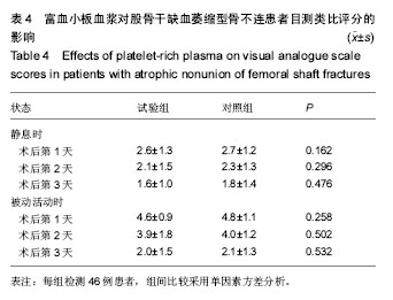
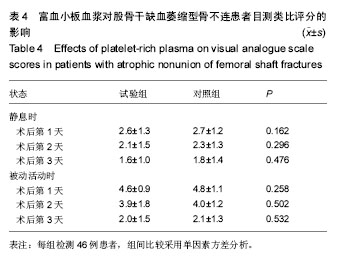
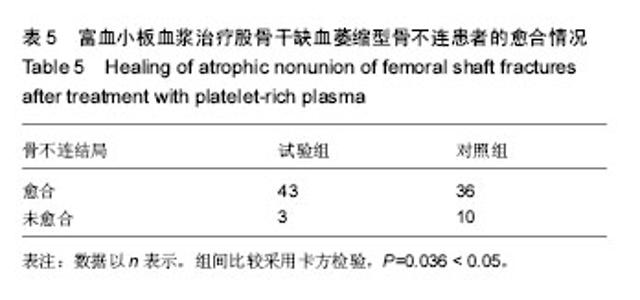
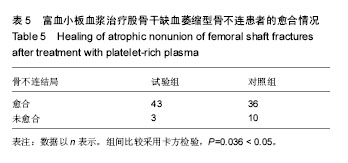
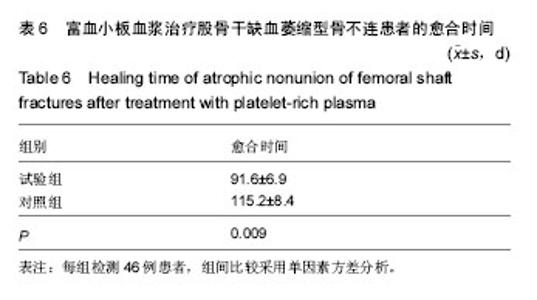
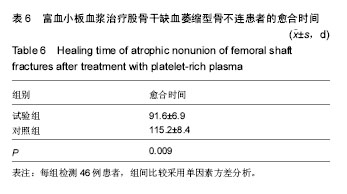
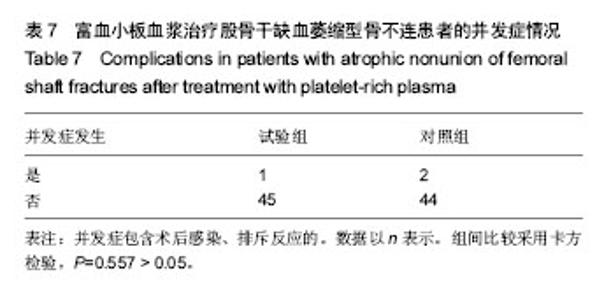
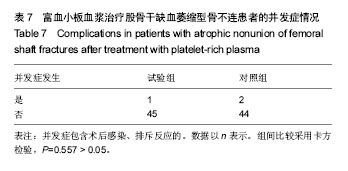
| [1] Zhao ZC, Li ZW, Tang BM, et al. Digital three-dimensional imaging models for repair of complex long bone fractures: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial with 6-month follow-up. Clin Transl Orthop. 2016;1(4):177-181.[2] Xu JJ. Safety and effectiveness of proximal femoral nail antirotation for the treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fracture: study protocol for a prospective case series. Clin Transl Orthop. 2016;1(3):90-99.[3] Yin PB, Long AH, Shen J, et al. Treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fracture with proximal femoral medial sustainable intramedullary nails: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Clin Transl Orthop. 2016; 1(2):44-50.[4] Tzioupis C, Giannoudis PV. Prevalence of long-bone non-unions. Injury. 2007;38 Suppl 2:S3-S9.[5] Milgram JW. Nonunion and pseudarthrosis of fracture healing. A histopathologic study of 95 human specimens. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991(268):203-213.[6] Frölke JP, Patka P. Definition and classification of fracture non-unions. Injury. 2007;38 Suppl 2:S19-S22.[7] Weber BG. Treatment of juvenile fractures: general introduction (author's transl). Langenbecks Arch Chir. 1976;342:283-286.[8] Nyary T, Scammell BE. Principles of bone and joint injuries and their healing. Surgery.2014;33(1):7-14.[9] Rodriguez-Merchan EC, Forriol F. Nonunion: general principles and experimental data. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004(419):4-12.[10] Roffi A, Filardo G, Kon E, et al. Does PRP enhance bone integration with grafts, graft substitutes, or implants? A systematic review. BMC Musculoskel Disord. 2013;14:330.[11] Fernandes G, Yang S. Application of platelet-rich plasma with stem cells in bone and periodontal tissue engineering. Bone Res. 2016;4:16036.[12] Cohn CS, Lockhart E. Autologous platelet-rich plasma: evidence for clinical use. Curr Opin Hematol. 2015;22(6): 527-532.[13] Assoian RK, Grotendorst GR, Miller DM, et al. Cellular transformation by coordinated action of three peptide growth factors from human platelets. Nature. 1984;309(5971): 804-806.[14] 张福田,刘瑞文,李慧,等.富血小板血浆复合自体髂骨治疗骨不连的临床疗效[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(6): 598-603.[15] 许洪涛,左振柏,庄建,等.自体复合富血小板凝胶在胫骨非感染性不愈合中的初步应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(2):92-94.[16] 孙涛,王建航,栾景杰. 自体富血小板血浆联合自体髂骨移植修复肱骨髁部骨缺损性骨不连的疗效[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2016,18(6):498-502.[17] 徐道志,王昱林,康涵威. 富血小板血浆结合锁定加压钢板内固定治疗四肢长管状骨骨折术后骨不连[J].创伤外科杂志,2015, 17(6):560,565.[18] 仇建军. 富血小板血浆促进骨修复的临床实验研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2009.[19] Jain A, Kumar S, Aggarwal AN, et al. Augmentation of bone healing in delayed and atrophic nonunion of fractures of long bones by partially decalcified bone allograft (decal bone). Indian J Orthop. 2015;49(6):637-642.[20] Ebraheim NA, Buchanan GS, Liu X, et al. Treatment of Distal Femur Nonunion Following Initial Fixation with a Lateral Locking Plate. Orthop Surg. 2016;8(3):323-330.[21] Monroy A, Urruela A, Singh P, et al. Distal femur nonunion patients can expect good outcomes. J Knee Surg. 2014; 27(1):83-87.[22] Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Nonunion following intramedullary nailing of the femur with and without reaming. Results of a multicenter randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(11):2093-2096.[23] Chen CE, Weng LH, Ko JY, et al. Management of nonunion associated with broken intramedullary nail of the femur. Orthopedics. 2008;31(1):78.[24] Rodriguez H, Ziran BH. Temporary antibiotic cement-covered gamma nail spacer for an infected nonunion of the proximal femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;454:270-274.[25] Steinberg EL, Keynan O, Sternheim A, et al. Treatment of diaphyseal nonunion of the femur and tibia using an expandable nailing system. Injury. 2009;40(3):309-314.[26] Weng LH, Wang JW. Nonunion of the femur treated with conventional osteosynthesis combined with autogenous and strut allogeneic bone grafts. Chang Gung Med J. 2004; 27(4):268-274.[27] Landesberg R, Roy M, Glickman RS. Quantification of growth factor levels using a simplified method of platelet-rich plasma gel preparation. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2000;58(3):297-300.[28] 吴孟超,吴在德,吴肇汉.外科学[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2013.[29] Langley GB, Sheppeard H. The visual analogue scale: its use in pain measurement. Rheumatol Int. 1985;5(4):145-148.[30] Schofer MD, Block JE, Aigner J, et al. Improved healing response in delayed unions of the tibia with low-intensity pulsed ultrasound: results of a randomized sham-controlled trial. BMC Musculoskel Disord. 2010;11:229-229.[31] Jingushi S, Mizuno K, Matsushita T, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound treatment for postoperative delayed union or nonunion of long bone fractures. J Orthop Sci. 2007;12(1): 35-41. [32] Watanabe Y, Arai Y, Takenaka N, et al. Three key factors affecting treatment results of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for delayed unions and nonunions: instability, gap size, and atrophic nonunion. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(5):803-810.[33] 赫兰学,马震卓,丁雪峰,等.富血小板血浆促进骨折愈合机制及研究进展[J].中国继续医学教育,2016,8(11):77-78. [34] 王金龙,祁全,陶学强,等.富血小板血浆在脊柱脊髓损伤治疗中的应用进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2016,16(9):1798-1800. [35] 刘一军,涂俊.富血小板血浆对肌骨系统损伤修复作用的研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报,2017,52(3):461-465. [36] 吴昭君,葛建华,季星利,等.自体富血小板血浆在周围神经损伤修复中的潜在价值[J].西南军医,2016,18(5):471-474.[37] 殷文靖,徐正良,盛加根,等.去白细胞和富白细胞富血小板血浆对软骨细胞增殖迁移的作用[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2016, 10(6):29-33. [38] 潘红娟,汪丽,刘铁梅.富血小板血浆成分及其作用的研究新进展[J].中国输血杂志,2016,29(12):1408-1412. [39] 叶露露,单桂秋,马静,等.富血小板血浆抑菌作用的研究进展[J].中国输血杂志,2014,27(2):216-219. [40] 贾伟涛,张长青.富血小板血浆的作用机制及其骨科临床应用进展[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2008,31(5):297-301. [41] 唐保明,杨爱荣,李钊伟,等.富含血小板血浆治疗慢性骨髓炎不愈合创面临床研究[J].青海医药杂志,2016,46(1):2-6. |