪细胞[14]。间充质干细胞的再生潜力,特别是它们的分泌蛋白质组学已经得到了广泛的研究[15-17]。目前,间充质干细胞的分化潜能已经被广泛证实,例如恢复受损的成人间质细胞组织和分化为运动神经元[18-20]。但是,人们普遍更倾向于间充质干细胞的旁分泌作用发挥主要功能,其分泌物具有很强的免疫调节作用,如细胞外囊泡、外泌体和细胞因子等,可以抑制细胞的纤维化与凋亡,促进细胞存活、分化以及血管生成[18,21]。因此,很多学者将间充质干细胞的条件性培养基作为一种无细胞治疗方法应用于心肌梗死、肝损伤、肾损伤等疾病[22-24],并取得了良好的治疗效果。Timmers等[22]初步证明了条件培养基中仅有一小部分产物起到了对心肌的保护作用,其团队进一步在2010年首次分离出胚胎干细胞条件培养基中的外泌体[25]。此后,打开了外泌体是干细胞治疗发挥疗效的主要因素的新视角。 外泌体属于细胞外囊泡,与细胞膜融合后释放到细胞外基质中,通过转运蛋白和核酸介导细胞间通信[7-8]。外泌体的表面标志与它的细胞起源有关。例如,所有间充质干细胞外泌体均表达CD63、CD9、CD81,脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体特异性表达Hsp70和TSG101,以及黏附分子CD29、CD44、CD73[26-28]。在透射电子显微镜下,人脐血间充质干细胞来源外泌体具有较明显异质性,呈圆形或椭圆形,其大小为(48.72±2.7) nm[29],粒子大小的主要峰值为65-75 nm,总体大小分布在60到200 nm之间[30],见图2。"

2.2.1 间充质干细胞来源外泌体调控固有免疫应答 间充质干细胞来源外泌体主要通过其内含的细胞因子发挥对巨噬细胞、NK细胞功能的影响,从而调节固有免疫。Kim等[31]研究发现,间充质干细胞来源外泌体中含有白细胞介素10、白细胞介素12、白细胞介素6、巨噬细胞刺激因子、转化生长因子β、前列腺素E2等细胞因子,肝细胞生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子、血小板衍生生长因子、血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子等生长因子,以维持组织稳态和平衡。 巨噬细胞是固有免疫中的重要细胞,其在微环境刺激下可以分为2型:促炎型巨噬细胞M1型和抗炎型巨噬细胞M2型[32]。在脂多糖刺激巨噬细胞的炎性培养环境中,人脐带间充质干细胞能降低烧伤大鼠模型血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β水平,提高白细胞介素10水平,从而减弱烧伤引起的炎症反应[33]。Domenis等[34]证明只有在细胞因子激活脂肪间充质干细胞的条件下,其产生的外泌体与单核细胞共培养,才能将M1型促炎巨噬细胞转分化为M2型抗炎巨噬细胞。此外,肥胖会导致白色脂肪组织的慢性炎症水平较低,从而引起胰岛素抵抗和代谢综合征,导致许多危及生命疾病的发生[35]。在肥胖个体的白色脂肪组织中不仅有巨噬细胞数量的增加,而且巨噬细胞向表达高水平一氧化氮合酶和肿瘤坏死因子α的M1型极化,从而导致胰岛素抵抗。而在瘦人的白色脂肪组织中大多数巨噬细胞表现出M2型激活状态,表达白细胞介素10和精氨酸酶1,这有助于保持局部免疫和新陈代谢的稳定性[36]。通过各种方法在肥胖个体中恢复M2巨噬细胞后,有助于改善相关炎症及胰岛素抵抗。Zhao等[37]发现脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体通过激活STAT3的转录,可以促使巨噬细胞向M2型极化,高度表达白细胞介素10和精氨酸酶1,抑制巨噬细胞的炎症反应。此外,间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以通过抑制Toll样受体信号来抑制巨噬细胞的激活[38],为先天免疫调节活动提供一个生理学相关背景。 NK细胞作为重要的效应细胞参与固有免疫[39],不仅与抗肿瘤、抗病毒感染和免疫调节有关,而且在某些情况下参与超敏反应和自身免疫性疾病的发生,能够识别靶细胞、杀伤递质[40]。研究表明间充质干细胞能抑制白细胞介素2、白细胞介素15所诱导的静息状态下NK细胞增殖,并且间充质干细胞的抑制作用与间充质干细胞和NK细胞的比例呈正相关,即间充质干细胞比例越高,其抑制作用越强;但是间充质干细胞并不能抑制激活状态下的NK细胞增殖[41]。间充质干细胞可以降低NK细胞表面标记的表达,如NKp30,NKG2D,NKp44和CD132,从而抑制NK细胞增殖。最新研究发现,人胎肝间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体可以抑制NK细胞增殖、活化和细胞毒性[42],当使用人胎肝间充质干细胞或人胎肝间充质干细胞来源外泌体处理NK细胞时,NKG2D和NKp30强烈下调。目前,并没有太多直接证据表明间充质干细胞来源外泌体能够抑制NK细胞的活化与增殖,更多的证据源于不同来源外泌体可以对NK细胞产生抑制作用[43-44]。由于间充质干细胞来源外泌体能部分模拟细胞的功能及细胞间的通讯[45],其对NK细胞的活性及增殖产生抑制作用。间充质干细胞来源外泌体与NK细胞之间的直接作用还需进一步研究。 2.2.2 间充质干细胞来源外泌体调控适应性免疫 T淋巴细胞在许多自身免疫性疾病和炎症性疾病的发生和发展中起着重要的作用。通过抑制淋巴细胞的增殖,间充质干细胞外泌体可以诱导淋巴细胞向抗炎型分化,起到免疫调节作用。脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以抑制T淋巴细胞的分化、激活、增殖以及促炎细胞因子干扰素γ的产生[46]。Chen等[47]研究将骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体和外周血单核细胞进行共培养,发现其能促进辅助性T细胞Th1向Th2方向转换,显著减少促炎因子白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α水平,提高抗炎性转化生长因子β水平。Álvarez等[48]发现,子宫内膜间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以抑制CD4+T细胞分化,并且子宫内膜间充质干细胞来源外泌体中转化生长因子β水平显著高于胞外囊泡所集中的上层清液。Treg细胞是具有负反馈调节的免疫细胞,Treg细胞与多种自身免疫疾病的发生密切相关,如多发性硬化和类风湿性关节炎。国内外已有报道,间充质干细胞来源外泌体能在体外诱导单核细胞株THP-1和外周血单核细胞向CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Treg细胞分化[49],上调白细胞介素10与转化生长因子β水平,从而促进Treg细胞的增殖和免疫抑制作用[50]。在移植物抗宿主病中,间充质干细胞来源外泌体能够促使单核细胞向M2型巨噬细胞分化,进而激活CD4+T细胞向Treg细胞分化并延迟免疫排斥反应的发生[49]。在哮喘病中,间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以上调外周血单核细胞分泌白细胞介素10与转化生长因子β水平,从而促进Treg细胞的增殖和免疫抑制作用,证明了间充质干细胞来源外泌体治疗哮喘病的潜能[50] 间充质干细胞来源外泌体能表达免疫调节分子,包括PD-L1、galectin-1和转化生长因子β[51-53]。三者均是负反馈调节分子,PD-L1抑制T细胞免疫反应并促进Treg细胞的增殖;galectin-1可以诱导已激活的T细胞凋亡;转化生长因子β则是诱导Treg细胞分化的主要功能分子。除蛋白类调节外,人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体能递送miR-181c,通过下调TLR4信号通路抑制炎症反应[33]。 B细胞也是重要的适应性免疫细胞,主要功能为介导体液免疫和分泌抗体。目前,间充质干细胞来源外泌体对B细胞的直接作用研究证据较少。Budoni等[54]研究表明,间充质干细胞的微泡可以通过计量依赖的方式抑制B细胞增殖和抗体分泌。迄今大多数研究主要聚焦于间充质干细胞与B细胞的研究,例如B细胞被间充质干细胞抑制在G0/G1期,其增殖被抑制[55]。当间充质干细胞与B细胞进行共培养时,间充质干细胞可以减少B细胞IgM、IgG、IgA的产生,也可以抑制B细胞趋化受体CXCR7、CXCR5、CXCR4的表达,从而改变其趋化特性[55-57]。以上间充质干细胞对B细胞的作用是来源于细胞间直接接触还是通过外泌体的调控作用,或两者皆有还需继续研究来确定。 2.2.3 间充质干细胞来源外泌体可调节抗原提呈 树突状细胞是目前所知功能最强的抗原提呈细胞,可摄取、加工处理抗原并提呈给T、B淋巴细胞,刺激并使其活化[58]。正常情况下体内绝大多数的树突状细胞属于未成熟树突状细胞,它们表达低水平的MHC-Ⅱ类分子。未成熟树突状细胞在摄取抗原或者受到细胞因子刺激时,如脂多糖、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β,未成熟树突状细胞就会逐渐分化成熟。成熟树突状细胞则会表达大量MHC-Ⅱ类分子,且其表面的共刺激分子和黏附分子表达也会显著增加,而病原体受体和Fc受体表达均下降,从而具备了激发免疫应答的能力。研究报道,间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以抑制树突状细胞的成熟,在间充质干细胞来源外泌体与单核细胞共培养条件下,未成熟树突状细胞经脂多糖刺激后表达成熟树突状细胞特异性标志CD83和共刺激分子CD80、CD86,这说明间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以维持树突状细胞在未成熟状态[59]。这一结果与间充质干细胞对单核细胞分化为树突状细胞的影响趋势相吻合[60]。此外,间充质干细胞来源外泌体还促进细胞因子的分泌[59],从而促进T细胞的增殖,并且增强了Treg细胞的分化。总之,在间充质干细胞来源外泌体的干预下,未成熟树突状细胞不能分化为成熟树突状细胞,因此无法完成抗原呈递作用,从而不能有效刺激T淋巴细胞增殖,而且促进Treg细胞增多,间接反映间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以增强机体的免疫耐受作用。 2.3 间充质干细胞来源外泌体在自身免疫疾病中的应用前景 前期研究证明了间充质干细胞既可以通过直接接触也可以通过旁分泌的方式招募和调节NK细胞、巨噬细胞、T细胞(辅助性及调节性)、树突状细胞的活化与功能[61],体内外实验还证明间充质干细胞培养上清(包含外泌体)在与活化T细胞共培养后可抑制T细胞的异常活化[8,62]。人们普遍认为,间充质干细胞抑制细胞因子的分泌和配体与受体的相互作用是行使其功能的关键。基于这一假设,间充质干细胞来源外泌体被认为是多发性硬化、系统性红斑狼疮、移植物抗宿病和1型糖尿病等自身免疫性疾病的潜在治疗手段。 多发性硬化是一种以神经脱髓鞘为特征的进行性神经功能障碍[63],其普遍应用的疾病模型为实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎[64]。课题组前期研究发现,间充质干细胞可以有效减缓多发性硬化患者的病程,改善生活质量[65-66]。有研究将间充质干细胞上清中分离出的细胞囊泡与实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠脾单核淋巴细胞进行共培养,发现细胞囊泡能够抑制自体淋巴细胞的增殖并促进白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β抗炎性细胞因子的分泌。流式细胞术检测发现,细胞囊泡表达间充质干细胞特异性的免疫耐受分子PD-L1、Gal-1和转化生长因子β,说明间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以作为诱发外周免疫耐受和调节免疫反应的有效介质[67]。根据多发性硬化的病理学基础,其治疗主要是针对神经系统的免疫反应和促进局部神经损伤的修复,但是间充质干细胞并不能穿过血脑屏障,而外泌体可以自由穿梭,因此可以推测,间充质干细胞是通过释放其外泌体,从而透过血脑屏障调控神经系统的免疫反应,并对神经的脱髓鞘进行修复,发挥其治疗多发性硬化的潜力。 系统性红斑狼疮是一种免疫介导的弥散性结缔组织疾病,其特点是免疫炎症和全身多器官受累,狼疮肾炎是其主要的合并症及死亡原因,其发病机制主要是由于T和B淋巴细胞激活效应导致机体损伤并引起重要器官中免疫复合物的沉积。前期研究发现,脐带间充质干细胞通过其分泌功能、对各种免疫细胞的免疫调节作用及其定植分化为受损组织细胞等多方面作用[68],从系统性红斑狼疮发生、发展的多阶段改善病情达到治疗疾病的目的。间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以有效抑制肾脏的炎症反应并保持关节的完整性,这两者都符合系统性红斑狼疮的病理过程。在急性肾损伤的小鼠模型中,间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以通过调控血尿素氮和肌酐水平,抑制慢性肾小管炎症、组织病理的发展和肾功能的损害[69]。在骨软骨缺损模型大鼠关节内注射间充质干细胞来源外泌体,其软骨和软骨下骨质得到了显著的修复[70]。 移植物抗宿主病是供体移植物中的T淋巴细胞识别宿主靶细胞抗原,并攻击宿主靶细胞或器官而产生病理损伤的疾病。Zhang等[49]研究表明,在小鼠同种异体皮肤移植模型中,皮下注射间充质干细胞来源外泌体将移植物抗宿病的发生延迟了2 d,并伴随着Treg细胞的增加。体外研究发现,间充质干细胞来源外泌体的激活作用依赖于MYD88信号通路,使单核细胞向巨噬细胞M2型分化,从而极化并激活CD4+T细胞分化为Treg细胞。国外有研究报道,间充质干细胞来源外泌体对移植物抗宿病患者取得了良好的治疗效果[71]。在这篇文章中,1例难治性移植物抗宿病患者接受了来自单个健康捐献者的间充质干细胞外泌体治疗,在没有明显不良反应的前提下,维持每两三天增加治疗剂量,移植物抗宿病的临床症状在2周内明显改善,并在稳定治疗4个月后,类固醇药物可以明显减少。Fujii等[72]最近发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以延长移植物抗宿病小鼠的生存时间并且减少其对靶器官的损害。在骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体治疗的小鼠中,CD4+和CD8+T细胞被抑制,并且CD62L-CD44+与CD62L+CD44-T细胞的比值降低,表明其抑制了T细胞从幼稚型向效应型的分化。 1型糖尿病是由于胰岛特异性抗原激活T细胞,促进T细胞浸润到胰岛并对胰岛β细胞产生自身免疫性破坏引起的,其中NOD小鼠是研究1型糖尿病最常见的自发性疾病模型。Rahman等[73]研究报道,胰岛间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体与NOD小鼠的脾细胞进行共培养,发现白细胞介素6、干扰素γ、肿瘤坏死因子α、单核细胞趋化蛋白1等细胞因子大量分泌,并激活了B细胞、T细胞和其他抗原提呈细胞。在NOD小鼠体内注射间充质干细胞来源外泌体2周后,在没有任何额外抗原的情况下,胰腺和腹股沟淋巴结细胞会释放大量的细胞因子和趋化因子,并且分泌干扰素γ的细胞和Th1细胞数量大量增多。这些结果表明间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以触发局部的自身免疫反应,可能是一种自体抗原的载体。2型糖尿病是由于外周胰岛素抵抗,胰腺β细胞损失和功能障碍为主要原因的疾病。Sun等[74]在高脂饮食和链霉素诱导的2型糖尿病动物模型中,静脉注射脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可降低血糖水平。脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体可部分逆转2型糖尿病胰岛素抵抗,间接促进糖代谢,使胰岛素受体底物1和蛋白激酶B在2型糖尿病中磷酸化(酪氨酸位点),促进葡萄糖转运蛋白4在肌肉中的表达和膜转运,增加肝糖原的储存,以维持葡萄糖稳态,还可抑制链霉素诱导的细胞凋亡,恢复2型糖尿病的胰岛素分泌功能;而且,Safwat等[75]也证明了脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以促进实验性糖尿病模型动物视网膜再生。 间充质干细胞来源外泌体治疗自身免疫疾病的文献汇总,见表1。"

| [1] Le Blanc K, Mougiakakos D. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells and the innate immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(5):383-396.[2] Prockop DJ, Oh JY. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs): role as guardians of inflammation. Mol Ther. 2012;20(1): 14-20.[3] Ren G, Zhang L, Zhao X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(2):141-150.[4] Liang X, Ding Y, Zhang Y, et al. Paracrine mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: current status and perspectives. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(9):1045-1059.[5] Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383.[6] Bobrie A, Colombo M, Raposo G, et al. Exosome secretion: molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic. 2011;12(12):1659-1668.[7] Hunter MP, Ismail N, Zhang X, et al. Detection of microRNA expression in human peripheral blood microvesicles. PLoS One. 2008;3(11):e3694.[8] Robbins PD, Morelli AE. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(3):195-208.[9] Kilpinen L, Impola U, Sankkila L, et al. Extracellular membrane vesicles from umbilical cord blood-derived MSC protect against ischemic acute kidney injury, a feature that is lost after inflammatory conditioning. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013; 2:21927-21934.[10] Bruno S, Camussi G. Exploring mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in acute kidney injury. Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1213:139-145.[11] Zhang J, Guan J, Niu X, et al. Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J Transl Med. 2015;13:49.[12] Yu B, Kim HW, Gong M, et al. Exosomes secreted from GATA-4 overexpressing mesenchymal stem cells serve as a reservoir of anti-apoptotic microRNAs for cardioprotection. Int J Cardiol. 2015;182:349-360.[13] Shabbir A, Cox A, Rodriguez-Menocal L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Induce Proliferation and Migration of Normal and Chronic Wound Fibroblasts, and Enhance Angiogenesis In Vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(14): 1635-1647.[14] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[15] Teixeira FG, Carvalho MM, Sousa N, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells secretome: a new paradigm for central nervous system regeneration. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(20): 3871-3882.[16] Salgado AJ, Sousa JC, Costa BM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells secretome as a modulator of the neurogenic niche: basic insights and therapeutic opportunities. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:249.[17] Konala VB, Mamidi MK, Bhonde R, et al. The current landscape of the mesenchymal stromal cell secretome: A new paradigm for cell-free regeneration. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(1): 13-24.[18] Donega V, Nijboer CH, Braccioli L, et al. Intranasal administration of human MSC for ischemic brain injury in the mouse: in vitro and in vivo neuroregenerative functions. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e112339.[19] Takeda YS, Xu Q. Neuronal Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using Exosomes Derived from Differentiating Neuronal Cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(8): e0135111.[20] Bagher Z, Azami M, Ebrahimi-Barough S, et al. Differentiation of Wharton's Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Motor Neuron-Like Cells on Three-Dimensional Collagen-Grafted Nanofibers. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(4): 2397-2408.[21] Teixeira FG, Carvalho MM, Neves-Carvalho A, et al. Secretome of mesenchymal progenitors from the umbilical cord acts as modulator of neural/glial proliferation and differentiation. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(2):288-297.[22] Timmers L, Lim SK, Arslan F, et al. Reduction of myocardial infarct size by human mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium. Stem Cell Res. 2007;1(2):129-137.[23] van Poll D, Parekkadan B, Cho CH, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules directly modulate hepatocellular death and regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology. 2008;47(5): 1634-1643.[24] Zarjou A, Kim J, Traylor AM, et al. Paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells in cisplatin-induced renal injury require heme oxygenase-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011;300(1):F254-262.[25] Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222.[26] Yu B, Zhang X, Li X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157.[27] Pachler K, Ketterl N, Desgeorges A, et al. An In Vitro Potency Assay for Monitoring the Immunomodulatory Potential of Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(7): E1413.[28] Sun L, Li D, Song K, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells protect against cisplatin-induced ovarian granulosa cell stress and apoptosis in vitro. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):2552.[29] Gong M, Yu B, Wang J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(28): 45200-45212.[30] Nakamura Y, Miyaki S, Ishitobi H, et al. Mesenchymal- stem-cell-derived exosomes accelerate skeletal muscle regeneration. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(11):1257-1265.[31] Kim HS, Choi DY, Yun SJ, et al. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. J Proteome Res. 2012;11(2):839-849.[32] Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41(1):14-20.[33] Li X, Liu L, Yang J, et al. Exosome Derived From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Mediates MiR-181c Attenuating Burn-induced Excessive Inflammation. EBioMedicine. 2016;8:72-82.[34] Domenis R, Cifù A, Quaglia S, et al. Pro inflammatory stimuli enhance the immunosuppressive functions of adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):13325.[35] Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(12):1821-1830.[36] Lumeng CN, Bodzin JL, Saltiel AR. Obesity induces a phenotypic switch in adipose tissue macrophage polarization. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(1):175-184.[37] Zhao H, Shang Q, Pan Z, et al. Exosomes From Adipose- Derived Stem Cells Attenuate Adipose Inflammation and Obesity Through Polarizing M2 Macrophages and Beiging in White Adipose Tissue. Diabetes. 2018;67(2): 235-247.[38] Phinney DG, Di Giuseppe M, Njah J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8472.[39] Marigo I, Dazzi F. The immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Semin Immunopathol. 2011;33(6): 593-602.[40] Biron CA, Nguyen KB, Pien GC, et al. Natural killer cells in antiviral defense: function and regulation by innate cytokines. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:189-220.[41] Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Becchetti S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-natural killer cell interactions: evidence that activated NK cells are capable of killing MSCs, whereas MSCs can inhibit IL-2-induced NK-cell proliferation. Blood. 2006;107(4):1484-1490.[42] Fan Y, Herr F, Vernochet A, et al. Human Fetal Liver Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Impair Natural Killer Cell Function. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(1):44-55.[43] Whiteside TL. Immune modulation of T-cell and NK (natural killer) cell activities by TEXs (tumour-derived exosomes). Biochem Soc Trans. 2013;41(1):245-251.[44] Reiners KS, Dassler J, Coch C, et al. Role of Exosomes Released by Dendritic Cells and/or by Tumor Targets: Regulation of NK Cell Plasticity. Front Immunol. 2014;5:91.[45] Fitzner D, Schnaars M, van Rossum D, et al. Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J Cell Sci. 2011;124(Pt 3):447-458.[46] Blazquez R, Sanchez-Margallo FM, de la Rosa O, et al. Immunomodulatory Potential of Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Exosomes on in vitro Stimulated T Cells. Front Immunol. 2014;5:556.[47] Chen W, Huang Y, Han J, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosome. Immunol Res. 2016;64(4):831-840.[48] Álvarez V, Sánchez-Margallo FM, Macías-García B, et al. The immunomodulatory activity of extracellular vesicles derived from endometrial mesenchymal stem cells on CD4+ T cells is partially mediated by TGFbeta. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(10):2088-2098.[49] Zhang B, Yin Y, Lai RC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells secrete immunologically active exosomes. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(11):1233-1244.[50] Du YM, Zhuansun YX, Chen R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell exosomes promote immunosuppression of regulatory T cells in asthma. Exp Cell Res. 2018;363(1):114-120.[51] Garín MI, Chu CC, Golshayan D, et al. Galectin-1: a key effector of regulation mediated by CD4+CD25+ T cells. Blood. 2007;109(5):2058-2065.[52] Pedemonte E, Benvenuto F, Casazza S, et al. The molecular signature of therapeutic mesenchymal stem cells exposes the architecture of the hematopoietic stem cell niche synapse. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:65.[53] Chen W, Jin W, Hardegen N, et al. Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25- naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp3. J Exp Med. 2003;198(12):1875-1886.[54] Budoni M, Fierabracci A, Luciano R, et al. The immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stromal cells on B lymphocytes is mediated by membrane vesicles. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(2):369-379.[55] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372.[56] Rosado MM, Bernardo ME, Scarsella M, et al. Inhibition of B-cell proliferation and antibody production by mesenchymal stromal cells is mediated by T cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2015; 24(1):93-103.[57] Tabera S, Pérez-Simón JA, Díez-Campelo M, et al. The effect of mesenchymal stem cells on the viability, proliferation and differentiation of B-lymphocytes. Haematologica. 2008; 93(9): 1301-1309.[58] Sozzani S, Del Prete A, Bosisio D. Dendritic cell recruitment and activation in autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 2017;85: 126-140.[59] Favaro E, Carpanetto A, Caorsi C, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells and derived extracellular vesicles induce regulatory dendritic cells in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 2016;59(2):325-333.[60] Spaggiari GM, Moretta L. Cellular and molecular interactions of mesenchymal stem cells in innate immunity. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013;91(1):27-31.[61] Porada CD, Almeida-Porada G. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutics and vehicles for gene and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(12):1156-1166.[62] Del Fattore A, Luciano R, Pascucci L, et al. Immunoregulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on T Lymphocytes. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(12): 2615-2627.[63] Noseworthy JH, Lucchinetti C, Rodriguez M, et al. Multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(13):938-952.[64] Martin R. Immunological aspects of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis and their application for new therapeutic strategies. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1997;49:53-67.[65] Hou ZL, Liu Y, Mao XH, et al. Transplantation of umbilical cord and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in a patient with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Cell Adh Migr. 2013;7(5):404-407.[66] Meng M, Liu Y, Wang W, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(1):212-223.[67] Mokarizadeh A, Delirezh N, Morshedi A, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells: potent organelles for induction of tolerogenic signaling. Immunol Lett. 2012; 147(1-2):47-54.[68] 白茹,戚燕,吕昭萍,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮3年随访[J].中国免疫学杂志, 2017,33(6): 905-909.[69] Bruno S, Grange C, Collino F, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33115.[70] Zhang S, Chu WC, Lai RC, et al. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016; 24(12):2135-2140.[71] Kordelas L, Rebmann V, Ludwig AK, et al. MSC-derived exosomes: a novel tool to treat therapy-refractory graft-versus-host disease. Leukemia. 2014;28(4):970-973.[72] Fujii S, Miura Y, Fujishiro A, et al. Graft-Versus-Host Disease Amelioration by Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Associated with Peripheral Preservation of Naive T Cell Populations. Stem Cells. 2018;36(3):434-445.[73] Rahman MJ, Regn D, Bashratyan R, et al. Exosomes released by islet-derived mesenchymal stem cells trigger autoimmune responses in NOD mice. Diabetes. 2014; 63(3):1008-1020.[74] Sun Y, Shi H, Yin S, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Alleviate Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Reversing Peripheral Insulin Resistance and Relieving β-Cell Destruction. ACS Nano. 2018;12(8):7613-7628.[75] Safwat A, Sabry D, Ragiae A, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuate retina degeneration of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rabbits. J Circ Biomark. 2018;7:1849454418807827.[76] Xu R, Greening DW, Zhu HJ, et al. Extracellular vesicle isolation and characterization: toward clinical application. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(4):1152-1162.[77] Willis GR, Kourembanas S, Mitsialis SA. Toward Exosome-Based Therapeutics: Isolation, Heterogeneity, and Fit-for-Purpose Potency. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017;4:63.[78] Rezaie J, Ajezi S, Avci ÇB, et al. Exosomes and their Application in Biomedical Field: Difficulties and Advantages. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(4):3372-3393.[79] Witwer KW, Buzás EI, Bemis LT, et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013;2: 20360-20384. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [4] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [5] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [6] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [7] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [8] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [9] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [10] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [11] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [12] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [13] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||