Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (29): 4714-4721.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1815
Previous Articles Next Articles
Therapeutic mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes in acute lung injury
Zhang Lishan, Zeng Mian
- Medical Intensive Care Unit, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2019-05-30Online:2019-10-18Published:2019-10-18 -
Contact:Zeng Mian, Master, Professor, Chief physician, Medical Intensive Care Unit, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Zhang Lishan, Master candidate, Medical Intensive Care Unit, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81670066 (to ZM); the Guangdong Provincial Scientific Research Project, No. 2016A020216009 and 2014A020212151 (both to ZM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Lishan, Zeng Mian. Therapeutic mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes in acute lung injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(29): 4714-4721.
share this article
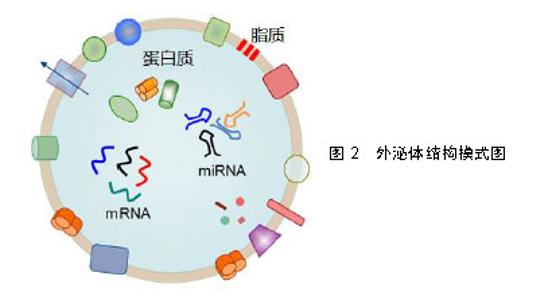
2.1 外泌体的概念与生物学特性 外泌体首次被发现于20世纪80年代,Tram等[8-9]观察到网织红细胞在其成熟期间会分泌一种含有转铁蛋白受体的小囊泡,介导转铁蛋白受体的清除。然而在此后的十余年间外泌体并未受到研究人员的关注,仅被看作是细胞清除代谢废物的手段。直到20世纪90年代末,Zitvogel等[10]研究表明外泌体可能是细胞间通讯的重要介质,才重新激起了人们对外泌体研究的兴趣。研究证实了人体中几乎所有类型的细胞均能产生外泌体,且已经从多种体液中分离出外泌体,包括血液、尿液、唾液、精液、乳汁、胆汁、羊水、腹水和脑脊液等[11]。随后,一系列的研究发现许多细胞(包括免疫细胞、肠上皮细胞和间充质干细胞等)能通过释放外泌体来参与炎症反应、免疫反应和受损细胞增殖修复的调节[12-14]。 外泌体是一种能被大多数细胞分泌的微小膜泡,具有脂质双层膜结构,见图2。根据国际细胞外囊泡学会的定义[15],外泌体是细胞外囊泡(Extracellular vesicles)最小的亚组(细胞外囊泡3个亚组分别为:外泌体、微泡以及凋亡小体),直径30-100 nm。细胞通过内吞作用形成早期内体(early endosome),再与高尔基复合体相互作用以形成晚期内体,进而融合形成多泡体(MVBs,multivesicle bodies),多泡体与质膜融合通过胞吐作用释放外泌体[16],这个过程依赖于转运必需内体分选复合物(ESCRT)的作用。外泌体携带与细胞来源相关的多种蛋白质、脂质和核酸,能作为信号分子传递给其他细胞参与细胞活动的重要调控。虽然外泌体的形成过程大致相同,但不同细胞来源的外泌体在不同状态下所包含的内容物各不相同。目前已经被识别存在于外泌体的蛋白包括:膜联蛋白和flotillin(与外泌体的转运和融合有关)、四跨膜蛋白(参与细胞靶向)、Alix和TSG101(参与外泌体从多泡体的生物发生)、热休克蛋白(热休克蛋白60、热休克蛋白70和热休克蛋白90)、细胞外基质和细胞表面蛋白质(例如胶原蛋白、整联蛋白和半乳糖凝集素)、细胞表面受体(EGFR)等[17-18]。与其起源细胞相比,外泌体富含胆固醇、神经酰胺、磷酸甘油酯以及不饱和的脂肪酰基链,参与维持外泌体结构的稳定性[19]。此外,外泌体中的核酸是来源细胞核酸的一个子集,包括DNA、lncRNA、tRNA、mRNA、microRNA等。"
| [1]Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016;315(8):788-800.[2]Sweeney RM, McAuley DF. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet. 2016;388(10058):2416-2430.[3]凌亚豪,魏金锋,王爱平,等.急性肺损伤和急性呼吸窘迫综合征发病机制的研究进展[J].癌变·畸变·突变,2017,29(2): 151-154.[4]Chang YS, Oh W, Choi SJ, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate hyperoxia- induced lung injury in neonatal rats. Cell Transplant. 2009; 18(8):869-886.[5]Kourembanas S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:13-27.[6]Aslam M, Baveja R, Liang OD, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate lung injury in a murine model of neonatal chronic lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009; 180(11):1122-1130.[7]Lavoie JR, Rosu-Myles M. Uncovering the secretes of mesenchymal stem cells. Biochimie. 2013;95(12):2212-2221.[8]Trams EG, Lauter CJ, Salem N Jr, et al. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645(1):63-70.[9]Johnstone RM, Adam M, Hammond JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19):9412-9420.[10]Zitvogel L, Regnault A, Lozier A, et al. Eradication of established murine tumors using a novel cell-free vaccine: dendritic cell-derived exosomes. Nat Med. 1998;4(5): 594-600.[11]Raposo G, Stoorvogel W. Extracellular vesicles: exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J Cell Biol. 2013;200(4):373-383.[12]Clayton A, Turkes A, Navabi H, et al. Induction of heat shock proteins in B-cell exosomes. J Cell Sci. 2005;118(Pt 16): 3631-3638.[13]Lai RC, Arslan F, Lee MM, et al. Exosome secreted by MSC reduces myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2010;4(3):214-222.[14]van Niel G, Raposo G, Candalh C, et al. Intestinal epithelial cells secrete exosome-like vesicles. Gastroenterology. 2001; 121(2):337-349.[15]Yáñez-Mó M, Siljander PR, Andreu Z, et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27066.[16]Huotari J, Helenius A. Endosome maturation. EMBO J. 2011;30(17):3481-3500.[17]Kim HS, Choi DY, Yun SJ, et al. Proteomic analysis of microvesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells. J Proteome Res. 2012;11(2):839-849.[18]Kourembanas S. Exosomes: vehicles of intercellular signaling, biomarkers, and vectors of cell therapy. Annu Rev Physiol. 2015;77:13-27.[19]Choi DS, Kim DK, Kim YK, et al. Proteomics, transcriptomics and lipidomics of exosomes and ectosomes. Proteomics. 2013;13(10-11):1554-1571.[20]Théry C, Amigorena S, Raposo G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3.22.[21]Lobb RJ, Becker M, Wen SW, et al. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27031.[22]Arslan F, Lai RC, Smeets MB, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes increase ATP levels, decrease oxidative stress and activate PI3K/Akt pathway to enhance myocardial viability and prevent adverse remodeling after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;10(3):301-312.[23]Lee C, Mitsialis SA, Aslam M, et al. Exosomes mediate the cytoprotective action of mesenchymal stromal cells on hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2012; 126(22):2601-2611.[24]Chen J, Chen LA. LATE-BREAKING ABSTRACT: Human mesenchymal stem cell exosomes attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of oxidative stress and the MAPK-NF-κB pathway. Eur Respir J. 2015; 46:OA4471.[25]Bruno S, Grange C, Collino F, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival in a lethal model of acute kidney injury. PLoS One. 2012;7(3): e33115.[26]Chen W, Lin YJ, Zhou XY, et al. Rosiglitazone protects rat liver against acute liver injury associated with the NF-κB signaling pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2016;94(1): 28-34.[27]Katsuda T, Tsuchiya R, Kosaka N, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete functional neprilysin-bound exosomes. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1197.[28]Herold S, Gabrielli NM, Vadász I. Novel concepts of acute lung injury and alveolar-capillary barrier dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013;305(10):L665-681.[29]Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(21):2063.[30]Lee JW, Krasnodembskaya A, McKenna DH, et al. Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cells in ex vivo human lungs injured with live bacteria. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187(7):751-760.[31]Tan CY, Lai RC, Wong W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote hepatic regeneration in drug-induced liver injury models. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014; 5(3):76.[32]Zhang S, Chu WC, Lai RC, et al. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016; 24(12):2135-2140.[33]Qin Y, Wang L, Gao Z, et al. Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21961.[34]Zhang Y, Chopp M, Zhang ZG, et al. Systemic administration of cell-free exosomes generated by human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured under 2D and 3D conditions improves functional recovery in rats after traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Int. 2017;111:69-81.[35]Zhu YG, Feng XM, Abbott J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):116-125.[36]Ionescu L, Byrne RN, van Haaften T, et al. Stem cell conditioned medium improves acute lung injury in mice: in vivo evidence for stem cell paracrine action. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012;303(11):L967-977.[37]杨尧,朱耀斌,李志强,等.间充质干细胞外泌体对大鼠急性肺损伤的保护作用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2017,31(7): 628-631.[38]Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6): 654-659.[39]Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(8):509-524.[40]Kubo H. Extracellular Vesicles in Lung Disease. Chest. 2018;153(1):210-216.[41]Park J, Jeong S, Park K, et al. Expression profile of microRNAs following bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6):5495-5502.[42]Velu CS, Baktula AM, Grimes HL. Gfi1 regulates miR-21 and miR-196b to control myelopoiesis. Blood. 2009;113(19): 4720-4728.[43]Chang SW, Yue J, Wang BC, et al. miR-503 inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by targeting E2F3. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10): 12853-12860.[44]Zeng Z, Gong H, Li Y, et al. Upregulation of miR-146a contributes to the suppression of inflammatory responses in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Exp Lung Res. 2013;39(7): 275-282.[45]Ghosh S, Hayden MS. New regulators of NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(11):837-848.[46]Song Y, Dou H, Li X, et al. Exosomal miR-146a Contributes to the Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Interleukin-1β-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Sepsis. Stem Cells. 2017; 35(5):1208-1221.[47]Tan KS, Choi H, Jiang X, et al. Micro-RNAs in regenerating lungs: an integrative systems biology analysis of murine influenza pneumonia. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:587.[48]Basu J, Ludlow JW. Exosomes for repair, regeneration and rejuvenation. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(4):489-506. [49]Spees JL, Olson SD, Whitney MJ, et al. Mitochondrial transfer between cells can rescue aerobic respiration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(5):1283-1288. [50]Schumacker PT, Gillespie MN, Nakahira K, et al. Mitochondria in lung biology and pathology: more than just a powerhouse. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014; 306(11):L962-L974.[51]Yamada M, Emmanuele V, Sanchez-Quintero MJ, et al. Genetic Drift Can Compromise Mitochondrial Replacement by Nuclear Transfer in Human Oocytes. Cell Stem Cell. 2016; 18(6):749-754.[52]Morrison TJ, Jackson MV, Cunningham EK, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Modulate Macrophages in Clinically Relevant Lung Injury Models by Extracellular Vesicle Mitochondrial Transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196(10):1275-1286.[53]Islam MN, Das SR, Emin MT, et al. Mitochondrial transfer from bone-marrow-derived stromal cells to pulmonary alveoli protects against acute lung injury. Nat Med. 2012;18(5): 759-765. [54]Torralba D, Baixauli F, Sánchez-Madrid F. Mitochondria Know No Boundaries: Mechanisms and Functions of Intercellular Mitochondrial Transfer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016;4:107.[55]Guescini M, Guidolin D, Vallorani L, et al. C2C12 myoblasts release micro-vesicles containing mtDNA and proteins involved in signal transduction. Exp Cell Res. 2010;316(12): 1977-1984.[56]Guescini M, Genedani S, Stocchi V, et al. Astrocytes and Glioblastoma cells release exosomes carrying mtDNA. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2010;117(1):1-4.[57]Hough KP, Trevor JL, Strenkowski JG, et al. Exosomal transfer of mitochondria from airway myeloid-derived regulatory cells to T cells. Redox Biol. 2018;18:54-64.[58]Riazifar M, Pone EJ, Lötvall J, et al. Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles: Extended Messages of Regeneration. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017;57:125-154. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [5] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [6] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [7] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [8] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [9] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [10] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [11] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [12] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [13] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [14] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [15] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||