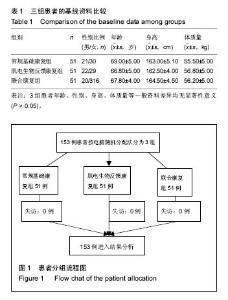
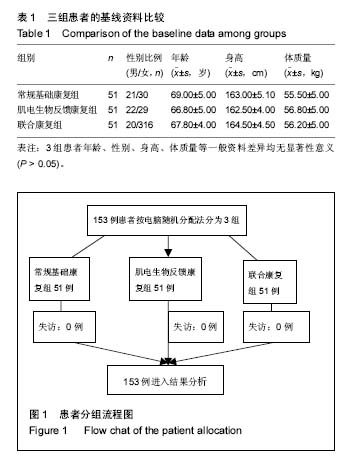
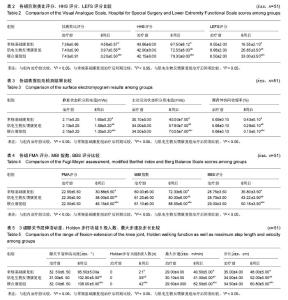
| [1] 谢青,鲍勇,汤亦婷.人工膝关节置换者康复治疗的特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(39):7759-7762.[2] 王世和.人工膝关节置换:技术发展与临床应用及评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(35):6587-6590.[3] 区广鹏,肖军,郑佐勇,李贝,刘伟,李干. 老年膝关节骨性关节炎患病危险因素的调查[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(50): 9463-9470.[4] 陈伟,吕红芝,张晓琳,等. 中国中老年人群膝关节骨性关节炎患病率流行病学调查设计[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2015, 36(4): 487-487.[5] 宋之明,张晓南,赵承武. 股四头肌功能练习对老年膝关节骨性关节炎清理术后疼痛的长期影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014, 34(8): 2270-2271.[6] Climov D, Lysy C, Berteau S, Dutrannois J. et al. Biofeedback on heart rate variability in cardiac rehabilitation: practical feasibility and psycho-physiological effects.Acta Cardiol. 2014;69(3):299-307.[7] Collins JD, Markham A, Service K. et al. A systematic literature review of the use and effectiveness of the Computer Assisted Rehabilitation Environment for research and rehabilitation as it relates to the wounded warrior. Work. 2015; 50(1):121-129. [8] De Nunzio A, Zucchella C, Spicciato F. et al. Biofeedback rehabilitation of posture and weightbearing distribution in stroke: a center of foot pressure analysis.Funct Neurol. 2014; 29(2):127-134.[9] Popa-Velea O, Purcarea VL. Psychological intervention - a critical element of rehabilitation in chronic pulmonary diseases. J Med Life. 2014;7(2):274-281. [10] Pietrosimone B, McLeod MM, Florea D. et al. Immediate increases in quadriceps corticomotor excitability during an electromyography biofeedback intervention.J Electromyogr Kinesiol.2015;25(2):316-322. [11] Giggins O, Sweeney KT, Caulfield B. et al. The use of inertial sensors for the classification of rehabilitation exercises.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014: 2965-2968.[12] 李志斌,冯尚武,黄顺仪,等.肌电生物反馈疗法对脑卒中偏瘫患者下肢运动功能的效果 [J].中国康复理论与实践,2013, 19(11):1046-1048.[13] Vadnerkar A, Figueiredo S, Mayo NE. et al. Classification of gait quality for biofeedback to improve heel-to-toe gait.Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:3626-3629. [14] Oravitan M, Avram C.The effectiveness of electromyographic biofeedback as part of a meniscal repair rehabilitation programme.J Sports Sci Med. 2013;12(3): 526-532.[15] Lainiala O, Eskelinen A, Elo P. et al. Adverse reaction to metal debris is more common in patients following MoM total knee replacement with a 36 mm femoral head than previously thought: results from a modern MoM follow-up programme.Bone Joint J. 2014;96(12):1610-1617. [16] Yano J, Shirahige C, Oki K.Effect of visual biofeedback of posterior tongue movement on articulation rehabilitation in dysarthria patients.J Oral Rehabil. 2015;42(8):571-579.[17] Moore A, Mannion J, Moran RW. The efficacy of surface electromyographic biofeedback assisted stretching for the treatment of chronic low back pain: a case-series.J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2015;19(1):8-16.[18] Eid MA, Aly SM, El-Shamy SM. Effect of Electromyographic Biofeedback Training on Pain, Quadriceps Muscle Strength, and Functional Ability in Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis.Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;95(12):921-930.[19] Rayegani SM, Raeissadat SA, Sedighipour L. et al. Effect of neurofeedback and electromyographic-biofeedback therapy on improving hand function in stroke patients.Top Stroke Rehabil. 2014;21(2):137-151. [20] Kim TE, Mariano ER. Developing a multidisciplinary fall reduction program for lower-extremity joint arthroplasty patients.Anesthesiol Clin. 2014;32(4):853-864. [21] Yu C, Wang Z, Yu Z. et al. Design of Rehabilitation Training System with Electromyography Feedback for Stroke Patients.Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2015;39(3):187-9, 205.[22] Azola AM, Sunday KL, Humbert IA. Kinematic Visual Biofeedback Improves Accuracy of Learning a Swallowing Maneuver and Accuracy of Clinician Cues During Training. Dysphagia. 2017;32(1):115-122.[23] Neblett R.Surface Electromyographic (SEMG) Biofeedback for Chronic Low Back Pain.Healthcare (Basel). 2016;4(2): E27.[24] 刘玲玲, 冯珍. 肌电生物反馈的临床研究及应用进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2012, 27(3):289-292.[25] 玛磊,宋鑫,李美,等. 肌电生物反馈疗法针对股内侧斜肌训练对髌股关节疼痛综合征的治疗作用[J]. 中国运动医学杂志, 2015, 34(12): 1202-1203.[26] Gálvez-Hernández CL, Rodríguez-Ortiz MD, Del Río-Portilla Y. Biofeedback treatment for acute whiplash patient.Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2016;54(4):480-489. |