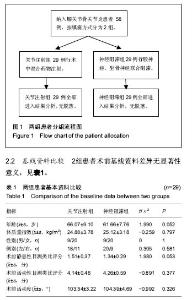
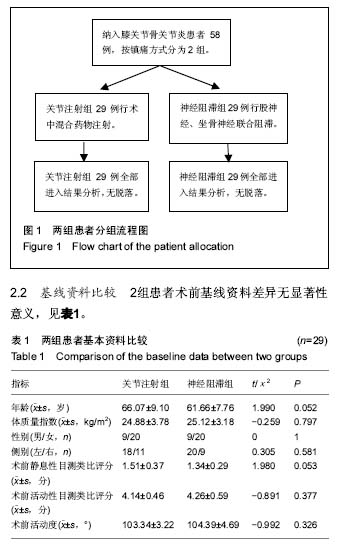
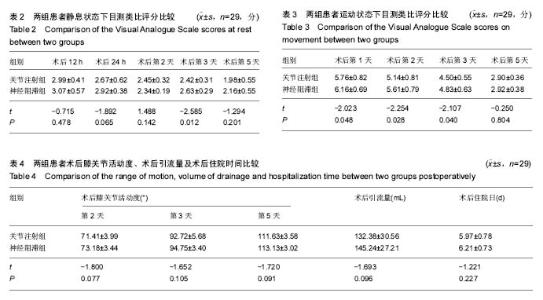
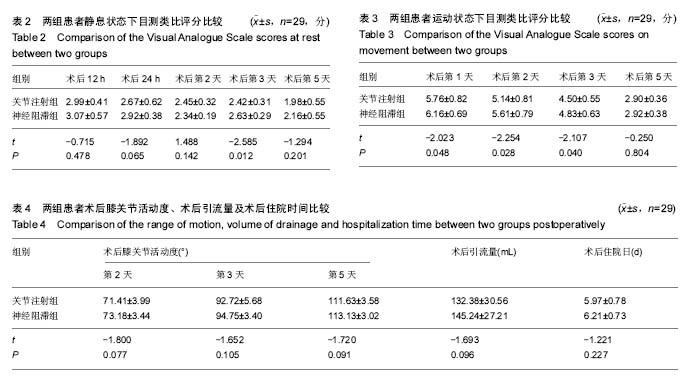
| [1] Buvanendran A, Kroin JS, Della VC, et al. Perioperative oral pregabalin reduces chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2010;110(1):199-207.[2] Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS. Pain management and accelerated rehabilitation for total hip and total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2007;22(7 Suppl 3):12-15.[3] Paul JE, Arya A, Hurlburt L, et al. Femoral nerve block improves analgesia outcomes after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology. 2010;113(5):1144-1162.[4] Vaishya R, Wani AM, Vijay V. Local Infiltration Analgesia reduces pain and hospital stay after primary TKA: randomized controlled double blind trial. Acta Orthop Belg.2015;81(4): 720-729.[5] Ilfeld BM, Hadzic A. Walking the tightrope after knee surgery: optimizing postoperative analgesia while minimizing quadriceps weakness. Anesthesiology. 2013;118(2):248-250.[6] Otten C, Dunn K. Mulitmodal analgesia for postoperative total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Nurs. 2011;30(6):373-380, 381-382.[7] Horlocker TT, Hebl JR, Kinney MA, et al. Opioid-free analgesia following total knee arthroplasty--a multimodal approach using continuous lumbar plexus (psoas compartment) block, acetaminophen, and ketorolac. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2002;27(1):105-108.[8] Capdevila X, Barthelet Y, Biboulet P, et al. Effects of perioperative analgesic technique on the surgical outcome and duration of rehabilitation after major knee surgery. Anesthesiology. 1999;91(1):8-15.[9] Horlocker TT, Wedel DJ. Neuraxial block and low-molecular-weight heparin: balancing perioperative analgesia and thromboprophylaxis. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 1998;23(6 Suppl 2):164-177.[10] 彭慧明,唐杞衡,钱文伟,等. 膝关节周围注射镇痛在全膝关节置换术后多模式镇痛方案中的作用[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(7): 406-412.[11] Busch CA, Shore BJ, Bhandari R, et al. Efficacy of periarticular multimodal drug injection in total knee arthroplasty. A randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(5):959-963.[12] 中华医学会骨科学分会. 预防骨科大手术深静脉血栓形成指南(草案)[J]. 中华骨科杂志, 2007,27(10):790-792.[13] Thomas T, Robinson C, Champion D, et al. Prediction and assessment of the severity of post-operative pain and of satisfaction with management. Pain. 1998;75(2-3):177-185.[14] Skinner HB, Shintani EY. Results of a multimodal analgesic trial involving patients with total hip or total knee arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2004;33(2):85-92, 92.[15] Estebe JP, Kerebel C, Brice C, et al. [Pain and tourniquet in orthopedic surgery]. Cah Anesthesiol. 1995;43(6):573-578.[16] Woolf CJ, Chong MS. Preemptive analgesia--treating postoperative pain by preventing the establishment of central sensitization. Anesth Analg. 1993;77(2):362-379.[17] Vendittoli PA, Makinen P, Drolet P, et al. A multimodal analgesia protocol for total knee arthroplasty. A randomized, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(2):282-289.[18] 林雪松. 局部浸润镇痛在全膝关节置换术后多模式镇痛中的临床研究[D]. 大连医科大学,2015.[19] Niemelainen M, Kalliovalkama J, Aho AJ, et al. Single periarticular local infiltration analgesia reduces opiate consumption until 48 hours after total knee arthroplasty. A randomized placebo-controlled trial involving 56 patients. Acta Orthop. 2014;85(6):614-619.[20] Bagsby DT, Ireland PH, Meneghini RM. Liposomal bupivacaine versus traditional periarticular injection for pain control after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(8):1687-1690.[21] Knudsen K, Beckman S M, Blomberg S, et al. Central nervous and cardiovascular effects of i.v. infusions of ropivacaine, bupivacaine and placebo in volunteers. Br J Anaesth. 1997;78(5):507-514.[22] 王冬娜,方洪亮,杨林. 罗哌卡因与布比卡因用于腰硬联合麻醉的对比临床观察[J]. 中国临床研究, 2010,23(6):485-486.[23] Bhutta MA, Ajwani SH, Shepard GJ, et al. Reduced Blood Loss and Transfusion Rates: Additional Benefits of Local Infiltration Anaesthesia in Knee Arthroplasty Patients. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(11):2034-2037.[24] Fu PL, Xiao J, Zhu YL, et al. Efficacy of a multimodal analgesia protocol in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. J Int Med Res. 2010;38(4):1404-1412.[25] Viscusi ER. Emerging techniques in the treatment of postoperative pain. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2004;61 Suppl 1:S11-S14.[26] Kim TW, Park SJ, Lim SH, et al. Which analgesic mixture is appropriate for periarticular injection after total knee arthroplasty? Prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(3):838-845.[27] Hirasawa Y, Okajima S, Ohta M, et al. Nerve distribution to the human knee joint: anatomical and immunohistochemical study. Int Orthop. 2000;24(1):1-4.[28] 余正红,蔡胥,赵卫东,等. 膝关节神经分布的解剖学研究及其临床意义[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2008,26(1):11-16.[29] Uesugi K, Kitano N, Kikuchi T, et al. Comparison of peripheral nerve block with periarticular injection analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled study. Knee. 2014;21(4):848-852. |