Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (23): 3658-3663.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.23.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Cognitive behavior therapy alleviates kinesiophobia after total knee arthroplasty
Cai Li-bai1, Liu Yan-jin1, Zhao Hui2, Xu Hui-ping2, Gao Huan-huan2, Dong Yue-zhi3
- 1Department of Nursing, 2Department of Orthopedics, 3Reproductive Medicine Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Online:2017-08-18Published:2017-09-01 -
Contact:Liu Yan-jin, Master, Chief nurse, Department of Nursing, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Cai Li-bai, Studying for master’s degree, Nurse, Department of Nursing, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Research Program of University in Henan Province, No. 16A320051
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cai Li-bai, Liu Yan-jin, Zhao Hui, Xu Hui-ping, Gao Huan-huan, Dong Yue-zhi. Cognitive behavior therapy alleviates kinesiophobia after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(23): 3658-3663.
share this article
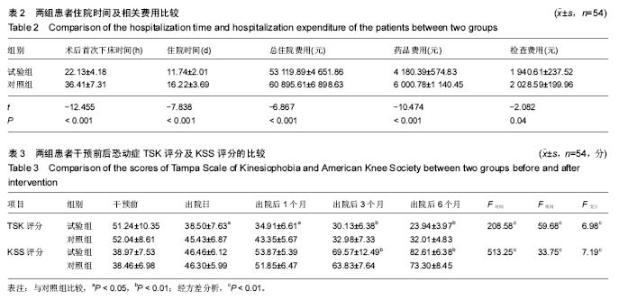
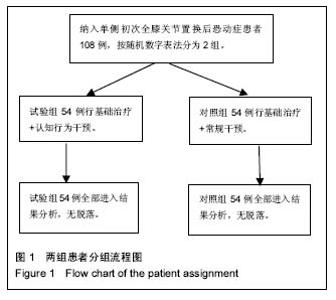
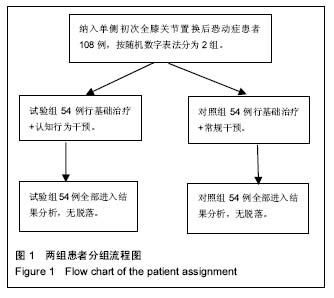
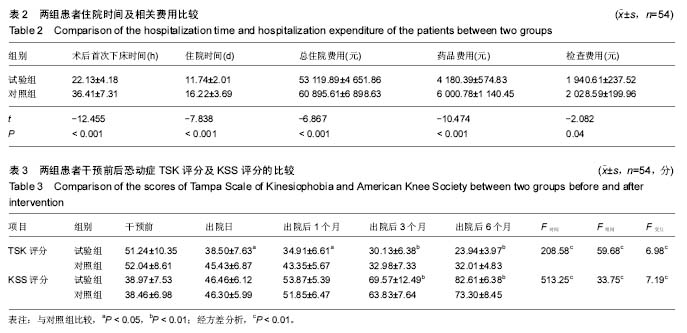
2.2 住院时间及相关费用的比较 相比于对照组患者,试验组首次下床时间以及住院时间缩短,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01);试验组患者检查费用较对照组低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),2组总住院费用、药品费用差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。见表2。 2.3 干预前后恐动症TSK评分及膝关节功能评分的比较 经单因素重复测量方差分析,显示恐动症患者的恐动症TSK评分以及KSS评分在时间效应、组间效应以及交互作用上,差异有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01)。 各时间点评分比较:2组患者干预前的恐动症TSK评分以及KSS评分比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);在出院日及出院后1个月时,2组患者的恐动症TSK评分差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);2组KSS比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);患者出院后3,6个月时,试验组患者的恐动症TSK评分低于对照组,KSS评分高于对照组,差异均有非常显著性意义(P < 0.01),见表3。 2.4 不良事件 所有患者置换术后均无假体脱落、假体周围骨折、术后切口感染、切口皮肤坏死及下肢静脉血栓等并发生的发生,随访期间患者架体稳定性良好。"
| [1] 徐高伟,董斌,崔海勇,等. 有限元分析全膝关节置换股骨假体置入定位参数及临床优化验证[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(17): 4411-4418.[2] Aumiller WD, Dollahite HA. Advances in total knee arthroplasty. JAAPA. 2016;29(3):27-31.[3] Canata GL, Casale V, Chiey A. Pain management in total knee arthroplasty: efficacy of a multimodal opiate-free protocol. Joints. 2016;4(4):222-227.[4] Baert I A, Lluch E, Mulder T, et al. Does pre-surgical central modulation of pain influence outcome after total knee replacement? A systematic review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(2):213-223.[5] Doury-Panchout F, Metivier JC, Fouquet B. Kinesiophobia negatively influences recovery of joint function following total knee arthroplasty. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2015;51(2):155-161.[6] Kori SH, Miller RP, Todd DD. Kinisophobia: A new view of chronic pain behavior. 1990;3(1):35-43.[7] Lee DY, Karim SA, Chang HC. Return to sports after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction-a review of patients with minimum 5-year follow-up. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2008; 37(4):273-278.[8] Wood DW, Haig AJ, Yamakawa KS. Fear of movement/(re)injury and activity avoidance in persons with neurogenic versus vascular claudication. Spine J. 2012;12(4):292-300.[9] 李星凤,熊钰,邓诗佳,等. 腰椎间盘突出症患者疼痛信念与生活质量的相关性分析[J].护理学杂志,2016,31(2):51-53.[10] 刘丽丽,王维宁. 疼痛日记对腰椎间盘突出症患者恐动症和恐惧回避信念的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2015,30(10):25-28.[11] 伍青,郭爱敏. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者呼吸困难信念的相关概念及测量[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2015,50(4):454-459.[12] Murphy WJ, Altman RD. Updated osteoarthritis reference standard. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1995;43:56-59.[13] Vlaeyen JW, Crombez G. Fear of movement/(re)injury, avoidance and pain disability in chronic low back pain patients. Man Ther. 1999;4(4):187-195.[14] 杜慧晴,梅迎雪,代文娟,等. 非药物干预对人工全膝关节置换术后患者疼痛的影响[J]. 宁夏医学杂志, 2016,38(4):349-350.[15] 唐侠. 早期功能锻炼对膝关节置换术后功能恢复的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2014,12(8):1331-1332,1343.[16] Severijns P, Vanslembrouck M, Vermulst J, et al. High-demand motor tasks are more sensitive to detect persisting alterations in muscle activation following total knee replacement . Gait Posture. 2016;50(3):151-158.[17] Fiala B, Rhodes RE, Blanchard C, et al. Using social-cognitive constructs to predict preoperative exercise before total joint replacement. Rehabil Psychol, 2013;58(2): 137-147.[18] Morone NE, Abebe KZ, Morrow LA, et al. Pain and decreased cognitive function negatively impact physical functioning in older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Pain Med. 2014;15(9): 1481-1487.[19] Focht BC, Garver MJ, Devor ST, et al. Improving maintenance of physical activity in older, knee osteoarthritis patients trial-pilot (IMPACT-P): design and methods. Contemp Clin Trials. 2012;33(5):976-982.[20] Kavak F, Unal S, Yilmaz E. Effects of Relaxation Exercises and Music Therapy on the Psychological Symptoms and Depression Levels of Patients with Schizophrenia. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016;30(5):508-512.[21] 刘薇,周小萍,邵艳霞,等. 放松训练对急性创伤患者心理健康的影响[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2015,37(21):2169-2173.[22] Neblett R, Hartzell MM, Mayer TG, et al. Establishing clinically meaningful severity levels for the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia (TSK-13). Eur J Pain. 2016;20(5):701-710.[23] Koho P, Borodulin K, Kautiainen H, et al. Finnish version of the Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia: Reference values in the Finnish general population and associations with leisure-time physical activity . J Rehabil Med. 2015;47(3):249-255.[24] Acar S, Savci S, Keskinoglu P, et al. Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia for Heart Turkish Version Study: cross-cultural adaptation, exploratory factor analysis, and reliability. J Pain Res. 2016;9(1):445-451.[25] 胡文. 简体中文版TSK和FABQ量表的文化调适及其在退行性腰腿痛中的应用研究[D]. 第二军医大学, 2012.[26] nsall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, et al. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (248):13-14.[27] Tjong VK, Devitt BM, Murnaghan ML, et al. A Qualitative Investigation of Return to Sport After Arthroscopic Bankart Repair: Beyond Stability. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(8): 2005-2011.[28] Maempel JF, Clement ND, Brenkel IJ, et al. Validation of a prediction model that allows direct comparison of the Oxford Knee Score and American Knee Society clinical rating system . Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(4):503-509.[29] Civinini R, Carulli C, Matassi F, et al. The Survival of Total Knee Arthroplasty: Current Data from Registries on Tribology: Review Article. HSS J. 2017;13(1):28-31.[30] Bunzli S, Smith A, Watkins R, et al. What Do People Who Score Highly on the Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia Really Believe? A Mixed Methods Investigation in People With Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain . Clin J Pain. 2015;31(7): 621-632.[31] Tait MA, Dredge C, Barnes CL. Preoperative Patient Education for Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Financial Benefit? J Surg Orthop Adv.2015;24(4):246-251.[32] Aasvang EK, Luna IE, Kehlet H. Challenges in postdischarge function and recovery: the case of fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115(6):861-866.[33] Monticone M, Ambrosini E, Cazzaniga D, et al. Adults with idiopathic scoliosis improve disability after motor and cognitive rehabilitation: results of a randomised controlled trial . Eur Spine J. 2016;25(10):3120-3129.[34] Richmond H. Using a CBT approach to manage low back pain. Nurs Times.2016;112(18):12-14.[35] Bragard I, Etienne AM, Faymonville ME, et al. A Nonrandomized Comparison Study of Self-Hypnosis, Yoga, and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy to Reduce Emotional Distress in Breast Cancer Patients. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2017;65(2):189-209.[36] Tanuma K, Watanabe F, Maeda H, et al. Development and Validation of a Training Program Using a Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Approach with the Purpose of Enabling Community Pharmacists to Provide Empathic Patient Counseling. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017;137(2):227-240.[37] Fagevik OM, Slobo M, Klarin L, et al. Physical function and pain after surgical or conservative management of multiple rib fractures - a follow-up study. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2016;24(1):128.[38] Brown ML, Plate JF, Von Thaer S, et al. Decreased Range of Motion After Total Knee Arthroplasty Is Predicted by the Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(4): 793-797.[39] Filardo G, Roffi A, Merli G, et al. Patient kinesiophobia affects both recovery time and final outcome after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24(10):3322-3328.[40] Schotanus MG, Boonen B, Kort NP. Patient specific guides for total knee arthroplasty are ready for primetime. World J Orthop. 2016;7(1):61-68. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Zhang Jichao, Dong Yuefu, Mou Zhifang, Zhang Zhen, Li Bingyan, Xu Xiangjun, Li Jiayi, Ren Meng, Dong Wanpeng. Finite element analysis of biomechanical changes in the osteoarthritis knee joint in different gait flexion angles [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1357-1361. |
| [3] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [4] | Zhuang Zhikun, Wu Rongkai, Lin Hanghui, Gong Zhibing, Zhang Qianjin, Wei Qiushi, Zhang Qingwen, Wu Zhaoke. Application of stable and enhanced lined hip joint system in total hip arthroplasty in elderly patients with femoral neck fractures complicated with hemiplegia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1429-1433. |
| [5] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [6] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [7] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [8] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [9] | Yang Kuangyang, Wang Changbing. MRI evaluation of graft maturity and knee function after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with autogenous bone-patellar tendon-bone and quadriceps tendon [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 963-968. |
| [10] | Liu Dongcheng, Zhao Jijun, Zhou Zihong, Wu Zhaofeng, Yu Yinghao, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Comparison of different reference methods for force line correction in open wedge high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 827-831. |
| [11] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [12] | Huang Hao, Hong Song, Wa Qingde. Finite element analysis of the effect of femoral component rotation on patellofemoral joint contact pressure in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 848-852. |
| [13] | Yuan Jing, Sun Xiaohu, Chen Hui, Qiao Yongjie, Wang Lixin. Digital measurement and analysis of the distal femur in adults with secondary knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 881-885. |
| [14] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [15] | Yang Yang, Li Naxi, Zhang Jian, Wang Mian, Gong Taifang, Gu Liuwei. Effect of tourniquet combined with exsanguination band use on short-term lower extremity venous thrombosis after knee arthroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 898-903. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||