Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (9): 1377-1383.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1600
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological characteristics of three kinds of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Wang Liudi, Liu Wei, Xie Yuanyuan, Gao Tianyun, Huang Feifei, Wang Bin
- Department of Clinical Stem Cell Research, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2018-11-07Online:2019-03-28Published:2019-03-28 -
Contact:Wang Bin, MD, Professor, Researcher, Department of Clinical Stem Cell Research, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wang Liudi, Department of Clinical Stem Cell Research, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing 210008, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research & Development Program of China in 2017, No. 2017YFA0104300 (to GN); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81571213 (to WB); the 13th-Batch Jiangsu Province Six Talent Peaks Project, No. WSN-155 (to WB); Nanjing “13th Five-Year Plan” Key Project, No. ZDX16005 (to WB); Nanjing “13th Five-Year” Youth Talent Project (Level 1), No. QRX17006 (to WB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Liudi, Liu Wei, Xie Yuanyuan, Gao Tianyun, Huang Feifei, Wang Bin. Biological characteristics of three kinds of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(9): 1377-1383.
share this article
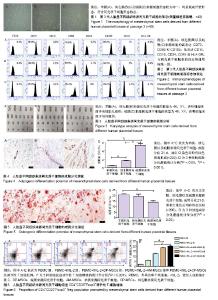
2.1 不同胎盘组织来源间充质干细胞的形态 接种48 h后,大部分细胞贴壁,72 h换液时可见少量细胞集落。细胞呈梭形或多角形,3-5 d后增殖加快,呈平行或漩涡状排列。培养5-7 d细胞可铺满瓶底80%以上。多次传代后细胞形态较为均一,均呈现成纤维形态,符合间充质干细胞形态特点,见图1。 2.2 不同胎盘组织来源间充质干细胞的表面标志物 流式细胞仪分析结果显示,羊膜、绒毛膜以及蜕膜来源细胞均高表达CD73、CD90和CD105,大于95%;低表达CD14、CD19、CD34、CD45和HLA-DR,小于2%,与间充质干细胞表面标志物通用标准一致,见图2。 2.3 不同胎盘组织来源间充质干细胞的核型分析 G-带染色结果显示3种细胞染色体结构正常。羊膜、绒毛膜来源间充质干细胞的核型为46,XY,表明细胞来源于男性胎儿组织;蜕膜来源间充质干细胞的核型为46,XX,表明细胞来源于母体组织,见图3。 2.4 不同人胎盘组织来源间充质干细胞的成脂、成骨分化能力比较 成脂诱导培养21 d后,油红O染色可见红色的脂滴,见图4;成骨诱导培养21 d后,茜素红染色均出现深红色的钙盐结节,见图5。统计分析结果表明:3种细胞都具有成脂成骨分化潜能,其中蜕膜来源间充质干细胞的成脂分化能力最强,依次为蜕膜来源间充质干细胞>绒毛膜来源间充质干细胞>羊膜来源间充质干细胞,各组间差异有显著性意义;而这3种细胞的成骨分化能力与成脂分化相反,成骨分化能力依次为羊膜来源间充质干细胞>绒毛膜来源间充质干细胞>蜕膜来源间充质干细胞,但仅羊膜来源间充质干细胞与蜕膜来源间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.5 不同人胎盘组织来源间充质干细胞对调节性T细胞增殖能力的影响 3种间充质干细胞与外周血单个核细胞在重组人白细胞介素2刺激下体外共培养5 d,均促进CD4+CD25+Foxp3+调节性T细胞增殖,见图6。羊膜、绒毛膜来源间充质干细胞高于蜕膜来源间充质干细胞,差异有显著性意义。绒毛膜来源间充质干细胞稍高于羊膜来源间充质干细胞,但是差异无显著性意义。"

| [1] Pop DM, Sori??u O, ?u?man S, et al. Potential of placental-derived human mesenchymal stem cells for osteogenesis and neurogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2015;56(3):989-996.[2] Sardesai VS, Shafiee A, Fisk NM, et al. Avoidance of Maternal Cell Contamination and Overgrowth in Isolating Fetal Chorionic Villi Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Term Placenta. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(4):1070-1084.[3] Consentius C, Reinke P, Volk HD. Immunogenicity of allogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells: what has been seen in vitro and in vivo. Regen Med. 2015;10(3):305-315.[4] Bellavia M, Altomare R, Cacciabaudo F, et al. Towards an ideal source of mesenchymal stem cell isolation for possible therapeutic application in regenerative medicine. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2014;158(3): 356-360.[5] Li M, Zhao Y, Hao H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for nonhealing wounds: today and tomorrow. Wound Repair Regen. 2015;23(4):465-482.[6] Kim R, Park SI, Lee CY, et al. Alternative new mesenchymal stem cell source exerts tumor tropism through ALCAM and N-cadherin via regulation of microRNA-192 and -218. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017;427(1-2):177-185.[7] Ruan H, Xiao R, Jiang X, et al. Biofunctionalized self-assembly of peptide amphiphile induces the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Jun 21. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3386-9. [Epub ahead of print][8] Dezawa M. Muse Cells Provide the Pluripotency of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Direct Contribution of Muse Cells to Tissue Regeneration. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(5):849-861.[9] Faghihi F, Mirzaei E, Ai J, et al. Erratum to: Differentiation Potential of Human Chorion-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Motor Neuron-Like Cells in Two- and Three-Dimensional Culture Systems. Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(3):1873.[10] Wang X, Lazorchak AS, Song L, et al. Immune modulatory mesenchymal stem cells derived from human embryonic stem cells through a trophoblast-like stage. Stem Cells. 2016;34(2): 380-391.[11] Valencia J, Blanco B, Yáñez R, et al. Comparative analysis of the immunomodulatory capacities of human bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells from the same donor. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(10):1297-1311.[12] Lim JY, Im KI, Lee ES, et al. Enhanced immunoregulation of mesenchymal stem cells by IL-10-producing type 1 regulatory T cells in collagen-induced arthritis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26851.[13] Ma OK, Chan KH. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells: Interplay between mesenchymal stem cells and regulatory lymphocytes. World J Stem Cells. 2016;8(9):268-278. [14] Wu M, Zhang R, Zou Q, et al. Comparison of the Biological Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from the Human Placenta and Umbilical Cord. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):5014.[15] Timmins NE, Kiel M, Günther M, et al. Closed system isolation and scalable expansion of human placental mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2012;109(7):1817-1826.[16] Du L, Lv R, Yang X, et al. Hypoxic conditioned medium of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells protects against scar formation. Life Sci. 2016;149:51-57.[17] Araújo AB, Salton GD, Furlan JM, et al. Comparison of human mesenchymal stromal cells from four neonatal tissues: Amniotic membrane, chorionic membrane, placental decidua and umbilical cord. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(5):577-585.[18] Eidem HR, Ackerman WE 4th, McGary KL, et al. Gestational tissue transcriptomics in term and preterm human pregnancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Genomics. 2015;8:27.[19] Gan WT, Sun X, Lu Y. Comparison of Biological Characteristics between Human Amnion Epithelial Cells and Human Amnion Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015;23(4):1120-1124.[20] Kwon A, Kim Y, Kim M, et al. Tissue-specific Differentiation Potency of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Perinatal Tissues. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23544.[21] Abumaree MH, Abomaray FM, Alshehri NA, et al. Phenotypic and Functional Characterization of Mesenchymal Stem/Multipotent Stromal Cells From Decidua Parietalis of Human Term Placenta. Reprod Sci. 2016;23(9):1193-1207.[22] Lobo SE, Leonel LC, Miranda CM, et al. The Placenta as an Organ and a Source of Stem Cells and Extracellular Matrix: A Review. Cells Tissues Organs. 2016;201(4):239-252.[23] James JL, Srinivasan S, Alexander M, et al. Can we fix it? Evaluating the potential of placental stem cells for the treatment of pregnancy disorders. Placenta. 2014;35(2):77-84.[24] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[25] Liu W, Xie Y, Gao T, et al. Reflection and observation: cell-based screening failing to detect HBV in HUMSCs derived from HBV-infected mothers underscores the importance of more stringent donor eligibility to reduce risk of transmission of infectious diseases for stem cell-based medical products. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):177.[26] Hong JQ, Gao Y, Song J, et al. Comparison of Biological Characteristics and Immunosuppressive Activity between Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2016;24(3):858-864.[27] Yi JZ, Chen ZH, Xu FH, et al. Interferon-γ suppresses the proliferation and migration of human placenta-derived mesenchmal stromal cells and enhances their ability to induce the generation of CD4+CXCR5+Foxp3+Treg subset. Cell Immunol. 2018;326:42-51.[28] Zhu Y, Yang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Placental mesenchymal stem cells of fetal and maternal origins demonstrate different therapeutic potentials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(2):48.[29] Ding C, Zou Q, Wang F, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells improve ovarian function in natural aging through secreting hepatocyte growth factor and epidermal growth factor. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):55.[30] Beegle JR, Magner NL, Kalomoiris S, et al. Preclinical evaluation of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing VEGF to treat critical limb ischemia. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2016;3: 16053.[31] Liang L, Li Z, Ma T, et al. Transplantation of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviates Critical Limb Ischemia in Diabetic Nude Rats. Cell Transplant. 2017; 26(1):45-61.[32] Gan L, Duan H, Xu Q, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stromal cell transplantation improves endometrial regeneration in rodent models of intrauterine adhesions. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(5):603-616.[33] Li J, Yu Q, Huang H, et al. Human chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation restores ovarian function in a chemotherapy-induced mouse model of premature ovarian failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):81.[34] Fu Q, Man X, Yu M, et al. Human decidua mesenchymal stem cells regulate decidual natural killer cell function via interactions between collagen and leukocyte?associated immunoglobulin?like receptor 1. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(3):2791-2798.[35] Kawai M, Rosen CJ. PPARγ: a circadian transcription factor in adipogenesis and osteogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010; 6(11):629-636.[36] Ye L, Fan Z, Yu B, et al. Histone demethylases KDM4B and KDM6B promotes osteogenic differentiation of human MSCs. Cell Stem Cell. 2012;11(1):50-61.[37] Yamahara K, Harada K, Ohshima M, et al. Comparison of angiogenic, cytoprotective, and immunosuppressive properties of human amnion- and chorion-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88319.[38] Pianta S, Bonassi Signoroni P, Muradore I, et al. Amniotic membrane mesenchymal cells-derived factors skew T cell polarization toward Treg and downregulate Th1 and Th17 cells subsets. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(3):394-407.[39] Ohshima M, Yamahara K, Ishikane S, et al. Systemic transplantation of allogenic fetal membrane-derived mesenchymal stem cells suppresses Th1 and Th17 T cell responses in experimental autoimmune myocarditis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;53(3):420-428.[40] Luz-Crawford P, Kurte M, Bravo-Alegría J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells generate a CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell population during the differentiation process of Th1 and Th17 cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(3):65.[41] Suzuki M, Jagger AL, Konya C, et al. CD8+CD45RA+CCR7+ FOXP3+ T cells with immunosuppressive properties: a novel subset of inducible human regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2012; 189(5):2118-2130.[42] Pelekanos RA, Sardesai VS, Futrega K, et al. Isolation and Expansion of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells Derived from Human Placenta Tissue. J Vis Exp. 2016;(112): 54204. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Li Cai, Zhao Ting, Tan Ge, Zheng Yulin, Zhang Ruonan, Wu Yan, Tang Junming. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of skeletal muscle myoblast [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1050-1055. |
| [14] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||