Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (4): 570-575.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0092
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression and significance of Wnt-5a gene in a model of intervertebral disc degeneration
Yang Xiao-ming, Zhao Quan-lai, Gao Zhi, Xu Hong-guang, Wang Hong, Liu Ping
- Department of Spine Surgery, Yijishan Hospital Affiliated to Wannan Medical University, Wuhu 241001, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2017-09-06Online:2018-02-08Published:2018-02-08 -
Contact:Xu Hong-guang, M.D., Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Spine Surgery, Yijishan Hospital Affiliated to Wannan Medical University, Wuhu 241001, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Yang Xiao-ming, Master, Attending physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Yijishan Hospital Affiliated to Wannan Medical University, Wuhu 241001, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the Middle-Aged Youth Foundation of Wannan Medical University, No. WK2014F02
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Xiao-ming, Zhao Quan-lai, Gao Zhi, Xu Hong-guang, Wang Hong, Liu Ping. Expression and significance of Wnt-5a gene in a model of intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 570-575.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
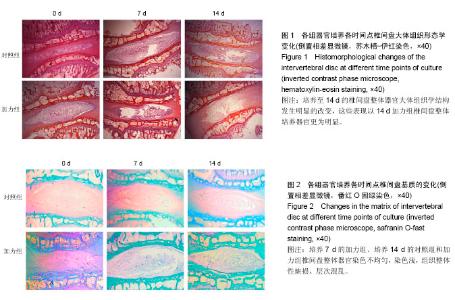
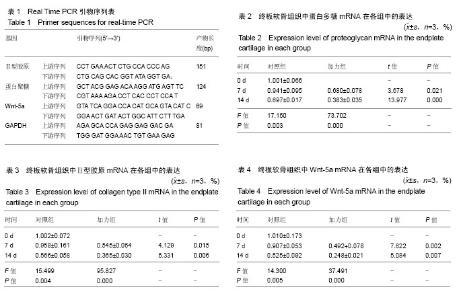
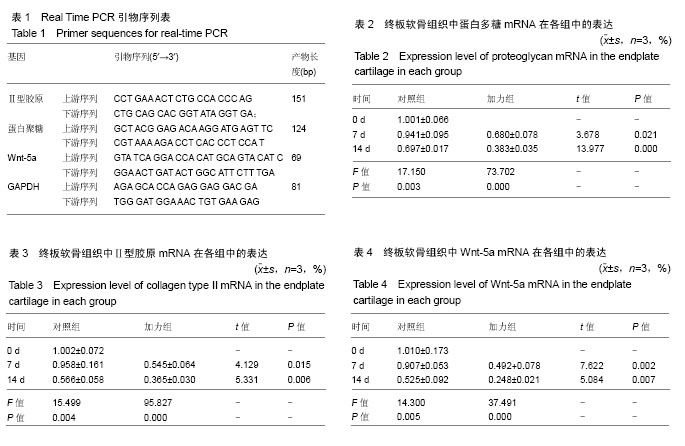
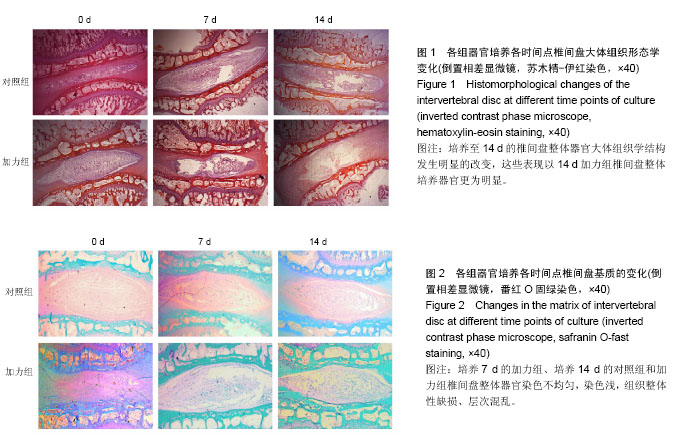
2.1 实验动物数量分析 纳入35只大白兔,随机分为5组,每组7只。其中5只因感染发生脱失,未脱失中每组随机取3只进行结果分析。 2.2 苏木精-伊红染色 观察椎间盘整体器官矢状面石蜡切片苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,与培养0 d相比较,加力组与对照组椎间盘整体培养器官,培养至7 d各组椎间盘大体形态结构完整;培养至14 d的椎间盘整体器官大体组织学结构发生明显的改变,表现为纤维环出现裂伤,结构紊乱,与髓核组织界限不清,髓核组织出现纤维化,体积缩小,这些表现以14 d加力组椎间盘整体培养器官更为明显,见图1。 2.3 番红O固绿染色 观察椎间盘整体器官冠状面石蜡切片番红O固绿染色结果显示,与培养0 d相比较,培养7 d对照组椎间盘整体培养器官显示基质完全匀称着色,组织整体性保持完好;培养7 d的加力组、培养14 d的对照组和加力组椎间盘整体器官染色不均匀,染色较培养7 d对照组浅,组织整体性缺损、层次混乱,见图2。 2.4 椎间盘整体器官软骨细胞表型基因以及Wnt-5a基因的检测 Real time PCR检测蛋白多糖表达:对照组14 d与0 d两两比较,蛋白多糖表达下调,且差异有显著性意义(P=0.003);培养7 d时2组比较,加力组蛋白多糖表达下调,且差异有显著性意义(P=0.021);培养14 d时2组比较,加力组蛋白多糖表达明显下调,且差异有显著性意义(P=0.000),见表2。 检测Ⅱ型胶原表达:对照组14 d与0 d两两比较,Ⅱ型胶原表达明显下调,且差异有显著性意义(P=0.004);培养7 d时2组比较,加力组Ⅱ型胶原表达下调,且差异有显著性意义(P=0.015);培养14 d时2组比较,加力组Ⅱ型胶原表达明显下调,且差异有显著性意义(P=0.006),见表3。 检测Wnt-5a基因表达:对照组14 d与0 d两两比较,Wnt-5a基因表达明显下调,且差异有显著性意义(P=0.005);培养7 d时2组比较,加力组Wnt-5a基因表达下"
| [1] Natvig B, Ihlebæk C, Grotle M, et al. Neck pain is often a part of widespread pain and is associated with reduced functioning. Spine. 2010;35(23):E1285-1289.[2] Yang H, Cao C, Wu C, et al. TGF-betal Suppresses Inflammation in Cell Therapy for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Sci Rep. 2015;5: 13254.[3] Manek NJ, MacGregor AJ. Epidemiology of back disorders: prevalence, risk factors, and prognosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2005;17(2):134-140.[4] Xu HG, Zheng Q, Song JX, et al. Intermittent cyclic mechanical tension promotes endplate cartilage degeneration via canonical Wnt signaling pathway and E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex cross-talk. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(1):158-168. [5] Wu B, Meng C, Wang H, et al. Changes of proteoglycan and collagen II of the adjacent intervertebral disc in the cervical instability models. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84: 754-758.[6] Tomaszewski KA, Adamek D, Pasternak A, et al. Degeneration and calcification of the cervical endplate is connected with decreased expression of ANK, ENPP-1, OPN and TGF-beta1 in the intervertebral disc. Pol J Pathol. 2014; 65(3):210-217.[7] Xu HG, Zhang XH, Wang H, et al. Intermittent Cyclic Mechanical Tension-Induced Calcification and downregulation of ankh gene expression of end plate chondrocytes. Spine. 2012;37(14):1192-1197.[8] Grant MP, Epure LM, Bokhari R, et al. Human cartilaginous endplate degeneration is induced by calcium and the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in the intervertebral disc. Eur Cell Mater. 2016;32:137-151.[9] Mariani E, Pulsatelli L, Facchini A. Signaling pathways in cartilage repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(5): 8667-8698.[10] Bradley EW, Drissi MH. WNT5A regulates chondrocyte differentiation through differential use of the CaN/NFAT and IKK/NF-kappaB pathways. Mol Endocrinol. 2010; 24(8): 1581-1593.[11] 徐宏光,章平治,宋俊兴,等. 循环机械压力诱导下兔椎间盘退变器官模型的建立及意义[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2014, 7(1):45-51.[12] Xu HG, Ma MM, Zheng Q, et al. P120-Catenin Protects Endplate Chondrocytes From Intermittent Cyclic Mechanical Tension Induced Degeneration by Inhibiting the Expression of RhoA/ROCK-1 Signaling Pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41(16): 1261-1271.[13] Xiao L, Xu HG, Wang H, et al. Intermittent Cyclic Mechanical Tension Promotes Degeneration of Endplate Cartilage via the Nuclear Factor-kappaB Signaling Pathway: an in Vivo Study. Orthop Surg. 2016;8(3):393-399.[14] Lindblom K. Intervertebral-disc degeneration considered as apressureatrophy. J Bone Joint Sur Br. 1957;39A: 933-945.[15] Huang YC, Urban JP, Luk KD. Intervertebral disc regeneration: do nutrients lead the way? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10(9): 561-566.[16] Colombier P, Clouet J, Hamel O, et al. The lumbar intervertebral disc: from embryonic development to degeneration. Joint Bone Spine. 2014;81(2): 125-129.[17] Louati K, Berenbaum F. Joint Biochemical Markers for Cartilage, Bone, Cartilage Degradation, Bone Remodeling, and Inflammation. 2016.[18] Gantenbein B, Illien-Junger S, Chan SC, et al. Organ culture bioreactors--platforms to study human intervertebral disc degeneration and regenerative therapy. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;10(4): 339-352.[19] Thompson JP, Pearce RH, Schechter MT, et al. Preliminary evaluation of scheme for grading the gross morphology of the human intervertebral disc. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1990;15 (5): 411-415.[20] Sobajima S, Kompel JF, Wallach CJ, et al. A slowly progresssive and reproducible animal model of intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by MRI, X-ray, and Histology. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1): 15-24.[21] Rieppo J, Toyras J, Nieminen MT, et al. Structure function relationships in enzymatically modified articular cartilage. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;175(3): 121-132.[22] Wodarz A, Nusse R. Mechanisms of Wnt signaling in development. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1998;14: 59-88.[23] Eisenmann DM. Wnt signaling. Worm Book, 2005: 1-17.[24] Bougault C, Briolay A, Boutet MA, et al. Wnt5a is expressed in spondyloarthritis and exerts opposite effects on enthesis and bone in murine organ and cell cultures. Transl Res. 2015; 166(6): 627-638.[25] 邓刚,司维柯,潘静,等. Wnt-5a基因在淋巴细胞系恶性肿瘤中的表达分析[J].第三军医大学学报,2008,30(19):1832-1835.[26] Miclea RL, Silbelt M, Finos L, et al. Inhiibion of Gsk3β in cartilage induces osteoarthritic features through activation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(11):1363.[27] Yang Y, Topol L, Lee H, et al. Wnt5a and Wnt5b exhibit distinct activities in coordinating chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Development. 2003;130(5): 1003-1015.[28] 贾瑞平,徐宏光,张小海. Wnt信号通路对软骨细胞影响研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学,2010,31(4):200-203.[29] Kuss P, Kraft K, Stumm J, et al. Regulation of cell polarity in the cartilage growth plate and perichondrium of metacarpal elements by HOXD13 and WNT5A. Dev Biol. 2014;385(1): 83-93.[30] Ge XP, Ma XC, Meng JH, et al. Role of Wnt-5a in Interleukin-1β-Induced Matrix Meta lloproteinase Expression in Rabbit Temporomandibular Joint Condylar Chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(9): 2714-2722.[31] Yang Y, Topol L, Lee H, et al. Wnt5a and Wnt5b exhibit distinct activities in coordinating chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Development. 2003;130(5):1003-1015.[32] Sassi N, Laadhar L, Allouche M, et al. Wnt signaling is involved in human articular chondrocyte de-differentiation in vitro. Biotech Histochem.2014;89(1):29-40. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||