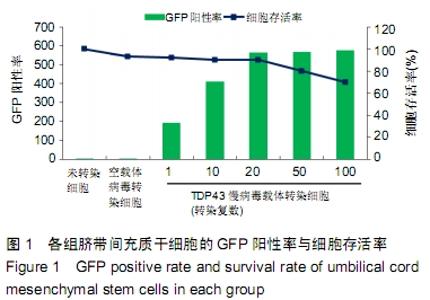
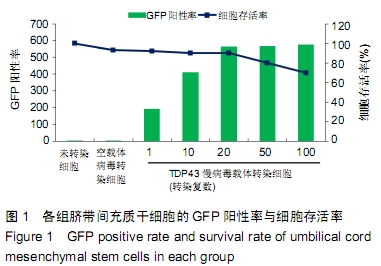
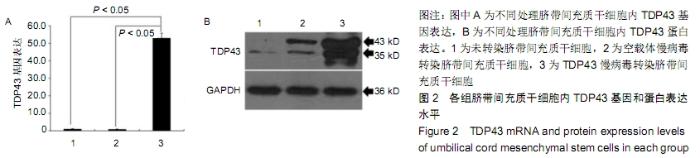
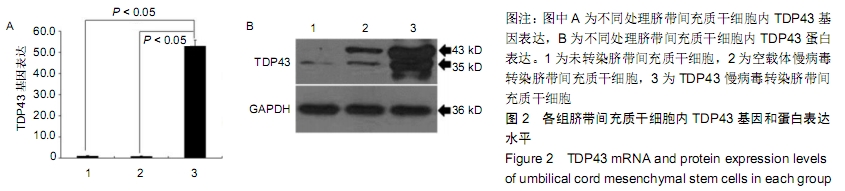
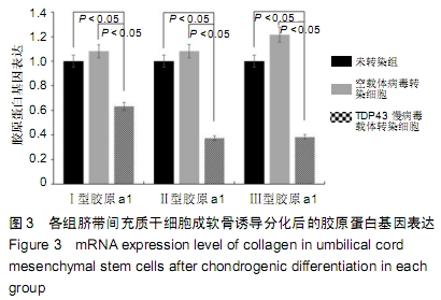
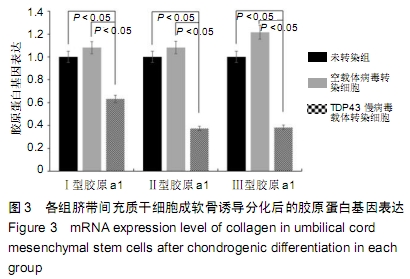
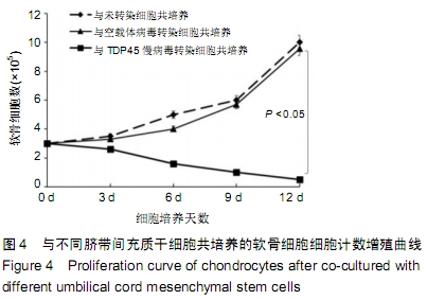
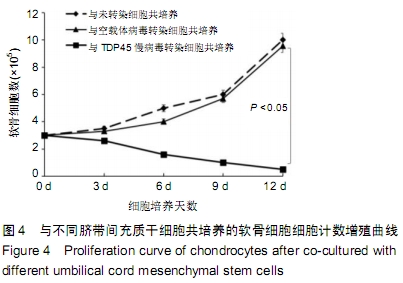
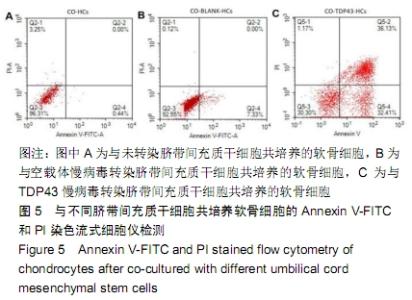
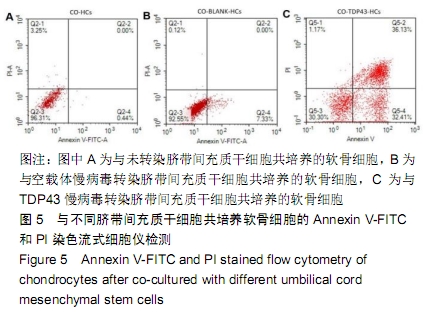
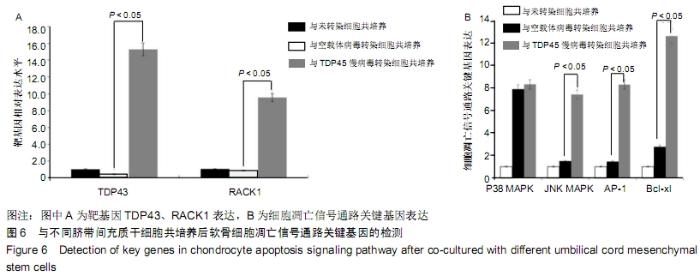
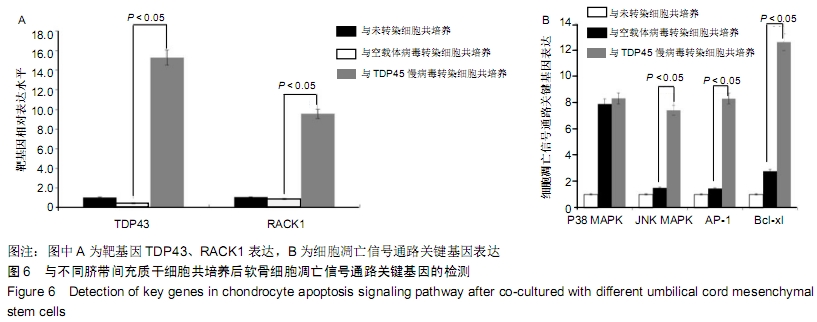
[1] GOLDRING MB.Osteoarthritis.J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(3):626-634.
[2] GIERMAN LM, VAN DER HAM F, KOUDIJS A, et al.Metabolic stress-induced inflammation plays a major role in the development of osteoarthritis in mice.Arthritis Rheum.2012; 64(4):1172-1181.
[3] TAKADA K, HIROSE J, SENBA K, et al.Enhanced apoptotic and reduced protective response in chondrocytes following endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritic cartilage.Int J Exp Pathol.2011;92(4):232-242.
[4] VONK LA, VAN DOOREMALEN SFJ, LIV N, et al.Mesenchymal Stromal/stem Cell-derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Human Cartilage Regeneration In intro. Theranostics.2018;8(4):906-920.
[5] WEI B, BAI X, CHEN K, et al.SP600125 enhances the anti-apoptotic capacity and migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells treated with tumor necrosis factor-α.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;475(4):301-307.
[6] ZHEN G, WEN C, JIA X, et al.Inhibition of TGF-β signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone attenuates osteoarthritis. Nat Med.2013;19(6):704-712.
[7] LEYH M, SEITZ A, DÜRSELEN L ,et al.Osteoarthritic cartilage explants affect extracellular matrix production and composition in cocultured bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and articular chondrocytes.Stem Cell Res Ther.2014;5(3):77.
[8] RYU JS, JUNG YH, CHO MY, et al.Co-culture with human synovium- derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibits inflammatory activity and increases cell proliferation of sodium nitroprusside-stimulated chondrocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2014;447(4):715-720.
[9] PRASADAM I, AKUIEN A, FRIIS TE, et al.Mixed cell therapy of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and articular cartilage chondrocytes ameliorates osteoarthritis development.Lab Invest. 2018;98(1):106-116.
[10] WATABE K, AKIYAMA K, KAWAKAMI E, et al.Adenoviral expression of TDP43 and FUS genes and shRNAs for protein degradation pathways in rodent motoneurons in vitro and in vivo.Neuropathology. 2014;34:83-98.
[11] MEYEROWITZ J, PARKER SJ, VELLA LJ, et al. C-Jun N-terminal kinase controls TDP43 accumulation in stress granules induced by oxidative stress.Mol Neurodegener.2011;6:57.
[12] ARIMOTO K, FUKUDA H, IMAJOH-OHMI S.Formation of stress granules inhibits apoptosis by suppressing stress-responsive MAPK pathways.Nat Cell Biol.2008;10(11):1324-1332.
[13] PLATAS J, GUILLÉN MI, PÉREZ DEL CAZ MD, et al.Paracrine effects of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in inflammatory stress-induced senescence features of osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Aging (Albany NY). 2016;8(8):1703-1717.
[14] DAVIES CM, GUILAK F, WEINBERG JB, et al.Reactive Nitrogen and Oxygen Species in İnterleukin- 1-Mediated DNA Damage Associated with Osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2008;16(5): 624-630.
[15] MARIN V, PROFIR D, SURDU T.Variation of Serum Level of Proinflammatory Cytokines after Mud Therapy in Patients with Osteoarthritis. Arch Balk Med Union.2011;45(1):69-74.
[16] KOLF CM, CHO E, TUAN RS.Mesenchymal stromal cells. Biology of adult mesenchymal stem cells: regulation of niche, self-renewal and differentiation.Arthritis Res Ther.2007;9:204.
[17] CAPLAN AI, DENNIS JE.Mesenchymal stem cells as trophic mediators. J Cell Biochem. 2006;98(5):1076-1084.
[18] LIM JY, IM KI, LEE ES, et al.Enhanced immunoregulation of mesenchymal stem cells by IL-10-producing type 1 regulatory T cells in collagen-induced arthritis.Sci Rep.2016;6:26851.
[19] JO CH, LEE YG, SHIN WH, et al.Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a proof-of-concept clinical trial.Stem Cells. 2014;32(5):1254-1266.
[20] SASAKI A, MIZUNO M, OZEKI N, et al.Canine mesenchymal stem cells from synovium have a higher chondrogenicpotential than those from infrapatellar fat pad, adipose tissue, and bone marrow.PLoS One. 2018;13(8):e0202922.
[21] BOHME K, WINTERHALTER KH, BRUCKNER P.Terminal differentiationof chondrocytes in culture is a spontaneous process and is arrestedby transforming growth factor-β2 and basic fibroblast growthfactor in synergy.Exp Cell Res.1995;216:191-198.
[22] D’ANGELO M, PACIFICI M.Articular chondrocytes produce factorsthat inhibit maturation of sternal chondrocytes in serum-freeagarose cultures: a TGF-β independent process.J Bone Miner Res.1997;12:1368-1377.
[23] OU SH, WU F, HARRICH D, et al.Cloning and characterization of a novel cellular protein, TDP43, that binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR DNA sequence motifs.J Virol.1995; 69(6):3584-3596.
[24] MURATA H, HATTORI T, MAEDA H, et al.Identification of transactivation-responsive DNA-binding protein 43 (TARDBP43;TDP43) as a novel factor for TNF-α expression upon lipopolysaccharide stimulation in human monocytes.J Periodontal Res.2015;50(4):452-460.
[25] LEE CC, LO Y, HO LJ, et al.A New Application of Parallel Synthesis Strategy for Discovery of Amide-Linked Small Molecules as Potent Chondroprotective Agents in TNF-α-Stimulated Chondrocytes. PLoS One. 2016; 11(3):e0149317.
[26] SWARUP V, PHANEUF D, DUPRÉ N, et al.Deregulation of TDP43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis triggers nuclear factor κB–mediated pathogenic pathways.J Exp Med.2011;208(12):2429-2447.
[27] ZHAN LH, XIE QJ, TIBBETTS RS.Opposing roles of p38 andJNKin a Drosophila model of TDP43 proteinopathy reveal oxidative stress and innate immunity as pathogenic components of neurodegeneration. Hum Mole Genet. 2015;24(3):757-772.
[28] YANG A, SUH WI, KANG NK, et al.MAPK/ERK and JNK pathways regulate lipid synthesis and cell growth of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii under osmotic stress, respectively.Sci Rep.2018; 8(1):13857.
[29] YAN S, WANG CE, WEI W, et al.TDP43 causes differential pathology in neuronal versus glial cells in the mouse brain. Hum Mol Genet.2014; 23(10):2678-2693.
[30] HANS F, ECKERT M, VON ZWEYDORF F, et al.Identification and characterization of ubiquitinylation sites in TAR DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP43).J Biol Chem.2018; 293(41):16083-16099.
|