Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (1): 79-84.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1528
Previous Articles Next Articles
Immune properties of human CD200+ sub-population from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Liu Ting, Ma Xiaona, Ma Haibin, Yang Tingting, Jin Yiran, Liang Xueyun
- Ningxia Human Stem Cell Institute, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2018-10-16Online:2019-01-08Published:2018-11-28 -
Contact:Liang Xueyun, Associate researcher, Master’s supervisor, Ningxia Human Stem Cell Institute, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liu Ting, Master, Assistant researcher, Ningxia Human Stem Cell Institute, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81460186 (to LXY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Ting, Ma Xiaona, Ma Haibin, Yang Tingting, Jin Yiran, Liang Xueyun. Immune properties of human CD200+ sub-population from human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(1): 79-84.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
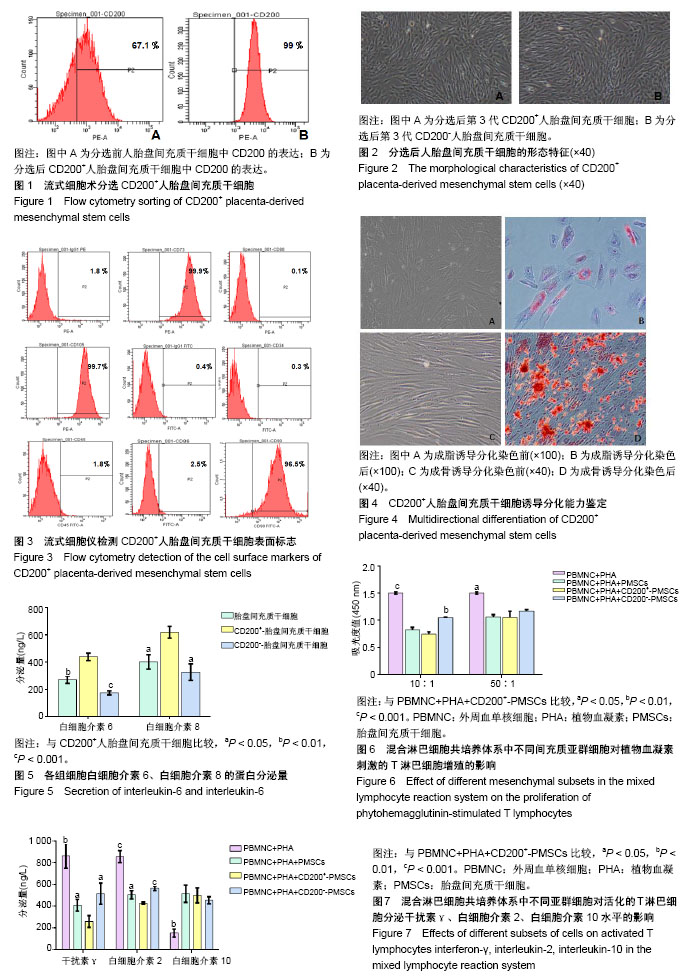
2.1 CD200+-PMSCs的分选结果 经流式细胞术检测,分选前PMSCs的CD200表达水平在60%-70%,分选后CD200+-PMSCs的CD200表达水平在90%以上,见图1。 2.2 CD200+-PMSCs的形态特征 分选获得的CD200+- PMSCs保持了间充质干细胞的形态特征,绝大多数细胞形态均一,细胞核较大,胞质透明,呈涡旋状生长,见图2A,而CD200--PMSCs没有表现出形态上的差异,见图2B。 2.3 CD200+-PMSCs表达与间充质干细胞一致的表面抗原 分选后CD200+-PMSCs高表达CD73、CD90和CD105,不表达CD34、CD45、CD80和CD86,见图3,具有典型的间充质干细胞表面标志。 2.4 CD200+-PMSCs亚群细胞具有多向分化潜能 成脂诱导分化3 d左右,细胞增殖停止,细胞开始逐渐变大,诱导分化12 d左右,镜下可见细胞形态呈不规则多边形,胞质内出现多个圆泡,油红O染色后可见圆泡被染成红色,即为脂滴,证明分选获得的CD200+-PMSCs成功诱导分化为脂肪细胞,见图4A,B。 成骨诱导分化5-7 d,细胞生长已经连成片,继续诱导至14 d左右,镜下可见细胞层层叠叠紧密生长,挤成一团,茜素红染色后可以观察到有多处成片细胞被染成红色,即为诱导产生的钙结节,证明分选获得的CD200+-PMSCs成功诱导分化为成骨细胞,见图4C,D。 2.5 CD200+-PMSCs的白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8因子分泌量 CD200+-PMSCs的白细胞介素6分泌量明显高于PMSCs(P < 0.01)和CD200--PMSCs(P < 0.001)。白细胞介素8的分泌量也高于PMSCs(P < 0.05)和CD200-- PMSCs(P < 0.05),差异均有显著性意义,见图5。 2.6 CD200+-PMSCs对PHA刺激的T淋巴细胞增殖有明显的抑制作用 当活化的T淋巴细胞分别与PMSCs、CD200+-PMSCs、CD200--PMSCs以10∶1的比例共培养时,这3种细胞均能明显抑制T淋巴细胞的增殖,其中CD200+-PMSCs的抑制作用明显强于CD200--PMSCs(P < 0.01),差异有显著性意义,而与PMSCs没有显著差异。当共培养细胞比例为50∶1时,T淋巴细胞的增殖仍能被抑制(P < 0.05),但是抑制作用有所减弱,并且3种细胞的抑制作用没有显著差异,见图6。 2.7 CD200+-PMSCs对PHA刺激的T淋巴细胞分泌因子的调节作用 见图7。活化的T淋巴细胞与间充质细胞以10∶1的比率共培养48 h后,CD200+-PMSCs能够明显下调干扰素γ水平,与PMSCs、CD200--PMSCs比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 CD200+-PMSCs同样能够明显下调活化的T淋巴细胞分泌白细胞介素2的水平,与PMSCs(P < 0.05)、CD200--PMSCs(P < 0.001)比较差异有显著性意义。 活化的T淋巴细胞分泌白细胞介素10的水平均能够被3种细胞显著上调,但是3种细胞的上调作用没有显著差异。"
| [1] Schuleri KH, Boyle AJ, Hare JM.Mesenchymal stem cells for cardiac regenerative therapy.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2007; (180):195-218. [2] Deda H, Inci MC, Kürekçi AE, et al. Treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients by autologous bone marrow-derived hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a 1-year follow-up. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(1):18-25. [3] Martinez HR, Gonzalez-Garza MT, Moreno-Cuevas JE, et al. Stem-cell transplantation into the frontal motor cortex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients.Cytotherapy. 2009; 11(1):26-34. . [4] Taupin P.OTI-010 Osiris Therapeutics/JCR Pharmaceuticals. Curr OpinInvestig Drugs. 2006;7(5):473-481. [5] Abdi R, Fiorina P, Adra CN, et al. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells: a potential therapeutic strategy for type 1 diabetes.Diabetes. 2008;57(7):1759-1767. [6] Yoshikawa T, Mitsuno H, Nonaka I, et al. Wound therapy by marrow mesenchymal cell transplantation.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008;121(3):860-877. [7] Le Blanc K, Tammik L, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility complex.Scand J Immunol. 2003;57(1): 11-20. [8] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF.Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses.Blood. 2005; 105(4):1815-1822. [9] Jiang XX, Zhang Y, Liu B, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit differentiation and function of monocyte-derived dendritic cells.Blood. 2005;105(10):4120-4126. [10] Beyth S, Borovsky Z, Mevorach D, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells alter antigen-presenting cell maturation and induce T-cell unresponsiveness.Blood. 2005;105(5):2214-2219. [11] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions.Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372. [12] Chan JL, Tang KC, Patel AP, et al. Antigen-presenting property of mesenchymal stem cells occurs during a narrow window at low levels of interferon-gamma.Blood. 2006; 107(12):4817-4824. [13] Stagg J, Pommey S, Eliopoulos N, et al. Interferon-gamma- stimulated marrow stromal cells: a new type of nonhematopoietic antigen-presenting cell.Blood. 2006;107(6): 2570-2577. [14] Stagg J.Immune regulation by mesenchymal stem cells: two sides to the coin.Tissue Antigens. 2007;69(1):1-9. [15] Nauta AJ, Westerhuis G, Kruisselbrink AB, et al. Donor-derived mesenchymal stem cells are immunogenic in an allogeneic host and stimulate donor graft rejection in a nonmyeloablative setting.Blood. 2006;108(6):2114-2120. [16] 郝贵亮,王立斌,陈冬梅,等.母体和胎儿来源的人胎盘间充质干细胞抑制小鼠皮肤移植免疫排斥作用的比较[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2015,31(5):609-614.[17] 马晓娜,刘婷,金毅然,等.母体来源人胎盘间充质细胞的分离培养及其分化能力的研究[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(34):3-5.[18] Syková E, Jendelová P, Urdzíková L, et al. Bone marrow stem cells and polymer hydrogels--two strategies for spinal cord injury repair.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006;26(7-8):1113-1129. [19] Satija NK, Singh VK, Verma YK, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy: a new paradigm in regenerative medicine. J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(11-12):4385-4402. [20] Patel DM, Shah J, Srivastava AS.Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine.Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:496218. [21] Parolini O, Alviano F, Bagnara GP, et al. Concise review: isolation and characterization of cells from human term placenta: outcome of the first international Workshop on Placenta Derived Stem Cells.Stem Cells. 2008;26(2):300-311. [22] Kadam S, Muthyala S, Nair P, et al. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and islet-like cell clusters generated from these cells as a novel source for stem cell therapy in diabetes.Rev Diabet Stud. 2010;7(2):168-182. [23] Lu GH, Zhang SZ, Chen Q, et al. Isolation and multipotent differentiation of human decidua basalis-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011;31(2):262-265. [24] Miao Z, Jin J, Chen L, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human placenta: comparison with human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Biol Int. 2006;30(9):681-687. [25] 张红艳,杨乃龙.胎盘来源间充质干细胞的生物学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2010,14(40):7535-7538.[26] Alviano F, Fossati V, Marchionni C, et al. Term Amniotic membrane is a high throughput source for multipotent Mesenchymal Stem Cells with the ability to differentiate into endothelial cells in vitro.BMC Dev Biol. 2007;7:11. [27] Wolbank S, Peterbauer A, Fahrner M, et al. Dose-dependent immunomodulatory effect of human stem cells from amniotic membrane: a comparison with human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue.Tissue Eng. 2007;13(6):1173-1183. [28] Portmann-Lanz CB, Schoeberlein A, Portmann R, et al. Turning placenta into brain: placental mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neurons and oligodendrocytes.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010;202(3):294. e1-294. e11. [29] Ventura C, Cantoni S, Bianchi F, et al. Hyaluronan mixed esters of butyric and retinoic Acid drive cardiac and endothelial fate in term placenta human mesenchymal stem cells and enhance cardiac repair in infarcted rat hearts.J Biol Chem. 2007;282(19):14243-14252. [30] 李治,赵伟,刘伟,等.玻璃酸钠及胎盘间充质干细胞和诱导的软骨细胞膝关节腔内注射:修复膝骨关节炎[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(50):8140-8146.[31] Li Z, Qin H, Feng Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-loaded amniotic membrane for the repair of radial nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(36): 3441-3448. [32] Ercal P, Pekozer GG, Gumru OZ, et al. Influence of STRO-1 selection on osteogenic potential of human tooth germ derived mesenchymal stem cells.Arch Oral Biol. 2017; 82:293-301. [33] Najar M, Crompot E, van Grunsven LA, et al. Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Activity in Adipose Tissue: Isolation and Gene Expression Profile of Distinct Sub-population of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells.Stem Cell Rev. 2018; 14(4): 599-611. [34] Lee HT, Chang HT, Lee S, et al. Role of IGF1R(+) MSCs in modulating neuroplasticity via CXCR4 cross-interaction.Sci Rep. 2016;6:32595. [35] Cao H, Yang J, Yu J, et al. Therapeutic potential of transplanted placental mesenchymal stem cells in treating Chinese miniature pigs with acute liver failure.BMC Med. 2012;10:56. [36] Geffner LF, Santacruz P, Izurieta M, et al. Administration of autologous bone marrow stem cells into spinal cord injury patients via multiple routes is safe and improves their quality of life: comprehensive case studies.Cell Transplant. 2008; 17(12):1277-1293. [37] Hoek RM, Ruuls SR, Murphy CA, et al. Down-regulation of the macrophage lineage through interaction with OX2 (CD200).Science. 2000;290(5497):1768-1771. [38] Jenmalm MC, Cherwinski H, Bowman EP, et al. Regulation of myeloid cell function through the CD200 receptor.J Immunol. 2006;176(1):191-199. [39] Gorczynski RM, Lee L, Boudakov I.Augmented Induction of CD4+CD25+ Treg using monoclonal antibodies to CD200R. Transplantation. 2005;79(9):1180-1183. [40] Kretz-Rommel A, Qin F, Dakappagari N, et al. CD200 expression on tumor cells suppresses antitumor immunity: new approaches to cancer immunotherapy.J Immunol. 2007; 178(9):5595-5605. [41] Coles SJ, Hills RK, Wang EC, et al. Increased CD200 expression in acute myeloid leukemia is linked with an increased frequency of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells.Leukemia. 2012;26(9):2146-2148. [42] Guo Y, Xu F, Lu T, et al. Interleukin-6 signaling pathway in targeted therapy for cancer.Cancer Treat Rev. 2012; 38(7): 904-910. [43] Ha H, Debnath B, Neamati N.Role of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 Axis in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases.Theranostics. 2017;7(6):1543-1588. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||