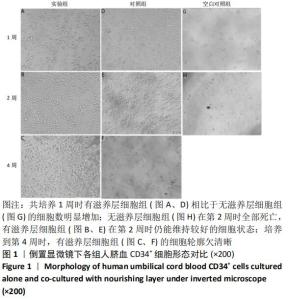
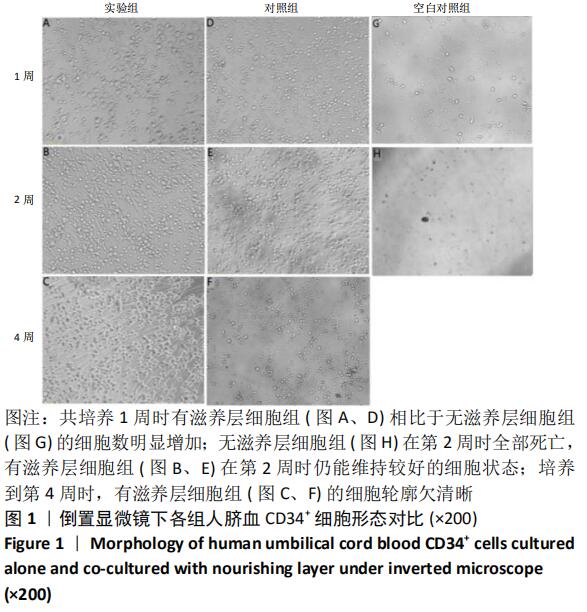
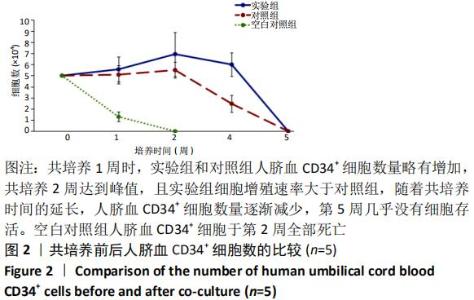
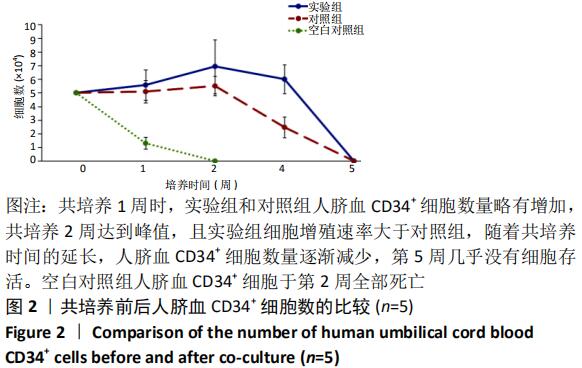
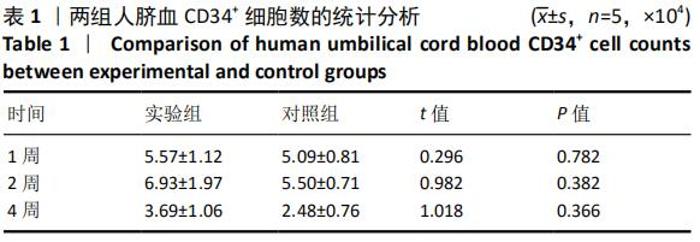
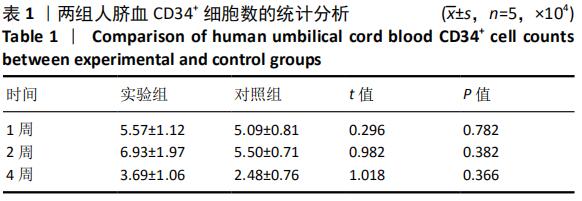
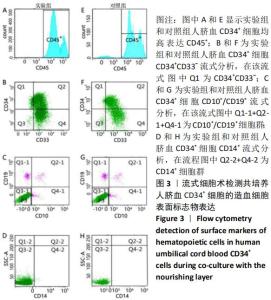
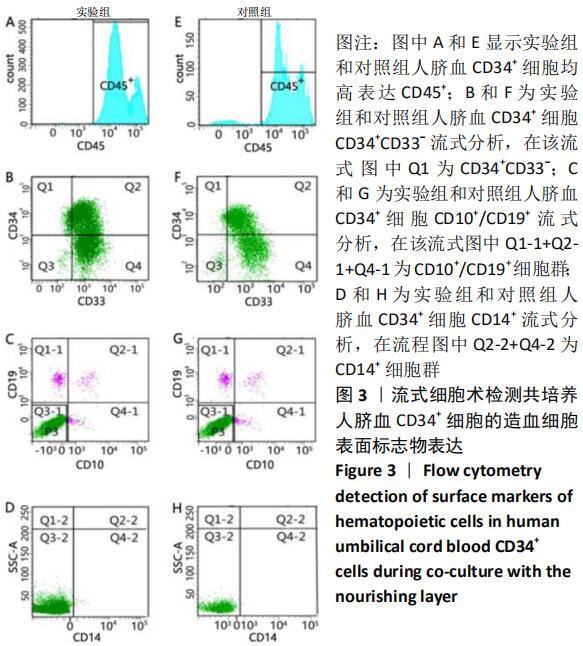
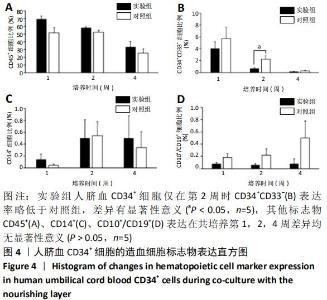
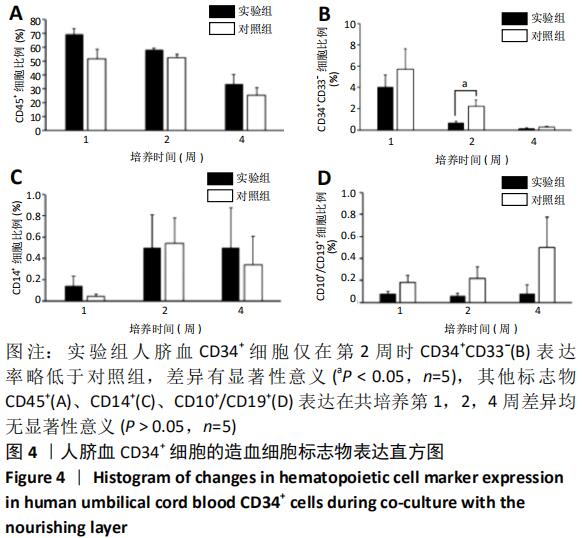
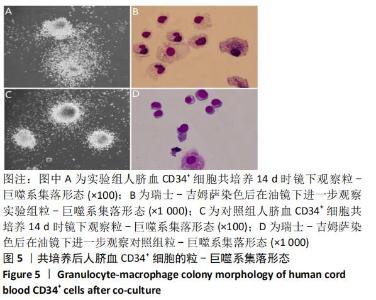
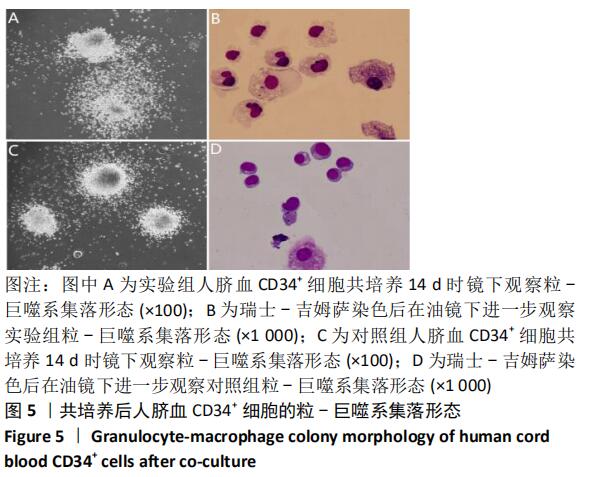
[1] ASADA N, KUNISAKI Y, PIERCE H, et al. Differential cytokine contributions of perivascular haematopoietic stem cell niches. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(3):214-223.
[2] 汪姝玥,林凡莉,钱怡,等.不同共培养模式下间充质干细胞对造血干细胞增殖的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(13): 2068-2074.
[3] LUCAS D. The Bone Marrow Microenvironment for Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1041:5-18.
[4] TIMARI H, SHAMSASENJAN K, MOVASSAGHPOUR A, et al. The Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles on Hematopoietic Stem Cells Fate. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017;7(4):531-546.
[5] MURRAY IR, BAILY JE, CHEN WCW, et al. Skeletal and cardiac muscle pericytes: Functions and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther. 2017; 171:65-74.
[6] SCHMIDT M, SCHÜLER SC, HÜTTNER SS, et al. Adult stem cells at work: regenerating skeletal muscle. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(13): 2559-2570.
[7] TEY SR, ROBERTSON S, LYNCH E, et al. Coding Cell Identity of Human Skeletal Muscle Progenitor Cells Using Cell Surface Markers: Current Status and Remaining Challenges for Characterization and Isolation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:284.
[8] 陈玉芳,王媛媛,王娟娟,等.具有造血能力的肌源性干细胞的研究进展[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2015,23(5):1523-1526.
[9] ZHENG B, CAO B, CRISAN M, et al. Prospective identification of myogenic endothelial cells in human skeletal muscle. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(9):1025-1034.
[10] 古晶晶,杨继辉,杨婷婷,等.多参数流式细胞术分选人骨骼肌源性血管内皮细胞和血管外膜细胞的方法[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(21): 3357-3364.
[11] BAI H, GAO Y, HOYLE DL, et al. Suppression of Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Delays Cellular Senescence and Preserves the Function of Endothelial Cells Derived from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(2):589-600.
[12] WILSON C, LEE MD, MCCARRON JG. Acetylcholine released by endothelial cells facilitates flow-mediated dilatation. J Physiol. 2016; 594(24):7267-7307.
[13] GUREL PEKOZER G, TORUN KOSE G, HASIRCI V. Influence of co-culture on osteogenesis and angiogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and aortic endothelial cells. Microvasc Res. 2016;108:1-9.
[14] SLUKVIN II. Generating human hematopoietic stem cells in vitro -exploring endothelial to hematopoietic transition as a portal for stemness acquisition. FEBS Lett. 2016;590(22):4126-4143.
[15] GARCIA-ALEGRIA E, MENEGATTI S, FADLULLAH MZH, et al. Early Human Hemogenic Endothelium Generates Primitive and Definitive Hematopoiesis In Vitro. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;11(5):1061-1074.
[16] GRITZ E, HIRSCHI KK. Specification and function of hemogenic endothelium during embryogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(8): 1547-1567.
[17] PERUCCA S, DI PALMA A, PICCALUGA PP, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) induce ex vivo proliferation and erythroid commitment of cord blood haematopoietic stem cells (CB-CD34+ cells). PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0172430.
[18] XU L, CHEN H, CHEN J, et al. The consensus on indications, conditioning regimen, and donor selection of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for hematological diseases in China-recommendations from the Chinese Society of Hematology. J Hematol Oncol. 2018;11(1): 33.
[19] DE WITTE T, BOWEN D, ROBIN M, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for MDS and CMML: recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood. 2017;129(13):1753-1762.
[20] GOLAY H, JURKOVIC MLAKAR S, MLAKAR V, et al. The Biological and Clinical Relevance of G Protein-Coupled Receptors to the Outcomes of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematized Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(16). pii: E3889.
[21] QIN M, GUAN X, WANG H, et al. An effective ex-vivo approach for inducing endothelial progenitor cells from umbilical cord blood CD34+ cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):25.
[22] NISHIKAWA E, MATSUMOTO T, ISIGE M, et al. Comparison of capacities to maintain hematopoietic stem cells among different types of stem cells derived from the placenta and umbilical cord. Regen Ther. 2016;4: 48-61.
[23] KADEKAR D, KALE V, LIMAYE L. Differential ability of MSCs isolated from placenta and cord as feeders for supporting ex vivo expansion of umbilical cord blood derived CD34(+) cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015; 6:201.
[24] 付亚茹,孙阳阳,王洪星,等.冻存脐带血中内皮祖细胞的分离培养及生物学特性鉴定[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2019,27(1):215-220.
[25] ZHANG Y, WANG C, WANG L, et al. Large-Scale Ex Vivo Generation of Human Red Blood Cells from Cord Blood CD34+ Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(8):1698-1709.
[26] 王鸣. 骨髓微环境中内皮细胞对造血干细胞扩增的调控研究[D].上海:上海师范大学, 2019.
[27] 董忱,赵龙,张斌,等.人脐带血来源造血干细胞体外扩增的研究进展[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版), 2019,9(1):44-49.
[28] GARBA A, ACAR DD, ROUKAERTS IDM, et al. Long-term culture and differentiation of porcine red bone marrow hematopoietic cells co-cultured with immortalized mesenchymal cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2017;191:44-50.
[29] LABARGE MA, BLAU HM. Biological progression from adult bone marrow to mononucleate muscle stem cell to multinucleate muscle fiber in response to injury. Cell. 2002;111(4):589-601.
[30] CAMARGO FD, GREEN R, CAPETANAKI Y, et al. Single hematopoietic stem cells generate skeletal muscle through myeloid intermediates. Nat Med. 2003;9(12):1520-1527.
[31] CAO B, ZHENG B, JANKOWSKI RJ, et al. Muscle stem cells differentiate into haematopoietic lineages but retain myogenic potential. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5(7):640-646. |