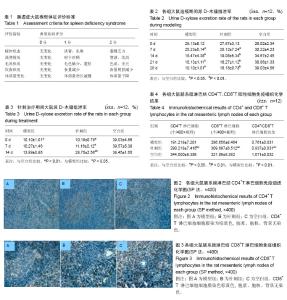
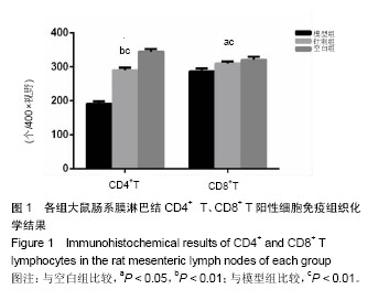
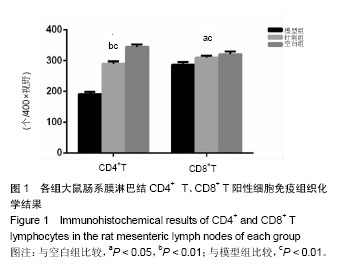
| [1] 施茵,吴焕淦.足三里穴在免疫功能调节中的应用[J]. 现代中医药, 2003,(3):3-6.[2] 刘子志,刘友章. 脾、小肠运化功能探析[J]. 安徽中医药大学学报,2001,20(4):8-9.[3] 陈玉龙,符仁,刘紫阳,等.脾虚证发生率研究[J]. 光明中医,2012, 27(3):614-615.[4] 陈玉龙,符仁,刘学俊,等.脾虚证症状规律的文献研究[J]. 中医学报,2013,28(1):150-152.[5] 何劲,周莉,陈家旭,等.中医脾虚证实质研究进展[J]. 吉林中医药, 2015,35(1):103-107.[6] 逄紫千,李秋明,袁洪平.针灸对脾虚证肠道局部免疫的作用机制[J].长春中医药大学学报,2007,23(2):84-85.[7] 叶芳旭,徐芳,张烁.由“气血津液”学说浅析脾虚证对胃肠免疫功能的影响[J].浙江中西医结合杂志,2017,27(9):808-810.[8] 张彩云,肖满珊,廖双叶,等.实验性大鼠脾气虚证模型的建立及指标检测[J].广东药学院学报,2015,31(6):808-810.[9] 陈雷.应用模糊数学中模式识别方法进行脾虚大鼠模型评价研究[D].辽宁中医学院,2004.[10] 张声生,胡玲,李茹柳.脾虚证中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J]. 中医杂志,2017,58(17):1525-1530.[11] 陈贵廷. 中医虚证辨证标准的客观化问题[J].中国中西医结合杂志,1983(2):73~76.[12] 修宗昌,余绍源,黄穗平.脾虚证临床诊断标准浅识[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2003,21(2):219-220.[13] 李灿,张海艇,陈玉龙.采用唾液淀粉酶和D-木糖排泄率对利血平脾虚证模型的评价研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2011(7): 746-748.[14] 高小玲,郭文峰,李茹柳,等. 四君子汤对脾虚大鼠尿木糖排泄率及肠黏膜ATP的影响[J].中药材,2009,32(8):1242-1245.[15] 李忠仁,方剑乔,易受乡,等.实验针灸学[M] .北京:中国中医药出版社,2003.[16] 田阳春,郑玲,袁英,等.不同深度针刺足三里穴对健康大鼠外周血细胞形态数量及淋巴细胞增殖能力和胸腺指数的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2008,12(29):5687-5690.[17] 李斌,侯伟龙,王彩霞,等.脾虚动物水液代谢特征研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2016(1):150-153.[18] 赵彬. 艾灸对脾虚泄泻大鼠尿D-木糖排泄率和唾液淀粉酶分泌的影响[D].辽宁中医药大学,2014.[19] Vignali DA,Collison LW,Workman CJ.How regulatory T cells work.Nature Reviews Immunology.2008;8(7):523.[20] Kägi D,Ledermann B,Bürki K,et al.Molecular mechanisms of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity and their role in immunological protection and pathogenesis in vivo. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:207-232. [21] 戴玉洁,于飞,胡绍先. CD4+T细胞表型转换及其调控机制的研究[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2015,19(1):55-57.[22] 王鹏鹏,柴长斌,汪洋. CD8+T细胞激活和免疫记忆形成的分子调节机制[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2015,35(7):541-545.[23] 王富春,逄紫千.针灸天枢穴对脾虚泄泻大鼠肠道功能影响的实验研究[J].长春中医药大学学报,2005,21(1):52-54.[24] Brandtzaeg P.The Secretory Immunoglobulin System: Regulation and Biological Significance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;503:1-16.[25] Hart AL, Lammers K, Brigidi P, et al. Modulation of human dendritic cell phenotype and function by probiotic bacteria. Gut. 2004;53(11):1602-1609.[26] 于茜楠,陈以国. 针灸对固有免疫双向调节研究简况[J].实用中医内科杂志,2015,29(3):137-139.[27] 杨丽霞.针刺调节慢性疲劳大鼠神经—免疫功能的研究[D]. 广州中医药大学,2007.[28] 韩晓伟,马贤德,孙宏伟,等.脾虚小鼠肠道感染白色念珠菌的局部黏膜免疫机制研究简[J].世界中西医结合杂志, 2016,11(8): 1037-1039.[29] 刘芬,刘艳菊,田春漫.苍术提取物对脾虚证大鼠胃粘膜及胃肠免疫功能的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2015,35(3):343-347.[30] 王为,周国华. 肠道相关淋巴样组织与肠道黏膜免疫[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(21):3720-3722.[31] 郑超伟,纪云西,周福生,等.脾虚证本质研究的困惑与出路[J].广州中医药大学学报,2011,28(3):314-316.[32] Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK. Metabonomics Techniques and Applications to Pharmaceutical Research & Development. Pharm Res.2006;23(6):1075-1088. |