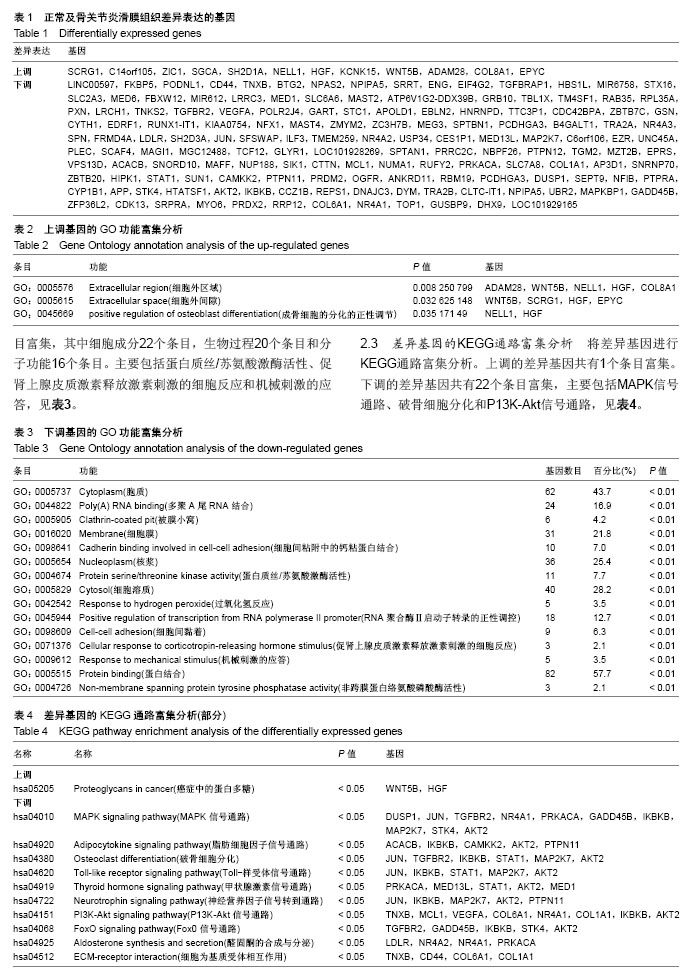
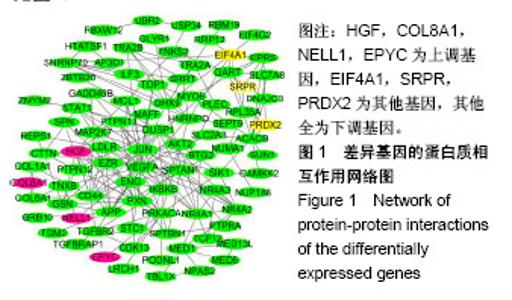
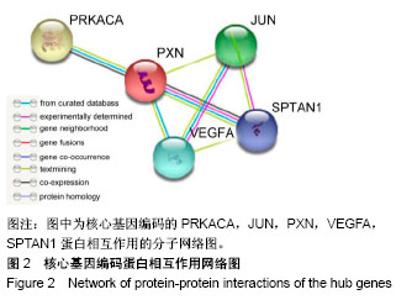
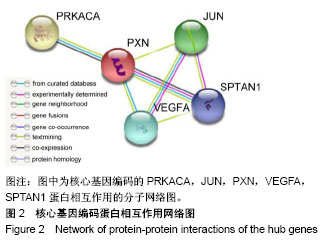
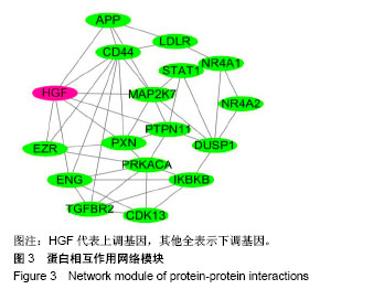
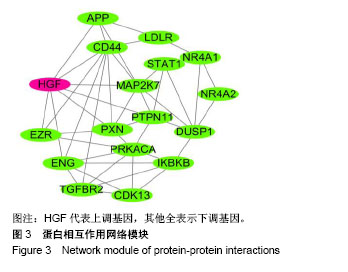
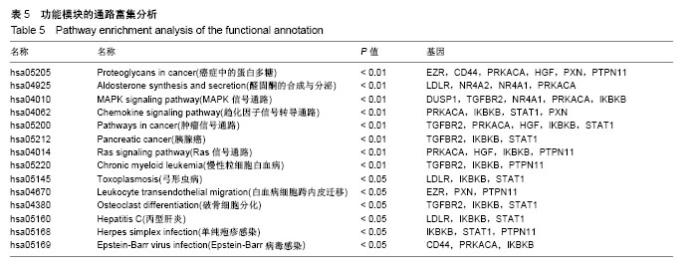
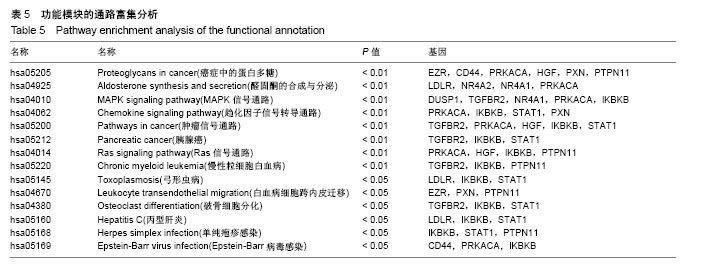
| [1] Neogi T, Zhang Y. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Rheumatic diseases clinics of North America. 2013;39(1):1-19.[2] Poulet B, Staines KA. New developments in osteoarthritis and cartilage biology. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016;28:8-13.[3] Allen KD, Golightly YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27(3):276-283.[4] Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233(1):233-255.[5] 张禄锴,李风波,马剑雄,等.破骨细胞分化通路的研究进展[J].生物医学工程与临床,2017,21(3):328-333.[6] 孙啸,王晔,何农跃,等.生物信息学在基因芯片中的应用[J].生物物理学报,2001,17(1):27-34.[7] Cui S, Zhang X, Hai S, et al. Molecular mechanisms of osteoarthritis using gene microarrays. Acta histochemica, 2015;117(1):62-68. [8] 李晓燕,张艳,董春萍,等.骨关节炎大鼠模型软骨组织中PI3K/ AKT信号通路功能与细胞凋亡的相关性研究[J].海南医学院学报,2017,23(11):1452-1455.[9] 陈蕾,王世鑫,刘萍,等.染矽尘大鼠早期肺组织差异基因表达谱的研究[J].中华预防医学杂志,2008,42(7):515-521.[10] Van Parys T, Melckenbeeck I, Houbraken M, et al. A Cytoscape app for motif enumeration with ISMAGS. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England). 2017;33(3):461-463.[11] 王君芳,王佳琦,毕庆伟,等.神经嵴细胞发育分子调控网络的生物信息学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(24):3621-3627.[12] Skoczynska A, Budzisz E, Podgorna K, et al. Paxillin and its role in the aging process of skin cells. Postepy higieny i medycyny doswiadczalnej (Online). 2016;70:1087-1094.[13] Sanz-Ramos P, Mora G, Ripalda P, et al. Identification of signalling pathways triggered by changes in the mechanical environment in rat chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(8):931-939.[14] Kuo CH, Liu CJ, Lu CY, et al. 17beta-estradiol inhibits mesenchymal stem cells-induced human AGS gastric cancer cell mobility via suppression of CCL5- Src/Cas/Paxillin signaling pathway. Int J Med Sci. 2014;11(1):7-16.[15] Tasken K, Solberg R, Zhao Y, et al. The gene encoding the catalytic subunit C alpha of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (locus PRKACA) localizes to human chromosome region 19p13.1. Genomics. 1996;36(3):535-538.[16] Banday AR, Azim S, Hussain MA, et al. Computational prediction and characterisation of ubiquitously expressed new splice variant of Prkaca gene in mouse. Cell Biol Int. 2013; 37(7):687-93.[17] Horinouchi T, Higa T, Aoyagi H, et al. Adenylate cyclase/cAMP/protein kinase A signaling pathway inhibits endothelin type A receptor-operated Ca(2)(+) entry mediated via transient receptor potential canonical 6 channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012;340(1):143-151.[18] Medina EA, Oberheu K, Polusani SR, et al. PKA/AMPK signaling in relation to adiponectin's antiproliferative effect on multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia. 2014;28(10):2080-2089.[19] 宣琪.胃癌及其癌前病变相关基因差异表达的研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2002.[20] 成撒诺,徐亚丽,戴晓波,等.Krüppel样转录因子8在肝细胞癌中经PI3K/Akt通路调控VEGFA的表达[J].肿瘤,2014,34(12): 1075-1081.[21] 谢锦伟,裴福兴.血管内皮生长因子与骨关节炎[J].国际骨科学杂志,2014,35(1):16-18.[22] Dhar S, Ray BK, Ray A. Escalated Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Osteoarthritis. Springer. New York, USA. 2013.[23] 丁浩.TGF-β和VEGF在OA患者滑膜组织中的表达及临床意义[D].石河子:石河子大学,2016.[24] Xing L, Xiu Y, Boyce BF. Osteoclast fusion and regulation by RANKL-dependent and independent factors. World J Orthop. 2012;3(12):212-22.[25] Sottnik JL,Keller ET. Understanding and targeting osteoclastic activity in prostate cancer bone metastases. Curr Mol Med. 2013;13(4):626-39.[26] Chen LL, Huang M, Tan J Y, et al. PI3K/AKT pathway involvement in the osteogenic effects of osteoclast culture supernatants on preosteoblast cells. Tissue engineering Part A. 2013;19(19-20):2226-2232.[27] Chapurlat R D, Palermo L, Ramsay P, et al. Risk of fracture among women who lose bone density during treatment with alendronate. The Fracture Intervention Trial. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16(7):842-848.[28] 王链链,郭晓英.破骨细胞分化过程中的信号通路及信号因子的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):742-748.[29] Lee HP, Lin CY, Shih JS, et al. Adiponectin promotes VEGF-A-dependent angiogenesis in human chondrosarcoma through PI3K, Akt, mTOR,and HIF-alpha pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6(34):36746-36761.[30] Grimaldi A M, Simeone E, Festino L, et al. Novel mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in melanoma: targeting the MAPK pathway. Discovery Med. 2015;19(107):455-461.[31] Fecher L A, Amaravadi R K, Flaherty K T. The MAPK pathway in melanoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20(2):183-189.[32] 高世超,殷海波,刘宏潇,等.MAPK信号通路在骨关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2014,27(5):441-444.[33] Kaminska B. MAPK signalling pathways as molecular targets for anti-inflammatory therapy-from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic benefits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1754(1-2): 253-262.[34] Yoon HS, Kim HA. Prologation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase is associated with cell death induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha in human chondrocytes. J Korean Med Sci. 2004;19(4): 567-573.[35] 孙琪.高压氧对白介素-1β诱导的炎性髁突软骨细胞JNK/c-Jun信号通路影响的研究[D].济南:山东大学,2017. |