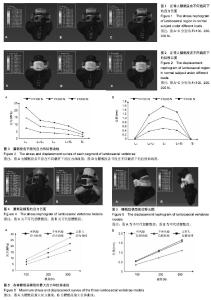
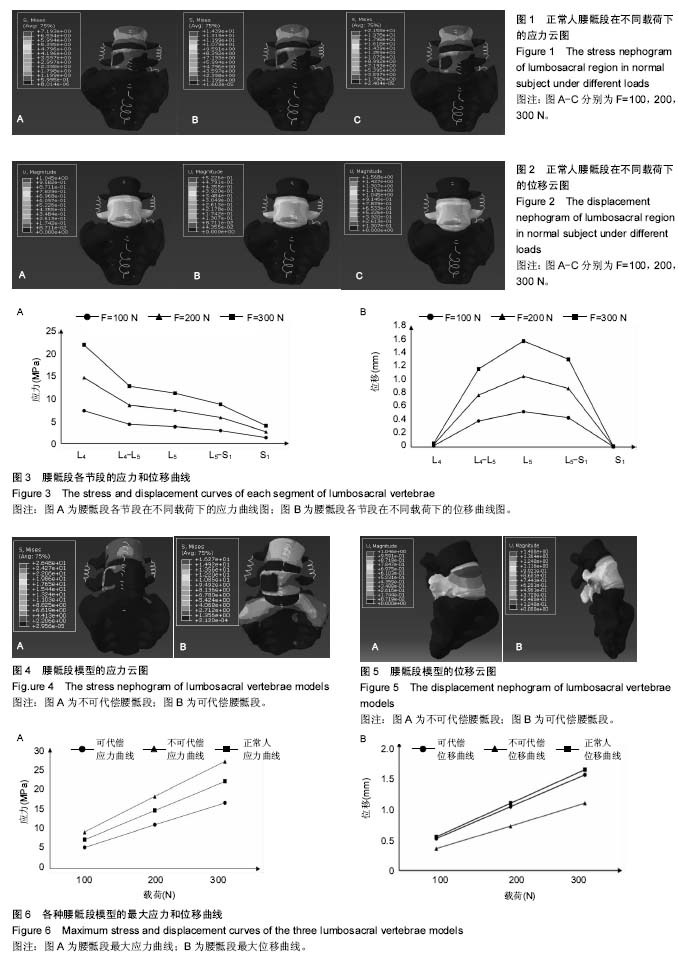
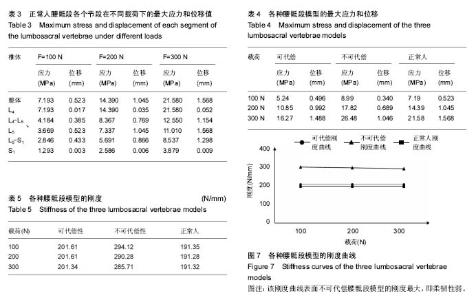
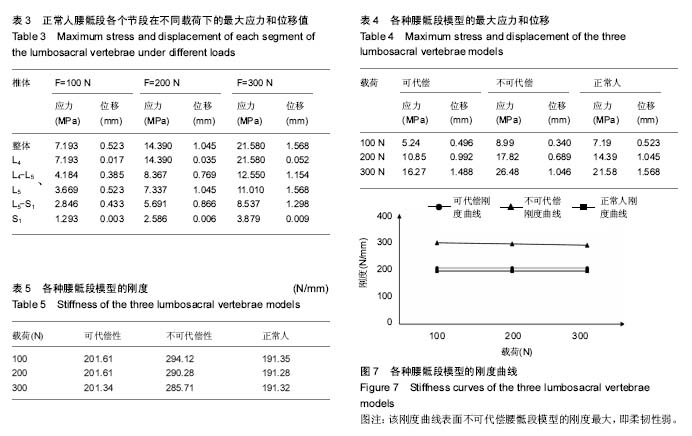
| [1] Viviani GR, Ghista DN, Lozada PJ, et al. Biomechanical analysis and simulation of scoliosis surgical correction. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(208):40-47.?[2] 黄盛佳,霍洪军.脊柱侧凸治疗进展中的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(4):651-656.[3] Salmingo RA, Tadano S, Fujisaki K, et al. Relationship of forces acting on implant rods and degree of scoliosis correction. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2013;28(2): 122-128. [4] 汪学松,吴志宏,王以朋,等.三维有限元法构建青少年特发性脊柱侧弯模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(44): 8610-8614.[5] Guo LX, Teo EC, Lee KK, et al. Vibration characteristics of the human spine under axial cyclic loads: effect of frequency and damping. Spine. 2005;30(6): 631-637. [6] Goel VK, Kong W, Han JS, et al. A combined finite element and optimization investigation of lumbar spine mechanics with and without muscles . Spine. 1993;18(11): 1531-1541.[7] Kurutz M, Oroszváry L. Finite element analysis of weightbath hydrotraction treatment of degenerated lumbar spine segments in elastic phase. J Biomech. 2010;43(3): 433-441. [8] Polikeit A, Nolte LP, Ferguson SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit: Finite-element analysis. Spine. 2003; 28(10):355–365.[9] Sylvestre PL, Villemure I, Aubin CÉ. Finite element modeling of the growth plate in a detailed spine model. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2007;45(10): 977-988.[10] 董凡,戴克戎,侯筱魁.小关节在腰椎结构刚度中的作用[J]. 中华外科杂志,1993,31(7):417-420.[11] Heth J, Hitchon P, Goel V, et al. A biomechanical comparison between anterior and transverse interbody fusion cages. Spine. 2001;26(12): e261-e267.[12] Yamamoto I, Panjabi M, Crisco T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine. Spine. 1989;14(11): 1256-1260.[13] Salmingo R, Tadano S, Fujisaki K, et al. Corrective force analysis for scoliosis from implant rod deformation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(6): 545-550.[14] Little JP, Izatt MT, Labrom RD, et al. An FE investigation simulating intra-operative corrective forces applied to correct scoliosis deformity. Scoliosis. 2013;8(1): 9.[15] Lafon Y, Lafage V, Dubousset J, et al. Intraoperative three-dimensional correction during rod rotation technique. Spine. 2009;34(5): 512-519. [16] 黄盛佳,霍洪军,杨学军,等. PUMCⅡd1型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸三维有限元模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(26): 4219-4223. [17] Gardner-Morse M, Stokes IA. Three-dimensional simulations of the scoliosis derotation maneuver with Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation. J Biomech. 1994;27(2): 177-181. ?[18] Stokes IA, Gardner-Morse M. Three-dimensional simulation of Harrington distraction instrumentation for surgical correction of scoliosis. Spine. 1993;18(16):2457-2464. ?[19] Duke K, Aubin CE, Dansereau J, et al. Biomechanical simulations of scoliotic spine correction due to prone position and anaesthesia prior to surgical instrumentation. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2005;20(9): 923-931. [20] Galbusera F, Schmidt H, Noailly J, et al. Comparison of four methods to simulate swelling in poroelastic finite element models of intervertebral discs. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2011; 4(7):1234-1241. ?[21] Xiao ZT, Wang LY, Gong H, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of three surgical scenarios of posterior lumbar interbody fusion by finite element analysis. Biomed Eng Online. 2012;11(1):31.[22] Schmidt H, Galbusera F, Wilke HJ, et al. Remedy for fictive negative pressures in biphasic finite element models of the intervertebral disc during unloading. Comp Methods Biomech Biomed Eng. 2011;14(3):293-303. ?[23] Kiapour A, Abdelgawad AA, Goel VK, et al. Relationship between limb length discrepancy and load distribution across the sacroiliac joint--a finite element study. J Orthop Res. 2012; 30(10):1577-1580.?[24] Stokes IA, Gardner-Morse M. A database of lumbar spinal mechanical behavior for validation of spinal analytical models. J Biomech. 2016;49(5):780-785. [25] Brummund M, Brailovski V, Facchinello Y, et al. Implementation of a 3D porcine lumbar finite element model for the simulation of monolithic spinal rods with variable flexural stiffness. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015: 917-920.[26] Naserkhaki S, Jaremko JL, Adeeb S, et al. On the load-sharing along the ligamentous lumbosacral spine in flexed and extended postures: Finite element study. J Biomech. 2016;49(6):974-982. [27] Wu Y, Wang Y, Wu J, et al. Study of Double-level Degeneration of Lower Lumbar Spines by Finite Element Model. World Neurosurg. 2016;86:294-299. [28] Pyles CO, Zhang J, Demetropoulos CK, et al. Material Parameter Determination of an L4-L5 Motion Segment Finite Element Model Under High Loading Rates. Biomed Sci Instrum. 2015;51:206-213.[29] 李晔,王以朋,沈建雄,等.先天性脊柱侧凸后路矫形固定术前腰骶段椎间角的变化与术后躯干偏移[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2016,96(1): 20-24.[30] Cegoñino J, Calvo-Echenique A, Pérez-del Palomar A. Influence of different fusion techniques in lumbar spine over the adjacent segments: A 3D finite element study. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(7):993-1000.[31] Wang H, Wang X, Chen W, et al. Biomechanical comparison of interspinous distraction device and facet screw fixation system on the motion of lumbar spine: a finite element analysis. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(11): 2078-2084. |