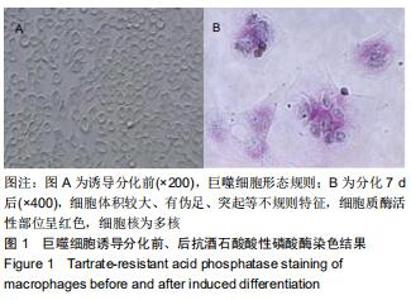
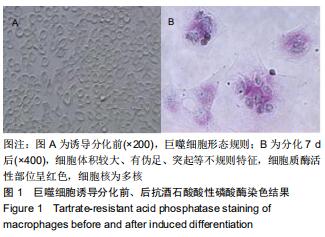
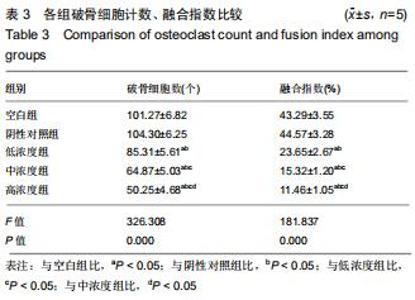
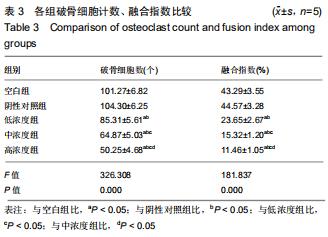
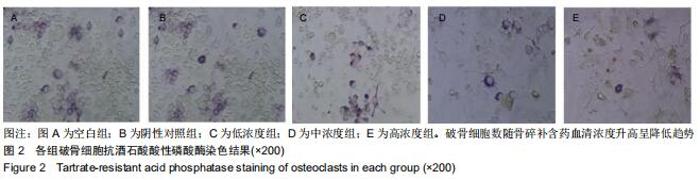
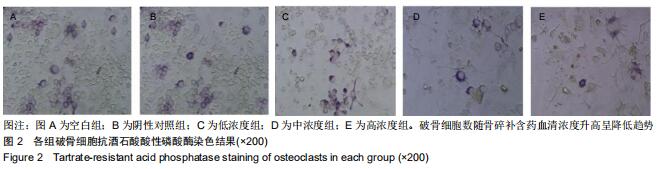
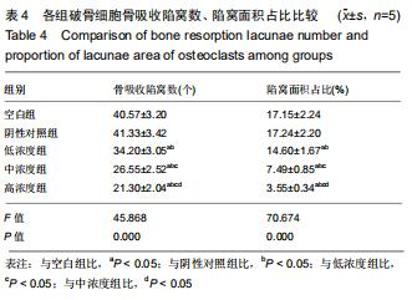
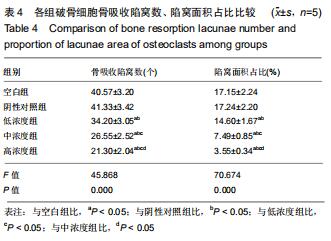
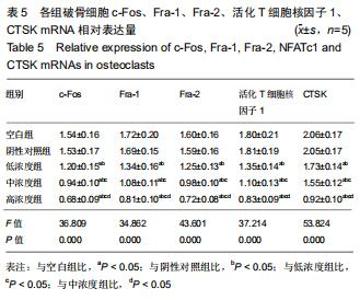
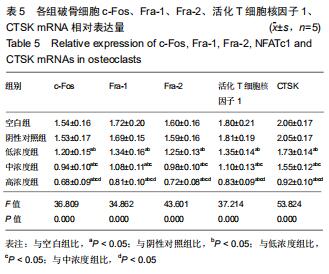
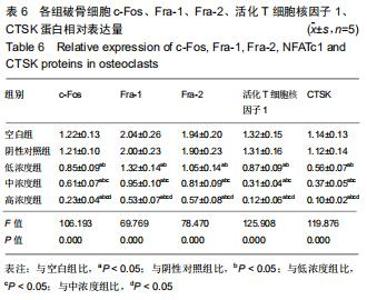
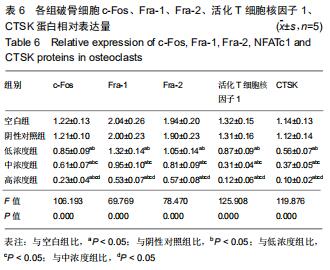
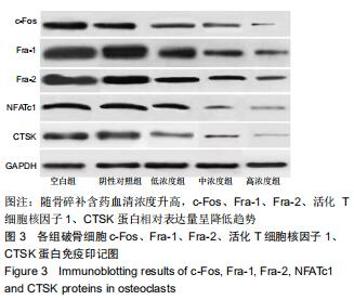
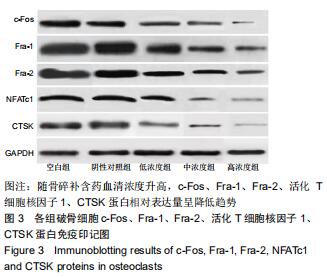
|
[1] 白璧辉,谢兴文,李鼎鹏,等.我国近5年来骨质疏松症流行病学研究现状[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(1):22-25.
[2] MA X, XU Z, DING S, et al. Alendronate promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation in ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis through interferon-β/signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 pathway.Exp Ther Med.2018;15(1): 182-190.
[3] 黄和涛,潘建科,刘军,等.骨质疏松症用药规律研究[J].中医学报, 2017,32(1):124-126.
[4] ZHANG Y, JIANG J, SHEN H, et al. Total flavonoids from Rhizoma Drynariae (Gusuibu) for treating osteoporotic fractures: implication in clinical practice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017;11(1):1881-1890.
[5] 尹文哲,邢成亮,王建业,等.失重下骨碎补总黄酮经ERK通路促成骨细胞增殖研究[J].中医药学报,2017,45(5):45-48.
[6] 黄继汉,黄晓晖,陈志扬,等.药理试验中动物间和动物与人体间的等效剂量换算[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2004,9(9): 1069-1072.
[7] BIJELIC R, MILICEVIC S, BALABAN J. Risk Factors for Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women.Med Arch. 2017; 71(1):25-28.
[8] 娄彦涛.振动训练改善中老年骨质疏松的安全性与有效性[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(42):6378-6384.
[9] GE Y, YANG G, WANG N, et al. Bone metabolism markers and hungry bone syndrome after parathyroidectomy in dialysis patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism.Int Urol Nephrol.2019;51(8):1443-1449.
[10] 刘慧,陈慧鸿,廖红兵.破骨细胞衍生的偶联因子鞘氨醇-1-磷酸及血小板衍生生长因子BB对成骨细胞的调节作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(23):3739-3745.
[11] FONTALIS A, KENANIDIS E, KOTRONIAS RA, et al. Current and emerging osteoporosis pharmacotherapy for women: state of the art therapies for preventing bone loss [J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother.2019;20(9):1123-1134.
[12] BURT LA, BILLINGTON EO, ROSE MS, et al. Effect of High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation on Volumetric Bone Density and Bone Strength: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA.2019;322(8):736-745.
[13] 尚奇,任辉,沈耿杨,等.基于肾主骨生髓理论探讨老年性骨质疏松症的中医治疗[J].中医杂志,2017,58(16):1433-1435.
[14] 姜自伟,曾景奇,黄枫,等.骨碎补总黄酮促进大鼠牵张成骨新骨形成的影像学研究[J].广州中医药大学学报,2017,34(3):390-393.
[15] 杨锋,孙玉华,吕中静,等.骨碎补总黄酮对骨质疏松症患者牙槽骨的影响[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2018,16(1):34-40.
[16] SONG S, GAO Z, LEI X, et al. Total Flavonoids of Drynariae Rhizoma Prevent Bone Loss Induced by Hindlimb Unloading in Rats.Molecules.2017;22(7):131-137.
[17] LEE KY, KIM JH, KIM EY, et al. Water extract of Cnidii Rhizoma suppresses RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW 264.7 cell by inhibiting NFATc1/c-Fos signaling and prevents ovariectomized bone loss in SD-rat.BMC Complement Altern Med.2019;19(1):207-215.
[18] HUSSEIN H, BOYAKA P, DULIN J, et al. Cathepsin K Localizes to Equine Bone In Vivo and Inhibits Bone Marrow Stem and Progenitor Cells Differentiation In Vitro.J Stem Cells Regen Med.2017;13(2):45-53.
[19] OUYANG Z, GUO X, CHEN X, et al. Hypericin targets osteoclast and prevents breast cancer-induced bone metastasis via NFATc1 signaling pathway.Oncotarget.2017; 9(2):1868-1884.
[20] RHO TW, LEE SY, HAN SY, et al. Glycyrrhizae Radix Inhibits Osteoclast Differentiation by Inhibiting c-Fos-Dependent NFATc1 Expression.Am J Chin Med.2017;45(2):283-298.
|