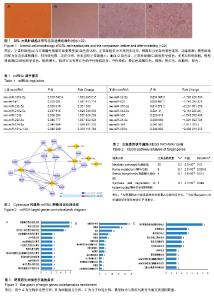
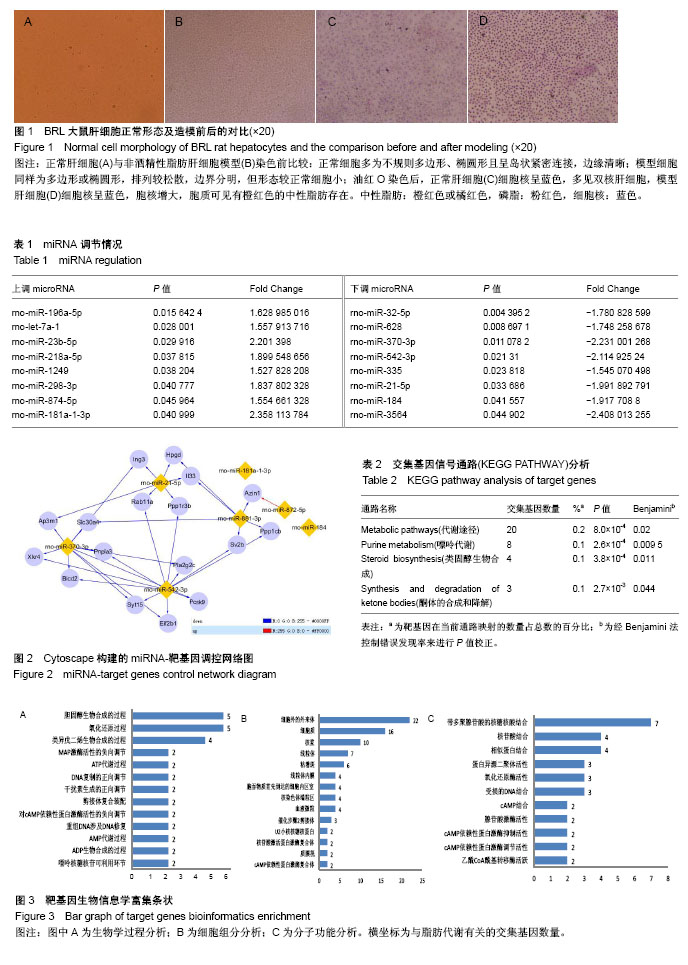
| [1] Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D,et al.Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology.2016;64(1):73-84.[2] Anstee QM, McPherson S, Day CP.How big a problem is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?BMJ. 2011;343:d3897.[3] 范晓棠,哈丽达•夏尔甫哈孜,陈新春,等.臭氧治疗非酒精性脂肪肝:细胞因子水平的变化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(7): 1047-1051.[4] Watanabe S, Hashimoto E, Ikejima K,et al.Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/ nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.J Gastroenterol. 2015;50(4): 364-377.[5] 郑刚.非酒精性脂肪性肝病与肝癌关系研究进展[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2012,21(3):216-220.[6] Popov VB, Lim JK.Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Role of Medical, Surgical, and Endoscopic Weight Loss.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2015;3(3):230-238.[7] 吕雪幼,叶国良.多烯磷脂酰胆碱治疗老年中重度脂肪肝的临床研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2016,32(15):1370-1373.[8] 刘锐,伍娟娟,甘国兴,等.多烯磷脂酰胆碱对非酒精性脂肪性肝病模型大鼠肝脏SREBP-1c与ABCA1蛋白表达的影响[J].广东医学,2011,32(18):2376-2378. [9] 朱梓铭,郑景辉,黄金龙,等.养心通脉有效部位方干预AMI大鼠BMSCs miRNA组学分析[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2017, 23(16):114-120.[10] 范建高,曾民德.脂肪性肝病[M].上海:上海医科大学出版社, 2000:153[11] 马富超,张泉洋,王帅,等.非酒精性脂肪性肝病动物模型研究进展[J].国际药学研究杂志,2017,44(5):409-414.[12] 王俊杰,方会龙,李纯伟,等.非酒精性脂肪肝模型小鼠的建立[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(24):4395-4399.[13] Wang HW, Cao LL, Fan MQ, et al. Effect of polyene phosphatidylcholine combined with fenofibrate capsules in treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2014;22(3):429-433.[14] 陈彬,林海雪.多烯磷脂酰胆碱对非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠的干预及其对肝锌指蛋白A20表达的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2018, 34(11):1353-1356.[15] 陈艳,郑意楠.茵栀黄及双歧杆菌三联活菌辅助光照治疗新生儿黄疸疗效分析[J].中国全科医学, 2012,15(21):2480-2481,2483.[16] 孙欣,高莹,杨云锋.环境微生物的宏基因组学研究新进展[J].生物多样性,2013,21(4):393-401.[17] 上官辉,谭淑燕,张积仁.肝癌易感性相关基因的文献计量学与生物信息学分析[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2015,22(4):305-311.[18] 成军,刘妍,陆荫英,等. 生物信息学技术与新基因的研究[J]. 世界华人消化杂志, 2003,11(4):474-477.[19] Brockhausen J, Tay SS, Grzelak CA,et al.miR-181a mediates TGF-β-induced hepatocyte EMT and is dysregulated in cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer.Liver Int. 2015;35(1): 240-253.[20] Lu CH, Hou QR, Deng LF,et al.MicroRNA-370 Attenuates Hepatic Fibrogenesis by Targeting Smoothened.Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60(7):2038-2048.[21] Li L, Li G, Yu C,et al.A role of microRNA-370 in hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury by targeting transforming growth factor-β receptor II.Liver Int. 2015;35(4):1124-1132. [22] Xu WP, Yi M, Li QQ,et al.Perturbation of MicroRNA-370/ Lin-28 homolog A/nuclear factor kappa B regulatory circuit contributes to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2013;58(6):1977-1991.[23] Zheng J, Yu L, Chen W,et al.Circulating exosomal microRNAs reveal the mechanism of Fructus Meliae Toosendan-induced liver injury in mice.ci Rep. 2018;8(1):2832.[24] Wen M, Cui J, Xu J,et al.Effects of dietary sea cucumber saponin on the gene expression rhythm involved in circadian clock and lipid metabolism in mice during nighttime-feeding.J Physiol Biochem. 2014;70(3):801-808.[25] Li Y, Yao L, Liu F,et al.Characterization of microRNA expression in serous ovarian carcinoma.Int J Mol Med. 2014; 34(2):491-498. [26] Benoit B, Plaisancié P, Awada M,et al.High-fat diet action on adiposity, inflammation, and insulin sensitivity depends on the control low-fat diet.Nutr Res. 2013;33(11):952-960.[27] Castrop H.Mediators of tubuloglomerular feedback regulation of glomerular filtration: ATP and adenosine.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2007;189(1):3-14.[28] Seo MS, Hong SW, Yeon SH,et al.Magnolia officinalis attenuates free fatty acid-induced lipogenesis via AMPK phosphorylation in hepatocytes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;157: 140-148.[29] 高燕翔,张勇,刘裕,等.SREBP-1c在白藜芦醇预防大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝发生中的作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(17): 1704-1708.[30] Xu G, Zhang Y, Wei J,et al.MicroRNA-21 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell proliferation through repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase 3.BMC Cancer. 2013;13:469.[31] Tomimaru Y, Eguchi H, Nagano H,et al.Circulating microRNA- 21 as a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2012;56(1):167-175.[32] Gougelet A, Colnot S. Hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis: Circulating microRNAs emerge as robust biomarkers.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016;40(4):367-369.[33] Zhang JJ, Zhang YZ, Peng JJ,et al.Atorvastatin exerts inhibitory effect on endothelial senescence in hyperlipidemic rats through a mechanism involving down-regulation of miR-21-5p/203a-3p.Mech Ageing Dev. 2018;169:10-18.[34] 魏益国,陈捷,石明巧,等.PNPLA3基因多态性与非酒精性脂肪性肝病肝损伤间相关性的系统评价[J].检验医学与临床, 2018, 15(2):157-160.[35] Tai CM, Huang CK, Tu HP,et al.Interactions of a PPARGC1A Variant and a PNPLA3 Variant Affect Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Severely Obese Taiwanese Patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(12):e3120.[36] Zain SM, Mohamed R, Mahadeva S,et al.A multi-ethnic study of a PNPLA3 gene variant and its association with disease severity in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Hum Genet. 2012; 131(7):1145-1152.[37] Petta S, Vanni E, Bugianesi E,et al.PNPLA3 rs738409 I748M is associated with steatohepatitis in 434 non-obese subjects with hepatitis C.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2015;41(10): 939-948.[38] Stättermayer AF, Traussnigg S, Aigner E, et al. Low hepatic copper content and PNPLA3 polymorphism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients without metabolic syndrome.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2017;39:100-107. [39] 耿宁,辛永宁,姜曼,等.PNPLA3基因I148M多态性与肝脏疾病炎症发展相关性研究[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(20):3345-3347.[40] Sookoian S, Pirola CJ.Meta-analysis of the influence of I148M variant of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (PNPLA3) on the susceptibility and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Hepatology. 2011;53(6): 1883-1894. |